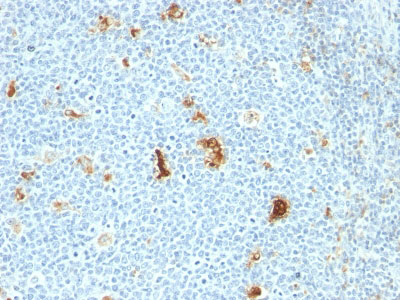
Macrophage L1 Protein Antibody - With BSA and Azide
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone SPM281 ]
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| IHC, IF, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P05109 |
| Other Accession | 6279 (S100A8/Calgranulin A/MRP-8), 6280 (S100A9/Calgranulin B/MRP-14), 416073 (S100A8/Calgranulin A/MRP-8), 112405 (S100A9/Calgranulin B/MRP-14), P06702 (S100A9/Calgranulin B/MRP-14) |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Monkey, Pig, Goat, Bovine, Baboon, Cat, Horse, Guinea Pig, Dog |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG1, kappa |
| Clone Names | SPM281 |
| Calculated MW | 10835 Da |
| Gene ID | 6279 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Protein S100-A8, Calgranulin-A, Calprotectin L1L subunit, Cystic fibrosis antigen, CFAG, Leukocyte L1 complex light chain, Migration inhibitory factor-related protein 8, MRP-8, p8, S100 calcium-binding protein A8, Urinary stone protein band A, Protein S100-A8, N-terminally processed, S100A8, CAGA, CFAG, MRP8 |
| Application Note | IHC~~1:100~500 IF~~1:50~200 FC~~1:10~50 |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | Macrophage L1 Protein Antibody - With BSA and Azide is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | S100A8 (HGNC:10498) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CAGA, CFAG, MRP8 |
| Function | S100A8 is a calcium- and zinc-binding protein which plays a prominent role in the regulation of inflammatory processes and immune response. It can induce neutrophil chemotaxis and adhesion. Predominantly found as calprotectin (S100A8/A9) which has a wide plethora of intra- and extracellular functions. The intracellular functions include: facilitating leukocyte arachidonic acid trafficking and metabolism, modulation of the tubulin-dependent cytoskeleton during migration of phagocytes and activation of the neutrophilic NADPH- oxidase. Also participates in regulatory T-cell differentiation together with CD69 (PubMed:26296369). Activates NADPH-oxidase by facilitating the enzyme complex assembly at the cell membrane, transferring arachidonic acid, an essential cofactor, to the enzyme complex and S100A8 contributes to the enzyme assembly by directly binding to NCF2/P67PHOX. The extracellular functions involve pro- inflammatory, antimicrobial, oxidant-scavenging and apoptosis-inducing activities. Its pro-inflammatory activity includes recruitment of leukocytes, promotion of cytokine and chemokine production, and regulation of leukocyte adhesion and migration. Acts as an alarmin or a danger associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule and stimulates innate immune cells via binding to pattern recognition receptors such as Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (AGER). Binding to TLR4 and AGER activates the MAP-kinase and NF-kappa-B signaling pathways resulting in the amplification of the pro-inflammatory cascade. Has antimicrobial activity towards bacteria and fungi and exerts its antimicrobial activity probably via chelation of Zn(2+) which is essential for microbial growth. Can induce cell death via autophagy and apoptosis and this occurs through the cross- talk of mitochondria and lysosomes via reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the process involves BNIP3. Can regulate neutrophil number and apoptosis by an anti-apoptotic effect; regulates cell survival via ITGAM/ITGB and TLR4 and a signaling mechanism involving MEK-ERK. Its role as an oxidant scavenger has a protective role in preventing exaggerated tissue damage by scavenging oxidants. Can act as a potent amplifier of inflammation in autoimmunity as well as in cancer development and tumor spread. The iNOS-S100A8/A9 transnitrosylase complex directs selective inflammatory stimulus-dependent S- nitrosylation of GAPDH and probably multiple targets such as ANXA5, EZR, MSN and VIM by recognizing a [IL]-x-C-x-x-[DE] motif; S100A8 seems to contribute to S-nitrosylation site selectivity. |
| Cellular Location | Secreted. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Note=Predominantly localized in the cytoplasm. Upon elevation of the intracellular calcium level, translocated from the cytoplasm to the cytoskeleton and the cell membrane. Upon neutrophil activation or endothelial adhesion of monocytes, is secreted via a microtubule-mediated, alternative pathway |
| Tissue Location | Calprotectin (S100A8/9) is predominantly expressed in myeloid cells. Except for inflammatory conditions, the expression is restricted to a specific stage of myeloid differentiation since both proteins are expressed in circulating neutrophils and monocytes but are absent in normal tissue macrophages and lymphocytes. Under chronic inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis and malignant disorders, also expressed in the epidermis. Found in high concentrations at local sites of inflammation or in the serum of patients with inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid, cystic fibrosis, inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, giant cell arteritis, cystic fibrosis, Sjogren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, and progressive systemic sclerosis. Involved in the formation and deposition of amyloids in the aging prostate known as corpora amylacea inclusions Strongly up-regulated in many tumors, including gastric, esophageal, colon, pancreatic, bladder, ovarian, thyroid, breast and skin cancers |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Recognizes the L1 or Calprotectin molecule, an intra-cytoplasmic antigen comprising of a 12kDa alpha chain and a 14kDa beta chain expressed by granulocytes, monocytes and by tissue macrophages. Macrophages usually arise from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. Under migration into tissues, the monocytes undergo further differentiation to become multifunctional tissue macrophages. They are classified into normal and inflammatory macrophages. Normal macrophages include macrophages in connective tissue (histiocytes), liver (Kupffer s cells), lung (alveolar macrophages), lymph nodes (free and fixed macrophages), spleen (free and fixed macrophages), bone marrow (fixed macrophages), serous fluids (pleural and peritoneal macrophages), skin (histiocytes, Langerhans's cell) and in other tissues. Inflammatory macrophages are present in various exudates. Macrophages are part of the innate immune system, recognizing, engulfing and destroying many potential pathogens including bacteria, pathogenic protozoa, fungi and helminthes. This MAb reacts with neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and squamous mucosal epithelia and has been shown as an important marker for identifying macrophages in tissue sections.
REFERENCES
Flavell DJ; Jones DB; Wright DH. Identification of tissue histiocytes on paraffin sections by a new monoclonal antibody. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 1987, 35(11):1217-26. |
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。