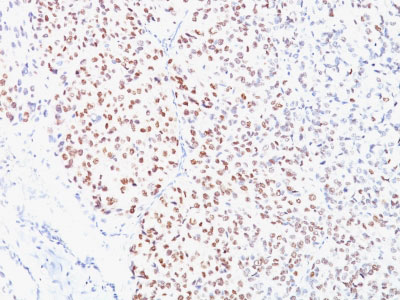
Microphthalmia Transcription Factor (MITF) Antibody - With BSA and Azide
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone D5 ]
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| IHC, IF, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O75030 |
| Other Accession | 4286, 166017, 618266 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG1, kappa |
| Clone Names | D5 |
| Calculated MW | 58795 Da |
| Gene ID | 4286 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 32, bHLHe32, MITF, BHLHE32 |
| Application Note | IHC~~1:100~500 IF~~1:50~200 FC~~1:10~50 |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | Microphthalmia Transcription Factor (MITF) Antibody - With BSA and Azide is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MITF {ECO:0000303|PubMed:8069297, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:7105} |
|---|---|
| Function | Transcription factor that acts as a master regulator of melanocyte survival and differentiation as well as melanosome biogenesis (PubMed:10587587, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:27889061, PubMed:9647758). Binds to M-boxes (5'-TCATGTG-3') and symmetrical DNA sequences (E-boxes) (5'-CACGTG-3') found in the promoter of pigmentation genes, such as tyrosinase (TYR) (PubMed:10587587, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:27889061, PubMed:9647758). Involved in the cellular response to amino acid availability by acting downstream of MTOR: in the presence of nutrients, MITF phosphorylation by MTOR promotes its inactivation (PubMed:36608670). Upon starvation or lysosomal stress, inhibition of MTOR induces MITF dephosphorylation, resulting in transcription factor activity (PubMed:36608670). Plays an important role in melanocyte development by regulating the expression of tyrosinase (TYR) and tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1) (PubMed:10587587, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:27889061, PubMed:9647758). Plays a critical role in the differentiation of various cell types, such as neural crest-derived melanocytes, mast cells, osteoclasts and optic cup-derived retinal pigment epithelium (PubMed:10587587, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:27889061, PubMed:9647758). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Lysosome membrane Note=When nutrients are present, recruited to the lysosomal membrane via association with GDP-bound RagC/RRAGC (or RagD/RRAGD): it is then phosphorylated by MTOR (PubMed:23401004, PubMed:36608670) Phosphorylation by MTOR promotes ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:36608670). Conversely, inhibition of mTORC1, starvation and lysosomal disruption, promotes dephosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus (PubMed:36608670). Phosphorylation by MARK3/cTAK1 promotes association with 14-3-3/YWHA adapters and retention in the cytosol (PubMed:16822840). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in melanocytes (at protein level). [Isoform C2]: Expressed in the kidney and retinal pigment epithelium. [Isoform H2]: Expressed in the kidney. [Isoform Mdel]: Expressed in melanocytes. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
MITF (microphthalmia transcription factor) is a basic helix-loop-helix-leucine-zipper (bHLH-Zip) transcription factor that regulates the development and survival of melanocytes and retinal pigment epithelium, and also is involved in transcription of pigmentation enzyme genes such as tyrosinase TRP1 and TRP2. MITF has been shown to be phosphorylated by MAP kinase in response to c-kit activation, resulting in upregulation of MITF transcriptional activity. Mutations of the MITF gene are associated with the autosomal dominant hereditary deafness and pigmentation condition, Waardenburg Syndrome type 2A. Multiple isoforms of MITF exist, including MITF-A, MITF-B, MITF-C, MITF-H, and MITF-M, which differ in the amino-terminal domain and in their expression patterns. The MITF-M isoform is restricted to the melanocyte cell lineage. Anti-MITF, D5, recognizes a nuclear protein, which is expressed in the majority of primary and metastatic epithelioid malignant melanomas as well as in normal melanocytes, benign nevi and dysplastic nevi.
REFERENCES
Hemesath P, et. al. MAP kinase links the transcription factor microphthalmia to c-Kit signalling in melanocytes. Nature. 1998, 391:298-301 | Weilbaecher KN, et. al. Age-resolving osteopetrosis: a rat model implicating microphthalmia and the related transcription factor TFE3. J. Exp.Med. 1998, 187: 775-78
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。