CD63 (Late Endosomes Marker) Antibody
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone SPM524 ]
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
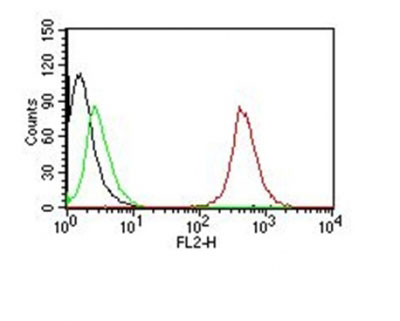
Application
| FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P08962 |
| Other Accession | 967, 445570 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG1, kappa |
| Clone Names | SPM524 |
| Calculated MW | 25637 Da |
| Gene ID | 967 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CD63 antigen, Granulophysin, Lysosomal-associated membrane protein 3, LAMP-3, Melanoma-associated antigen ME491, OMA81H, Ocular melanoma-associated antigen, Tetraspanin-30, Tspan-30, CD63, CD63, MLA1, TSPAN30 |
| Application Note | FC~~1:10~50 |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | CD63 (Late Endosomes Marker) Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CD63 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MLA1, TSPAN30 |
| Function | Functions as a cell surface receptor for TIMP1 and plays a role in the activation of cellular signaling cascades. Plays a role in the activation of ITGB1 and integrin signaling, leading to the activation of AKT, FAK/PTK2 and MAP kinases. Promotes cell survival, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, spreading and migration, via its role in the activation of AKT and FAK/PTK2. Plays a role in VEGFA signaling via its role in regulating the internalization of KDR/VEGFR2. Plays a role in intracellular vesicular transport processes, and is required for normal trafficking of the PMEL luminal domain that is essential for the development and maturation of melanocytes. Plays a role in the adhesion of leukocytes onto endothelial cells via its role in the regulation of SELP trafficking. May play a role in mast cell degranulation in response to Ms4a2/FceRI stimulation, but not in mast cell degranulation in response to other stimuli. |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Lysosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Late endosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endosome, multivesicular body. Melanosome. Secreted, extracellular exosome. Cell surface. Note=Also found in Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial cells (PubMed:10793155). Located in platelet dense granules (PubMed:7682577). Detected in a subset of pre-melanosomes Detected on intralumenal vesicles (ILVs) within multivesicular bodies (PubMed:21962903). |
| Tissue Location | Detected in platelets (at protein level). Dysplastic nevi, radial growth phase primary melanomas, hematopoietic cells, tissue macrophages. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The tetraspanins are integral membrane proteins expressed on cell surface and granular membranes of hematopoietic cells and are components of multi-molecular complexes with specific integrins. The tetraspanin CD63 is a lysosomal membrane glycoprotein that translocates to the plasma membrane after platelet activation. CD63 is expressed on activated platelets, monocytes and macrophages, and is weakly expressed on granulocytes, T cell and B cells. It is located on the basophilic granule membranes and on the plasma membranes of lymphocytes and granulocytes. CD63 is a member of the TM4 superfamily of leukocyte glycoproteins that includes CD9, CD37 and CD53, which contain four transmembrane regions. CD63 may play a role in phagocytic and intracellular lysosome-phagosome fusion events. CD63 deficiency is associated with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome and is strongly expressed during the early stages of melanoma progression.
REFERENCES
C. Vennegoor et al., Int. J. Cancer 35: 287-295, 1985. | AA Palmer et al., Pathology 17: 335-339, 1985. | EC Hagen et al., Histopathology 10: 689-700, 1986
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。