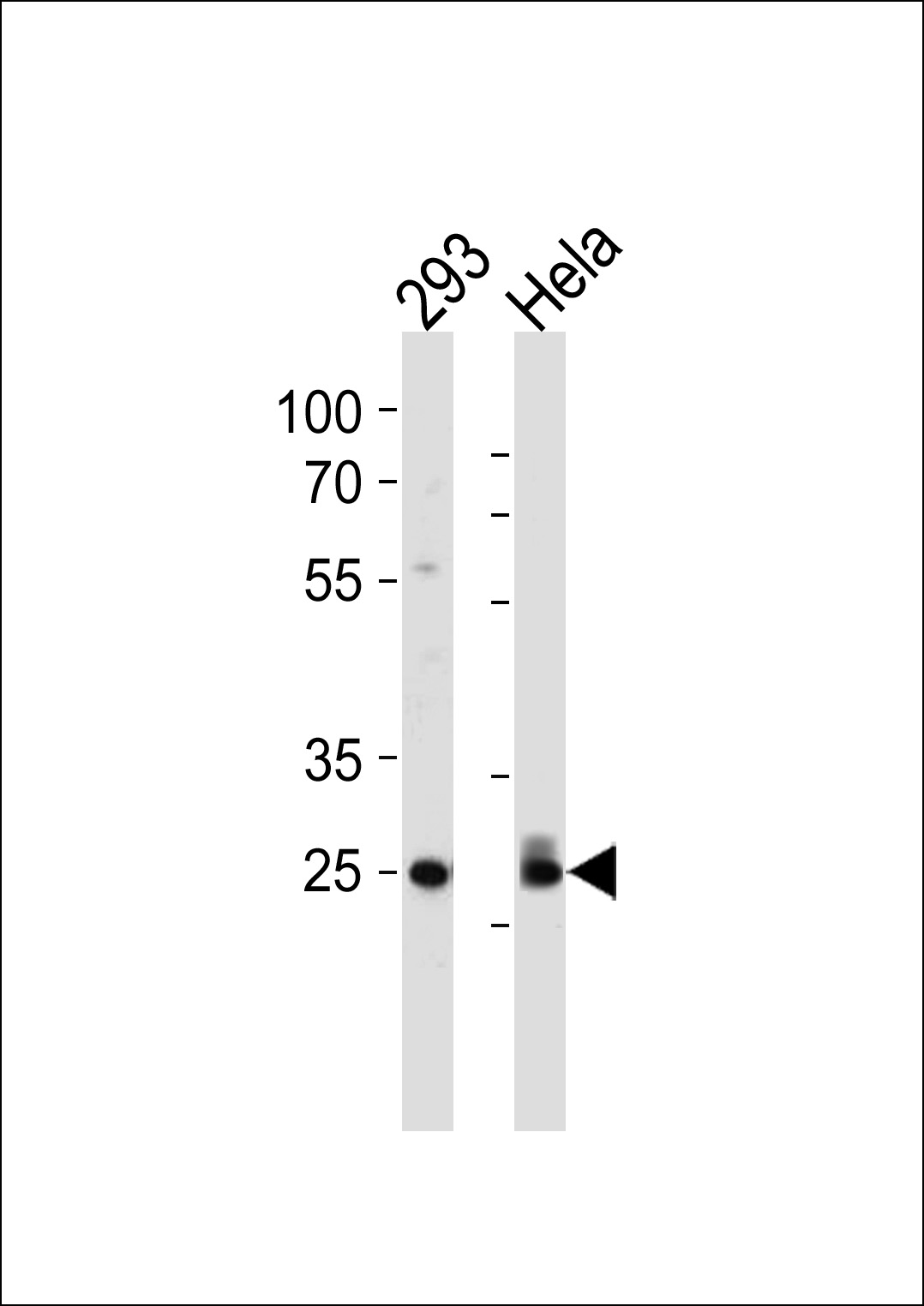
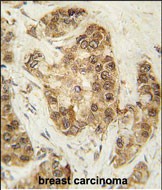
CDK2 Antibody (T14)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 2
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| IHC-P, WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P24941 |
| Other Accession | Q80YP0, Q00526, P23437, Q63699, P97377, O55076, Q5E9Y0 |
| Reactivity | Human, Rat, Mouse |
| Predicted | Bovine, Hamster, Mouse, Rat, Xenopus |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 33930 Da |
| Antigen Region | 1-30 aa |
| Gene ID | 1017 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, Cell division protein kinase 2, p33 protein kinase, CDK2, CDKN2 |
| Target/Specificity | This CDK2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from human CDK2. |
| Dilution | IHC-P~~1:100~500 WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | CDK2 Antibody (T14) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CDK2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CDKN2 |
| Function | Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in the control of the cell cycle; essential for meiosis, but dispensable for mitosis (PubMed:10499802, PubMed:10884347, PubMed:10995386, PubMed:10995387, PubMed:11051553, PubMed:11113184, PubMed:12944431, PubMed:15800615, PubMed:17495531, PubMed:19966300, PubMed:20935635, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:21596315, PubMed:28216226, PubMed:28666995). Phosphorylates CABLES1, CTNNB1, CDK2AP2, ERCC6, NBN, USP37, p53/TP53, NPM1, CDK7, RB1, BRCA2, MYC, NPAT, EZH2 (PubMed:10499802, PubMed:10995386, PubMed:10995387, PubMed:11051553, PubMed:11113184, PubMed:12944431, PubMed:15800615, PubMed:19966300, PubMed:20935635, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:21596315, PubMed:28216226). Triggers duplication of centrosomes and DNA (PubMed:11051553). Acts at the G1-S transition to promote the E2F transcriptional program and the initiation of DNA synthesis, and modulates G2 progression; controls the timing of entry into mitosis/meiosis by controlling the subsequent activation of cyclin B/CDK1 by phosphorylation, and coordinates the activation of cyclin B/CDK1 at the centrosome and in the nucleus (PubMed:18372919, PubMed:19238148, PubMed:19561645). Crucial role in orchestrating a fine balance between cellular proliferation, cell death, and DNA repair in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) (PubMed:18372919, PubMed:19238148, PubMed:19561645). Activity of CDK2 is maximal during S phase and G2; activated by interaction with cyclin E during the early stages of DNA synthesis to permit G1-S transition, and subsequently activated by cyclin A2 (cyclin A1 in germ cells) during the late stages of DNA replication to drive the transition from S phase to mitosis, the G2 phase (PubMed:18372919, PubMed:19238148, PubMed:19561645). EZH2 phosphorylation promotes H3K27me3 maintenance and epigenetic gene silencing (PubMed:20935635). Cyclin E/CDK2 prevents oxidative stress- mediated Ras-induced senescence by phosphorylating MYC (PubMed:19966300). Involved in G1-S phase DNA damage checkpoint that prevents cells with damaged DNA from initiating mitosis; regulates homologous recombination-dependent repair by phosphorylating BRCA2, this phosphorylation is low in S phase when recombination is active, but increases as cells progress towards mitosis (PubMed:15800615, PubMed:20195506, PubMed:21319273). In response to DNA damage, double- strand break repair by homologous recombination a reduction of CDK2- mediated BRCA2 phosphorylation (PubMed:15800615). Involved in regulation of telomere repair by mediating phosphorylation of NBN (PubMed:28216226). Phosphorylation of RB1 disturbs its interaction with E2F1 (PubMed:10499802). NPM1 phosphorylation by cyclin E/CDK2 promotes its dissociates from unduplicated centrosomes, thus initiating centrosome duplication (PubMed:11051553). Cyclin E/CDK2-mediated phosphorylation of NPAT at G1-S transition and until prophase stimulates the NPAT-mediated activation of histone gene transcription during S phase (PubMed:10995386, PubMed:10995387). Required for vitamin D-mediated growth inhibition by being itself inactivated (PubMed:20147522). Involved in the nitric oxide- (NO) mediated signaling in a nitrosylation/activation-dependent manner (PubMed:20079829). USP37 is activated by phosphorylation and thus triggers G1-S transition (PubMed:21596315). CTNNB1 phosphorylation regulates insulin internalization (PubMed:21262353). Phosphorylates FOXP3 and negatively regulates its transcriptional activity and protein stability (By similarity). Phosphorylates ERCC6 which is essential for its chromatin remodeling activity at DNA double-strand breaks (PubMed:29203878). Acts as a regulator of the phosphatidylinositol 3- kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction by mediating phosphorylation of the C-terminus of protein kinase B (PKB/AKT1 and PKB/AKT2), promoting its activation (PubMed:24670654). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Nucleus, Cajal body. Cytoplasm. Endosome Note=Localized at the centrosomes in late G2 phase after separation of the centrosomes but before the start of prophase. Nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking is mediated during the inhibition by 1,25-(OH)(2)D(3) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
CDK2 is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28, and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase, and essential for cell cycle G1/S phase transition. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin A or E, CDK inhibitor p21Cip1 (CDKN1A) and p27Kip1 (CDKN1B). Its activity is also regulated by its protein phosphorylation.
REFERENCES
Moshinsky, D.J., et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 310(3):1026-1031 (2003).
Chow, J.P., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 278(42):40815-40828 (2003).
O'Nions, J., et al., Oncogene 22(46):7181-7191 (2003).
Yun, J., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 278(38):36966-36972 (2003).
Izumiya, Y., et al., J. Virol. 77(17):9652-9661 (2003).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.
|
Anonymous
2016-08-24 09:20:44
1
2
3
4
5
|
Species tested
Human,Mouse
Application tested
WB
Organization tested
Hela,293T,Jurkat,K562,A431,MCF-7,Lung(M),Spleen(M),Lung (R)
Barcode encoding
Brief protocol
1. Block with 3% skim milk for 1 hour at room temperature.
2. Incubate overnight with Abgent primary antibody 1:1000 in 3% skim milk at 4℃
3. Wash 5*5 min with TBST.
4. Incubate with HRP-conjugated secondary antibody 1:5000 in 3% skim milk for 1 hour at room temperature.
5. Wash 5*5 min with TBST.
6. Incubate with ECL substrates and expose
|






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。