SQSTM1 (p62) Antibody (C-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 33
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
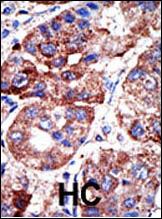
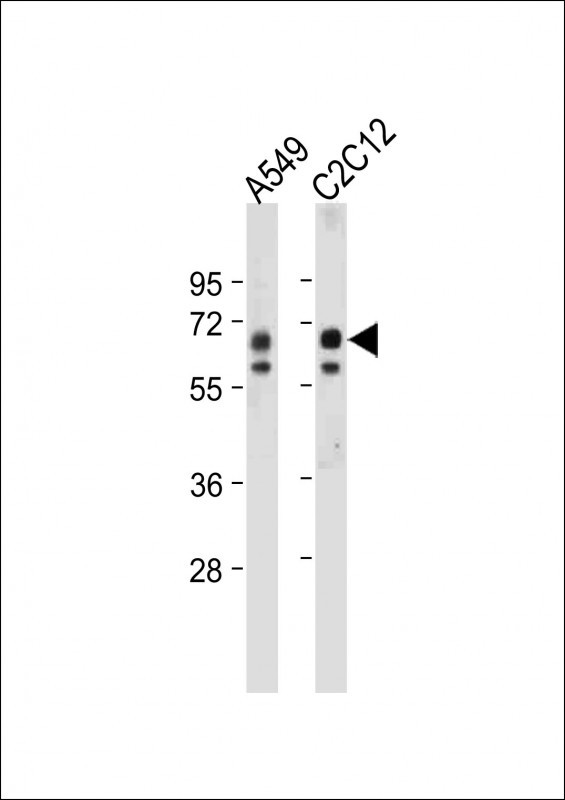
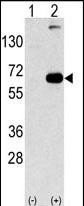
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q13501 |
| Other Accession | O08623, Q64337 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Predicted | Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 47687 Da |
| Antigen Region | 317-346 aa |
| Gene ID | 8878 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Sequestosome-1, EBI3-associated protein of 60 kDa, EBIAP, p60, Phosphotyrosine-independent ligand for the Lck SH2 domain of 62 kDa, Ubiquitin-binding protein p62, SQSTM1, ORCA, OSIL. |
| Target/Specificity | This SQSTM1 (p62) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 317-346 amino acids of human SQSTM1 (p62). |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC-P~~1:100~500 IF~~1:200 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | SQSTM1 (p62) Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SQSTM1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:16286508, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:11280} |
|---|---|
| Function | Molecular adapter required for selective macroautophagy (aggrephagy) by acting as a bridge between polyubiquitinated proteins and autophagosomes (PubMed:15340068, PubMed:15953362, PubMed:16286508, PubMed:17580304, PubMed:20168092, PubMed:22017874, PubMed:22622177, PubMed:24128730, PubMed:28404643, PubMed:29343546, PubMed:29507397, PubMed:31857589, PubMed:33509017, PubMed:34471133, PubMed:34893540, PubMed:35831301, PubMed:37306101, PubMed:37802024). Promotes the recruitment of ubiquitinated cargo proteins to autophagosomes via multiple domains that bridge proteins and organelles in different steps (PubMed:16286508, PubMed:20168092, PubMed:22622177, PubMed:24128730, PubMed:28404643, PubMed:29343546, PubMed:29507397, PubMed:34893540, PubMed:37802024). SQSTM1 first mediates the assembly and removal of ubiquitinated proteins by undergoing liquid-liquid phase separation upon binding to ubiquitinated proteins via its UBA domain, leading to the formation of insoluble cytoplasmic inclusions, known as p62 bodies (PubMed:15911346, PubMed:20168092, PubMed:22017874, PubMed:24128730, PubMed:29343546, PubMed:29507397, PubMed:31857589, PubMed:37802024). SQSTM1 then interacts with ATG8 family proteins on autophagosomes via its LIR motif, leading to p62 body recruitment to autophagosomes, followed by autophagic clearance of ubiquitinated proteins (PubMed:16286508, PubMed:17580304, PubMed:20168092, PubMed:22622177, PubMed:24128730, PubMed:28404643, PubMed:37802024). SQSTM1 is itself degraded along with its ubiquitinated cargos (PubMed:16286508, PubMed:17580304, PubMed:37802024). Also required to recruit ubiquitinated proteins to PML bodies in the nucleus (PubMed:20168092). Also involved in autophagy of peroxisomes (pexophagy) in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS) by acting as a bridge between ubiquitinated PEX5 receptor and autophagosomes (PubMed:26344566). Acts as an activator of the NFE2L2/NRF2 pathway via interaction with KEAP1: interaction inactivates the BCR(KEAP1) complex by sequestering the complex in inclusion bodies, promoting nuclear accumulation of NFE2L2/NRF2 and subsequent expression of cytoprotective genes (PubMed:20452972, PubMed:28380357, PubMed:33393215, PubMed:37306101). Promotes relocalization of 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitinated STING1 to autophagosomes (PubMed:29496741). Involved in endosome organization by retaining vesicles in the perinuclear cloud: following ubiquitination by RNF26, attracts specific vesicle-associated adapters, forming a molecular bridge that restrains cognate vesicles in the perinuclear region and organizes the endosomal pathway for efficient cargo transport (PubMed:27368102, PubMed:33472082). Sequesters tensin TNS2 into cytoplasmic puncta, promoting TNS2 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation (PubMed:25101860). May regulate the activation of NFKB1 by TNF, nerve growth factor (NGF) and interleukin-1 (PubMed:10356400, PubMed:10747026, PubMed:11244088, PubMed:12471037, PubMed:16079148, PubMed:19931284). May play a role in titin/TTN downstream signaling in muscle cells (PubMed:15802564). Adapter that mediates the interaction between TRAF6 and CYLD (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome. Preautophagosomal structure. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Nucleus, PML body. Late endosome. Lysosome. Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum. Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08623}. Note=In cardiac muscle, localizes to the sarcomeric band (By similarity). Localizes to cytoplasmic membraneless inclusion bodies, known as p62 bodies, containing polyubiquitinated protein aggregates (PubMed:11786419, PubMed:20357094, PubMed:22017874, PubMed:29343546, PubMed:29507397, PubMed:31857589, PubMed:37306101, PubMed:37802024). In neurodegenerative diseases, detected in Lewy bodies in Parkinson disease, neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease, and HTT aggregates in Huntington disease (PubMed:15158159). In protein aggregate diseases of the liver, found in large amounts in Mallory bodies of alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, hyaline bodies in hepatocellular carcinoma, and in SERPINA1 aggregates (PubMed:11981755) Enriched in Rosenthal fibers of pilocytic astrocytoma (PubMed:11786419). In the cytoplasm, observed in both membrane-free ubiquitin-containing protein aggregates (sequestosomes) and membrane- surrounded autophagosomes (PubMed:15953362, PubMed:17580304) Colocalizes with TRIM13 in the perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:22178386). Co-localizes with TRIM5 in cytoplasmic bodies (PubMed:20357094). When nuclear export is blocked by treatment with leptomycin B, accumulates in PML bodies (PubMed:20168092) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08623, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11786419, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11981755, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15158159, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15953362, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17580304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20168092, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20357094, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22017874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22178386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29343546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29507397, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31857589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37306101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37802024} |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
SQSTM1/p62 is an adapter protein which binds ubiquitin and may regulate the activation of NFKB1 by TNF-alpha, nerve growth factor (NGF) and interleukin-1. This protein may play a role in titin/TTN downstream signaling in muscle cells, and may also regulate signaling cascades through ubiquitination. This protein is involved in cell differentiation, apoptosis, immune response and regulation of K(+) channels. SQSTM1/p62 also appears to play a role in macroautophagic removal of intracellular protein aggregates. Cellular depletion studies of SQSTM1/p62 have indicated a role for association with LC3 and aggregate proteins in order to facilitate normal formation of the autophagosome.
REFERENCES
References for protein:
1.Seibenhener, M.L., et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 24(18):8055-8068 (2004).
2.Eekhoff, E.W., et al., Arthritis Rheum. 50(5):1650-1654 (2004).
3.Brajenovic, M., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 279(13):12804-12811 (2004).
4.Kuusisto, E., et al., J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 62(12):1241-1253 (2003).
5. Johnson-Pais, T.L., et al., J. Bone Miner. Res. 18(10):1748-1753 (2003).
References for U251 cell line:
1. Westermark B.; Pontén J.; Hugosson R. (1973).” Determinants for the establishment of permanent tissue culture lines from human gliomas”. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 81:791-805. [PMID: 4359449].
2. Pontén, J.,Westermark B. (1978).” Properties of Human Malignant Glioma Cells in Vitro”. Medical Biology 56: 184-193.[PMID: 359950].
3. Geng Y.;Kohli L.; Klocke B.J.; Roth K.A.(2010). “Chloroquine-induced autophagic vacuole accumulation and cell death in glioma cells is p53 independent”. Neuro Oncol. 12(5): 473–481.[ PMID: 20406898].
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
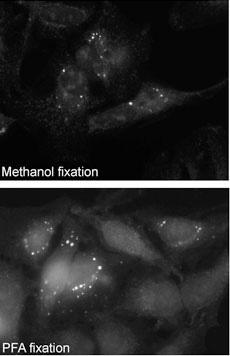
_(C-term)_-_U251_CQ.jpg)