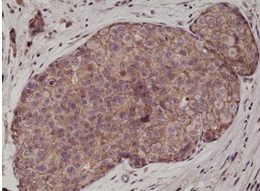
Anti-E-Cadherin (CDH1) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P12830 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 97456 Da |
| Gene ID | 999 |
|---|---|
| Positive Control | WB: MCF-7 cells; IHC: human breast cancer tissues |
| Application & Usage | IHC: 1:500 -1:1000 dilution; WB: 1:1000 - 1:2000 dilution |
| Alias Symbol | CDH1 |
| Other Names | P-cadherin, N-Cadherin, E-Cadherin, K-Cadherin, M-jadherin, R-Cadherin |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Formulation | In 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide |
| Reconstitution & Storage | -20 °C |
| Background Descriptions | |
| Precautions | Anti-E-Cadherin (CDH1) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CDH1 (HGNC:1748) |
|---|---|
| Function | Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion proteins (PubMed:11976333). They preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells; cadherins may thus contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell types. CDH1 is involved in mechanisms regulating cell-cell adhesions, mobility and proliferation of epithelial cells (PubMed:11976333). Promotes organization of radial actin fiber structure and cellular response to contractile forces, via its interaction with AMOTL2 which facilitates anchoring of radial actin fibers to CDH1 junction complexes at the cell membrane (By similarity). Plays a role in the early stages of desmosome cell-cell junction formation via facilitating the recruitment of DSG2 and DSP to desmosome plaques (PubMed:29999492). Has a potent invasive suppressor role. It is a ligand for integrin alpha-E/beta-7. |
| Cellular Location | Cell junction, adherens junction. Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein Endosome. Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network. Cytoplasm. Cell junction, desmosome. Note=Colocalizes with DLGAP5 at sites of cell-cell contact in intestinal epithelial cells. Anchored to actin microfilaments through association with alpha-, beta- and gamma- catenin. Sequential proteolysis induced by apoptosis or calcium influx, results in translocation from sites of cell-cell contact to the cytoplasm. Colocalizes with RAB11A endosomes during its transport from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane. Recruited to desmosomes at the initial assembly phase and also accumulates progressively at mature desmosome cell-cell junctions (PubMed:25208567, PubMed:29999492) Localizes to cell-cell contacts as keratinocyte differentiation progresses (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P09803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25208567, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29999492} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in granuloma macrophages (at protein level) (PubMed:27760340). Expressed in the skin (at protein level) (PubMed:22294297). Expressed in the liver (PubMed:3263290) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Cadherins comprise a family of Ca-dependent adhesion molecules that function to mediate cell-cell binding critical to the maintenance of tissue structure and morphogenesis. Cadherins consist of large extracellular domains characterized by a series of five homologous NH2 terminal repeats. The most distal of cadherins is thought to be responsible for binding specificity, transmembrane domains and carboxy terminal domains. The relative short intracellular domains interact with a variety of cytoplasmic proteins, such as β-catenin, to regulate cadherin function.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。