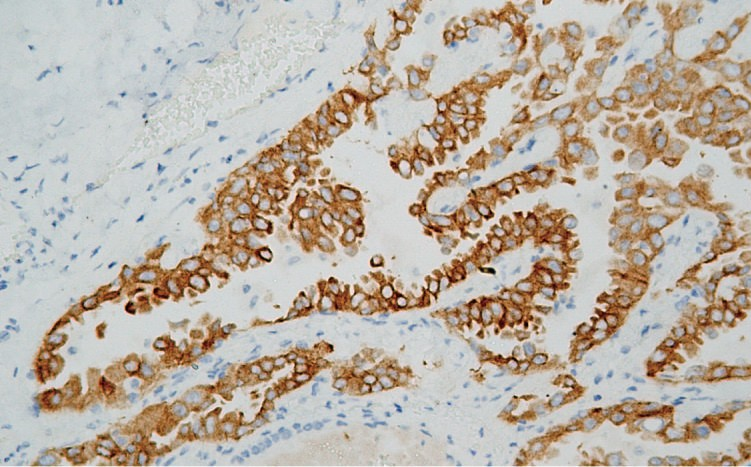
ALK
Mouse Monoclonal antibody(Mab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UM73 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 137E9E8 |
| Calculated MW | 176442 Da |
| Gene ID | 238 |
|---|---|
| Gene Name | ALK |
| Other Names | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor, 2.7.10.1, Anaplastic lymphoma kinase, CD246, ALK {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9174053, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:427} |
| Dilution | IHC-P~~Ready-to-use |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C. |
| Precautions | ALK Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ALK {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9174053, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:427} |
|---|---|
| Function | Neuronal receptor tyrosine kinase that is essentially and transiently expressed in specific regions of the central and peripheral nervous systems and plays an important role in the genesis and differentiation of the nervous system (PubMed:11121404, PubMed:11387242, PubMed:16317043, PubMed:17274988, PubMed:30061385, PubMed:34646012, PubMed:34819673). Also acts as a key thinness protein involved in the resistance to weight gain: in hypothalamic neurons, controls energy expenditure acting as a negative regulator of white adipose tissue lipolysis and sympathetic tone to fine-tune energy homeostasis (By similarity). Following activation by ALKAL2 ligand at the cell surface, transduces an extracellular signal into an intracellular response (PubMed:30061385, PubMed:33411331, PubMed:34646012, PubMed:34819673). In contrast, ALKAL1 is not a potent physiological ligand for ALK (PubMed:34646012). Ligand-binding to the extracellular domain induces tyrosine kinase activation, leading to activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway (PubMed:34819673). Phosphorylates almost exclusively at the first tyrosine of the Y-x-x-x-Y-Y motif (PubMed:15226403, PubMed:16878150). Induces tyrosine phosphorylation of CBL, FRS2, IRS1 and SHC1, as well as of the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 (PubMed:15226403, PubMed:16878150). ALK activation may also be regulated by pleiotrophin (PTN) and midkine (MDK) (PubMed:11278720, PubMed:11809760, PubMed:12107166, PubMed:12122009). PTN-binding induces MAPK pathway activation, which is important for the anti-apoptotic signaling of PTN and regulation of cell proliferation (PubMed:11278720, PubMed:11809760, PubMed:12107166). MDK-binding induces phosphorylation of the ALK target insulin receptor substrate (IRS1), activates mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and PI3-kinase, resulting also in cell proliferation induction (PubMed:12122009). Drives NF-kappa-B activation, probably through IRS1 and the activation of the AKT serine/threonine kinase (PubMed:15226403, PubMed:16878150). Recruitment of IRS1 to activated ALK and the activation of NF-kappa-B are essential for the autocrine growth and survival signaling of MDK (PubMed:15226403, PubMed:16878150). May function as regulator of gastric epithelial differentiation (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein Note=Membrane attachment is essential for promotion of neuron-like differentiation and cell proliferation arrest through specific activation of the MAP kinase pathway. |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in brain and CNS. Also expressed in the small intestine and testis, but not in normal lymphoid cells |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.
¥ 913.00
Cat# AD80132























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。