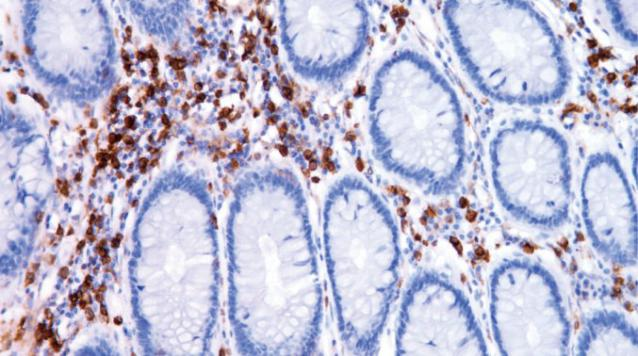
Annexin A1
Rabbit Monoclonal antibody(Mab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P04083 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 705B1F6 |
| Calculated MW | 38714 Da |
| Gene ID | 301 |
|---|---|
| Gene Name | ANXA1 |
| Other Names | Annexin A1, Annexin I, Annexin-1, Calpactin II, Calpactin-2, Chromobindin-9, Lipocortin I, Phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein, p35, Annexin Ac2-26, ANXA1, ANX1, LPC1 |
| Dilution | IHC-P~~Ready-to-use |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C. |
| Precautions | Annexin A1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ANXA1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ANX1, LPC1 |
| Function | Plays important roles in the innate immune response as effector of glucocorticoid-mediated responses and regulator of the inflammatory process. Has anti-inflammatory activity (PubMed:8425544). Plays a role in glucocorticoid-mediated down-regulation of the early phase of the inflammatory response (By similarity). Contributes to the adaptive immune response by enhancing signaling cascades that are triggered by T-cell activation, regulates differentiation and proliferation of activated T-cells (PubMed:17008549). Promotes the differentiation of T-cells into Th1 cells and negatively regulates differentiation into Th2 cells (PubMed:17008549). Has no effect on unstimulated T cells (PubMed:17008549). Negatively regulates hormone exocytosis via activation of the formyl peptide receptors and reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton (PubMed:19625660). Has high affinity for Ca(2+) and can bind up to eight Ca(2+) ions (By similarity). Displays Ca(2+)-dependent binding to phospholipid membranes (PubMed:2532504, PubMed:8557678). Plays a role in the formation of phagocytic cups and phagosomes. Plays a role in phagocytosis by mediating the Ca(2+)-dependent interaction between phagosomes and the actin cytoskeleton (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell projection, cilium {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P46193}. Cell membrane. Membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Endosome membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P07150}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P07150}. Basolateral cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51662}. Apical cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10107}. Lateral cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10107}. Secreted. Secreted, extracellular space. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Extracellular side. Secreted, extracellular exosome. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle lumen. Cell projection, phagocytic cup {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10107}. Early endosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P19619}. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P19619}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P19619}. Note=Secreted, at least in part via exosomes and other secretory vesicles. Detected in exosomes and other extracellular vesicles (PubMed:25664854). Alternatively, the secretion is dependent on protein unfolding and facilitated by the cargo receptor TMED10; it results in the protein translocation from the cytoplasm into ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment) followed by vesicle entry and secretion (PubMed:32272059). Detected in gelatinase granules in resting neutrophils (PubMed:10772777). Secretion is increased in response to wounding and inflammation (PubMed:25664854). Secretion is increased upon T-cell activation (PubMed:17008549). Neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cells stimulates secretion via gelatinase granules, but foreign particle phagocytosis has no effect (PubMed:10772777). Colocalizes with actin fibers at phagocytic cups (By similarity). Displays calcium-dependent binding to phospholipid membranes (PubMed:2532504, PubMed:8557678) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10772777, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17008549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2532504, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25664854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32272059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8557678} |
| Tissue Location | Detected in resting neutrophils (PubMed:10772777). Detected in peripheral blood T-cells (PubMed:17008549). Detected in extracellular vesicles in blood serum from patients with inflammatory bowel disease, but not in serum from healthy donors (PubMed:25664854) Detected in placenta (at protein level) (PubMed:2532504). Detected in liver. |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.
¥ 1,250.00
Cat# AD80052























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。