HLA-DRB (MHC II) Antibody - With BSA and Azide
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone HLA-DRB/1067 ]
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
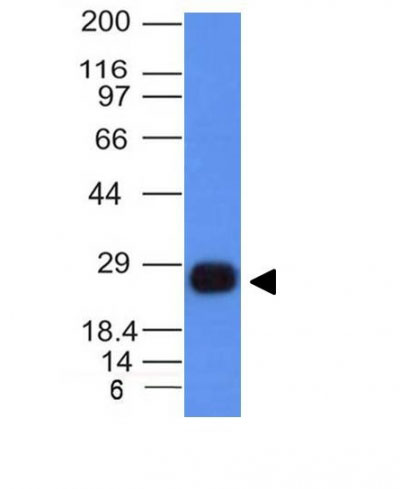
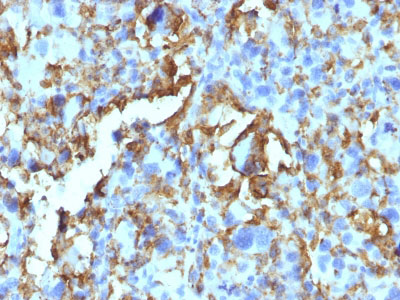
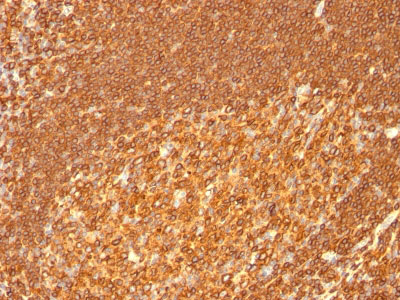
Application
| WB, IHC, IF, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P01911 |
| Other Accession | 3123, 534322 |
| Reactivity | Human, Monkey |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b, kappa |
| Clone Names | HLA-DRB/1067 |
| Calculated MW | 29966 Da |
| Gene ID | 3123 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1-15 beta chain, DW2.2/DR2.2, MHC class II antigen DRB1*15, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB2 |
| Application Note | WB~~1:1000 IHC~~1:100~500 IF~~1:50~200 FC~~1:10~50 |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | HLA-DRB (MHC II) Antibody - With BSA and Azide is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | HLA-DRB1 (HGNC:4948) |
|---|---|
| Function | A beta chain of antigen-presenting major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) molecule. In complex with the alpha chain HLA- DRA, displays antigenic peptides on professional antigen presenting cells (APCs) for recognition by alpha-beta T cell receptor (TCR) on HLA-DRB1-restricted CD4-positive T cells. This guides antigen-specific T-helper effector functions, both antibody-mediated immune response and macrophage activation, to ultimately eliminate the infectious agents and transformed cells (PubMed:15265931, PubMed:16148104, PubMed:22327072, PubMed:27591323, PubMed:29884618, PubMed:31495665, PubMed:8642306). Typically presents extracellular peptide antigens of 10 to 30 amino acids that arise from proteolysis of endocytosed antigens in lysosomes (PubMed:8145819). In the tumor microenvironment, presents antigenic peptides that are primarily generated in tumor- resident APCs likely via phagocytosis of apoptotic tumor cells or macropinocytosis of secreted tumor proteins (PubMed:31495665). Presents peptides derived from intracellular proteins that are trapped in autolysosomes after macroautophagy, a mechanism especially relevant for T cell selection in the thymus and central immune tolerance (PubMed:17182262, PubMed:23783831). The selection of the immunodominant epitopes follows two processing modes: 'bind first, cut/trim later' for pathogen-derived antigenic peptides and 'cut first, bind later' for autoantigens/self-peptides (PubMed:25413013). The anchor residue at position 1 of the peptide N-terminus, usually a large hydrophobic residue, is essential for high affinity interaction with MHCII molecules (PubMed:8145819). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Lysosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Late endosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Autolysosome membrane Note=The MHC class II complex transits through a number of intracellular compartments in the endocytic pathway until it reaches the cell membrane for antigen presentation (PubMed:18305173). Component of immunological synapses at the interface between T cell and APC (PubMed:29884618). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in professional APCs: monocyte/macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells (at protein level) (PubMed:19830726, PubMed:23783831, PubMed:31495665). Expressed in thymic epithelial cells (at protein level) (PubMed:23783831) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This MAb reacts with the beta-chain of HLA-DRB1 antigen, a member of MHC class II molecules. It does not cross react with HLA-DP and HLA-DQ. Its epitope is different from that of MAb L243. HLA-DR is a heterodimeric cell surface glycoprotein comprised of a 36kDa alpha (heavy) chain and a 28kDa beta (light) chain. It is expressed on B-cells, activated T-cells, monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells and other non-professional APCs. In conjunction with the CD3/TCR complex and CD4 molecules, HLA-DR is critical for efficient peptide presentation to CD4+ T cells. It is an excellent histiocytic marker in paraffin sections producing intense cytoplasmic staining. True histiocytic neoplasms are similarly positive. HLA-DR antigens also occur on a variety of epithelial cells and their corresponding neoplastic counterparts. Loss of HLA-DR expression is related to tumor microenvironment and predicts adverse outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
REFERENCES
Marder RJ, et al. 1985. Lab. Invest. 52:497.2. Norton AJ and Isaacson PG. 1987. Am. J. Pathol. 128:225.3. Hua ZX, et al. 1998. Hum. Pathol. 29(12):1441
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。