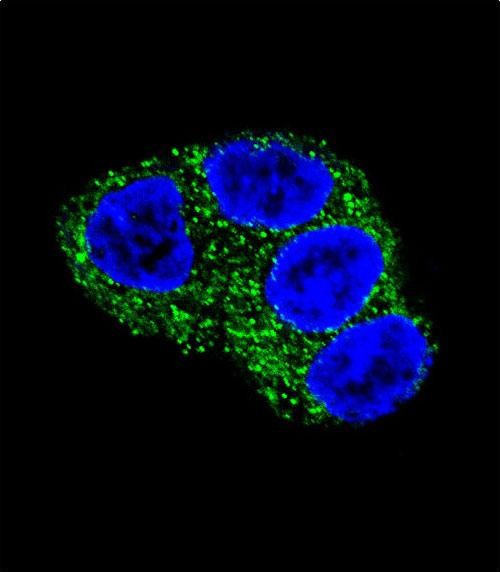
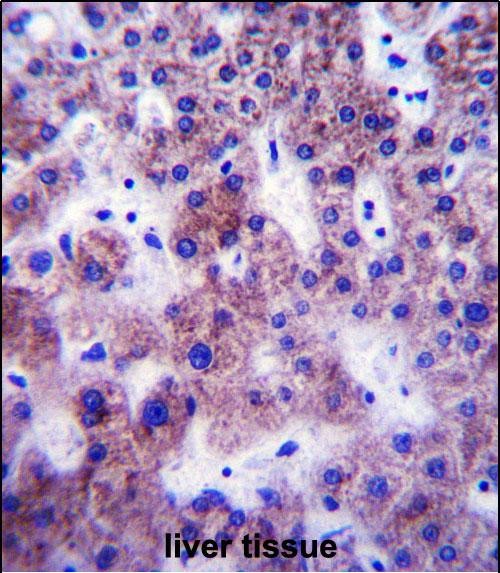
UGT1A1 Antibody (N-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 1
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P22309 |
| Other Accession | NP_000454.1 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 59591 Da |
| Antigen Region | 65-90 aa |
| Gene ID | 54658 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-1, UDPGT 1-1, UGT1*1, UGT1-01, UGT11, Bilirubin-specific UDPGT isozyme 1, hUG-BR1, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-A, UGT-1A, UGT1A, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1, UGT1A1, GNT1, UGT1 |
| Target/Specificity | This UGT1A1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 65-90 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human UGT1A1. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IF~~1:10~50 IHC-P~~1:100~500 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | UGT1A1 Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | UGT1A1 (HGNC:12530) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | GNT1, UGT1 |
| Function | [Isoform 1]: UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) that catalyzes phase II biotransformation reactions in which lipophilic substrates are conjugated with glucuronic acid to increase the metabolite's water solubility, thereby facilitating excretion into either the urine or bile (PubMed:12181437, PubMed:15472229, PubMed:18004206, PubMed:18004212, PubMed:18719240, PubMed:19830808, PubMed:23288867, PubMed:15231852, PubMed:21422672, PubMed:38211441). Essential for the elimination and detoxification of drugs, xenobiotics and endogenous compounds (PubMed:12181437, PubMed:18004206, PubMed:18004212). Catalyzes the glucuronidation of endogenous estrogen hormones such as estradiol, estrone and estriol (PubMed:15472229, PubMed:18719240, PubMed:23288867). Involved in the glucuronidation of bilirubin, a degradation product occurring in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates (PubMed:17187418, PubMed:18004206, PubMed:19830808, PubMed:24525562). Involved in the glucuronidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and AA-derived eicosanoids including 15-HETE, 20- HETE, PGB1 and F2-isoprostane (8-iso-PGF2alpha) (PubMed:15231852, PubMed:38211441). Involved in the glucuronidation of the phytochemical ferulic acid at the phenolic or the carboxylic acid group (PubMed:21422672). Also catalyzes the glucuronidation the isoflavones genistein, daidzein, glycitein, formononetin, biochanin A and prunetin, which are phytoestrogens with anticancer and cardiovascular properties (PubMed:18052087, PubMed:19545173). Involved in the glucuronidation of the AGTR1 angiotensin receptor antagonist losartan, a drug which can inhibit the effect of angiotensin II (PubMed:18674515). Involved in the biotransformation of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN-38), the pharmacologically active metabolite of the anticancer drug irinotecan (PubMed:12181437, PubMed:18004212, PubMed:20610558). |
| Cellular Location | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region |
| Tissue Location | [Isoform 1]: Expressed in liver, colon and small intestine. Not expressed in kidney, esophagus and skin |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, an enzyme of the glucuronidation pathway that transforms small lipophilic molecules, such as steroids, bilirubin, hormones, and drugs, into water-soluble, excretable metabolites. This gene is part of a complex locus that encodes several UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. The locus includes thirteen unique alternate first exons followed by four common exons. Four of the alternate first exons are considered pseudogenes. Each of the remaining nine 5' exons may be spliced to the four common exons, resulting in nine proteins with different N-termini and identical C-termini. Each first exon encodes the substrate binding site, and is regulated by its own promoter. The preferred substrate of this enzyme is bilirubin, although it also has moderate activity with simple phenols, flavones, and C18 steroids. Mutations in this gene result in Crigler-Najjar syndromes types I and II and in Gilbert syndrome.
REFERENCES
Italia, K.Y., et al. Clin. Biochem. 43 (16-17), 1329-1332 (2010) :
Justenhoven, C., et al. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 124(1):289-292(2010)
Hu, M., et al. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 20(10):634-637(2010)
Sai, K., et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol 70(2):222-233(2010)
Kilic, I., et al. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 48(8):504-508(2010)
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。