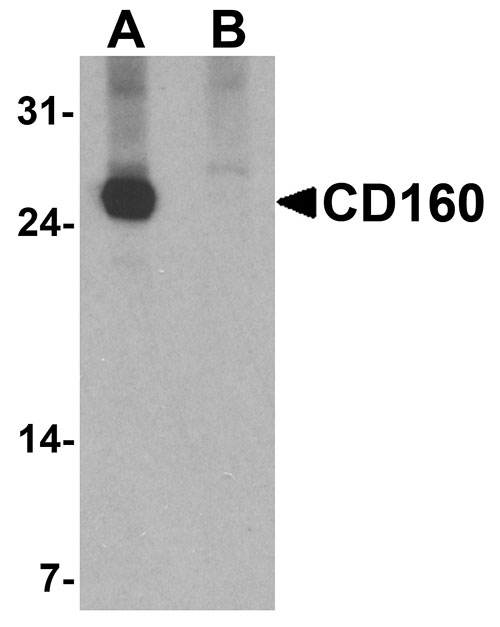
CD160 Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O95971 |
| Other Accession | NP_008984, 5901910 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 19810 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | CD160 antibody can be used for detection of CD160 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. |
| Gene ID | 11126 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CD160 antigen, Natural killer cell receptor BY55, CD160, CD160, BY55 |
| Target/Specificity | CD160; CD160 antibody is human and mouse reactive. Multiple isoforms of CD160 are known to exist. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | CD160 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | CD160 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CD160 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:16809620, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:17013} |
|---|---|
| Function | [CD160 antigen]: Receptor on immune cells capable to deliver stimulatory or inhibitory signals that regulate cell activation and differentiation. Exists as a GPI-anchored and as a transmembrane form, each likely initiating distinct signaling pathways via phosphoinositol 3-kinase in activated NK cells and via LCK and CD247/CD3 zeta chain in activated T cells (PubMed:11978774, PubMed:17307798, PubMed:19109136). Receptor for both classical and non-classical MHC class I molecules (PubMed:12486241, PubMed:9973372). In the context of acute viral infection, recognizes HLA-C and triggers NK cell cytotoxic activity, likely playing a role in anti-viral innate immune response (PubMed:12486241). On CD8+ T cells, binds HLA-A2-B2M in complex with a viral peptide and provides a costimulatory signal to activated/memory T cells (PubMed:9973372). Upon persistent antigen stimulation, such as occurs during chronic viral infection, may progressively inhibit TCR signaling in memory CD8+ T cells, contributing to T cell exhaustion (PubMed:25255144). On endothelial cells, recognizes HLA-G and controls angiogenesis in immune privileged sites (PubMed:16809620). Receptor or ligand for TNF superfamily member TNFRSF14, participating in bidirectional cell-cell contact signaling between antigen presenting cells and lymphocytes. Upon ligation of TNFRSF14, provides stimulatory signal to NK cells enhancing IFNG production and anti-tumor immune response (By similarity). On activated CD4+ T cells, interacts with TNFRSF14 and down-regulates CD28 costimulatory signaling, restricting memory and alloantigen-specific immune response (PubMed:18193050). In the context of bacterial infection, acts as a ligand for TNFRSF14 on epithelial cells, triggering the production of antimicrobial proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | [CD160 antigen]: Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor, GPI-anchor |
| Tissue Location | Expression is restricted to functional NK and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Expressed in viral-specific effector memory and terminally differentiated effector memory CD8+ T cells. Expressed in memory and activated CD4+ T cell subsets (at protein level) (PubMed:11978774, PubMed:18193050, PubMed:25255144, PubMed:9743336) Expressed at high levels in intraepithelial lymphocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:9743336). Expressed in both alpha-beta and gamma-delta CD8+ T cell subsets (at protein level) (PubMed:11978774, PubMed:18193050, PubMed:9743336). Expressed in umbilical vein endothelial cells (at protein level) (PubMed:16809620). Expressed in monocytes and at lower levels in B cells (PubMed:23761635). Isoform 3: Expressed exclusively in activated NK cells (at protein level) (PubMed:19109136). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
CD160, also known as BY55, is a lipid-anchored cell membrane glycoprotein that contains one immunoglobulin-like domain (1). It is expressed in small intestine, spleen and functional NK and T cytotoxic lymphocytes (1,2). CD160 exists as a disulfide-linked homomultimer that functions as a receptor for MHC (major histocompatability complex) molecules and is thought to regulate the function of NK cells (2,3). Additionally, CD160 interacts with TNFRSF14 and, via this interaction, is able to negatively regulate CD4+ T cell activation, indicating a role in immune system regulation (4).
REFERENCES
Anumanthan A, Bensussan A, Boumsell L, et al. Cloning of BY55, a novel Ig superfamily member expressed on NK cells, CTL, and intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1998; 161:2780-90.
Agrawal S, Marquet J, Freeman GJ, et al. Cutting edge: MHC class I triggering by a novel cell surface ligand costimulates proliferation of activated human T cells. J. Immunol. 1999; 162:1223-6.
Le Bouteiller P, Tabiasco J, Polgar B, et al. CD160: a unique activating NK cell receptor. Immunol. Lett. 2011;138:93-6
Chabot S, Jabrane-Ferrat N, Bigot K, et al. A novel antiangiogenic and vascular normalization therapy targeted against human CD160 receptor. J. Exp. Med. 2011; 208:973-86.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。