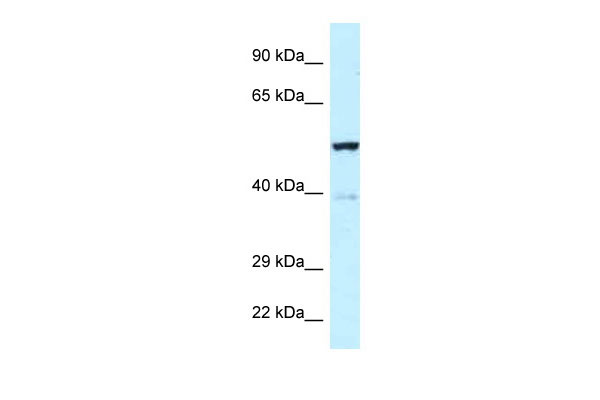
Trp63 antibody - middle region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9WV31 |
| Other Accession | NM_018790, NP_061260 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish, Dog, Bovine |
| Predicted | Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 45321 Da |
| Gene ID | 11838 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | AI462811, Ket, MGC115972, P51/P63, P63, P73l, Tp63, Trp53rp1 |
| Other Names | Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein, ARC/ARG3.1, mArc, Activity-regulated gene 3.1 protein homolog, Arg3.1, Arc {ECO:0000312|EMBL:AAD43586.1, ECO:0000312|MGI:MGI:88067} |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-Trp63 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Trp63 antibody - middle region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | Arc {ECO:0000312|MGI:MGI:88067} |
|---|---|
| Function | Master regulator of synaptic plasticity that self-assembles into virion-like capsids that encapsulate RNAs and mediate intercellular RNA transfer in the nervous system (By similarity). ARC protein is released from neurons in extracellular vesicles that mediate the transfer of ARC mRNA into new target cells, where ARC mRNA can undergo activity-dependent translation (By similarity). ARC capsids are endocytosed and are able to transfer ARC mRNA into the cytoplasm of neurons (By similarity). Acts as a key regulator of synaptic plasticity: required for protein synthesis-dependent forms of long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD) and for the formation of long- term memory (PubMed:24094104, PubMed:29264923, PubMed:31151856). Regulates synaptic plasticity by promoting endocytosis of AMPA receptors (AMPARs) in response to synaptic activity: this endocytic pathway maintains levels of surface AMPARs in response to chronic changes in neuronal activity through synaptic scaling, thereby contributing to neuronal homeostasis (PubMed:17088213, PubMed:20211139, PubMed:20228806). Acts as a postsynaptic mediator of activity-dependent synapse elimination in the developing cerebellum by mediating elimination of surplus climbing fiber synapses (PubMed:23791196). Accumulates at weaker synapses, probably to prevent their undesired enhancement (By similarity). This suggests that ARC-containing virion- like capsids may be required to eliminate synaptic material (By similarity). Required to transduce experience into long-lasting changes in visual cortex plasticity and for long-term memory (PubMed:17088210, PubMed:20228806). Involved in postsynaptic trafficking and processing of amyloid-beta A4 (APP) via interaction with PSEN1 (PubMed:22036569). In addition to its role in synapses, also involved in the regulation of the immune system: specifically expressed in skin-migratory dendritic cells and regulates fast dendritic cell migration, thereby regulating T-cell activation (PubMed:28783680). |
| Cellular Location | Extracellular vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63053}; Lipid-anchor. Postsynaptic cell membrane; Lipid-anchor. Synapse {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63053} Postsynaptic density {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63053}. Early endosome membrane. Cell projection, dendrite. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63053}. Cytoplasm, cell cortex {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63053}. Cell projection, dendritic spine {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63053}. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, acrosome. Cytoplasmic vesicle, clathrin- coated vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7LC44}. Note=Forms virion-like extracellular vesicles that are released from neurons (By similarity). Enriched in postsynaptic density of dendritic spines (By similarity). Targeted to inactive synapses following interaction with CAMK2B in the kinase inactive state (By similarity). Accumulation at weaker synapses may be required to prevent their undesired enhancement (By similarity). Associated with the cell cortex of neuronal soma and dendrites (By similarity). Associated with the sperm tail (PubMed:12493697). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63053, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12493697} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in brain and testis (PubMed:12493697). In primary visual cortex, detected in all cortical layers with the exception of layer 5: present at highest level in layers 2/3 and 4, the predominant sites of ocular dominance plasticity (at protein level) (PubMed:20228806). Also expressed in skin-migratory dendritic cells (PubMed:28783680). |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。