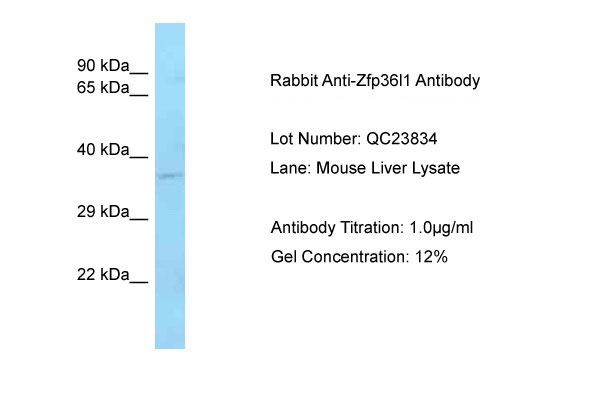
Zfp36l1 antibody - C-terminal region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P23950 |
| Other Accession | NM_007564, NP_031590 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Zebrafish, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 36385 Da |
| Gene ID | 12192 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | AW742437, AW743212, Berg36, Brf1, D530020L18Rik, ERF1, TIS11b, cMG1 |
| Other Names | Zinc finger protein 36, C3H1 type-like 1, Butyrate response factor 1, Protein TIS11B, Zfp36l1, Brf1, Tis11b |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-Zfp36l1 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Zfp36l1 antibody - C-terminal region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | Zfp36l1 {ECO:0000312|MGI:MGI:107946} |
|---|---|
| Function | Zinc-finger RNA-binding protein that destabilizes several cytoplasmic AU-rich element (ARE)-containing mRNA transcripts by promoting their poly(A) tail removal or deadenylation, and hence provide a mechanism for attenuating protein synthesis (PubMed:22701344, PubMed:24700863, PubMed:24733888, PubMed:27102483). Acts as a 3'- untranslated region (UTR) ARE mRNA-binding adapter protein to communicate signaling events to the mRNA decay machinery (By similarity). Functions by recruiting the CCR4-NOT deadenylating complex and components of the cytoplasmic RNA decay machinery to the bound ARE- containing mRNAs, and hence promotes ARE-mediated mRNA deadenylation and decay processes (By similarity). Also induces the degradation of ARE-containing mRNAs even in absence of poly(A) tail (By similarity). Binds to 3'-UTR ARE of numerous mRNAs (PubMed:22701344, PubMed:24700863, PubMed:24733888). Positively regulates early adipogenesis by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of immediate early genes (IEGs) (PubMed:22701344). Promotes ARE-mediated mRNA decay of mineralocorticoid receptor NR3C2 mRNA in response to hypertonic stress (PubMed:24700863). Negatively regulates hematopoietic/erythroid cell differentiation by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of the transcription factor STAT5B mRNA (By similarity). Positively regulates monocyte/macrophage cell differentiation by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK6 mRNA (By similarity). Promotes degradation of ARE-containing pluripotency-associated mRNAs in embryonic stem cells (ESCs), such as NANOG, through a fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-induced MAPK-dependent signaling pathway, and hence attenuates ESC self-renewal and positively regulates mesendoderm differentiation (PubMed:24733888). May play a role in mediating pro- apoptotic effects in malignant B-cells by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of BCL2 mRNA (By similarity). In association with ZFP36L2 maintains quiescence on developing B lymphocytes by promoting ARE- mediated decay of several mRNAs encoding cell cycle regulators that help B cells progress through the cell cycle, and hence ensuring accurate variable-diversity-joining (VDJ) recombination and functional immune cell formation (PubMed:27102483). Together with ZFP36L2 is also necessary for thymocyte development and prevention of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) transformation by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of the oncogenic transcription factor NOTCH1 mRNA (PubMed:20622884). Involved in the delivery of target ARE-mRNAs to processing bodies (PBs) (By similarity). In addition to its cytosolic mRNA-decay function, plays a role in the regulation of nuclear mRNA 3'- end processing; modulates mRNA 3'-end maturation efficiency of the DLL4 mRNA through binding with an ARE embedded in a weak noncanonical polyadenylation (poly(A)) signal in endothelial cells (By similarity). Also involved in the regulation of stress granule (SG) and P-body (PB) formation and fusion (By similarity). Plays a role in vasculogenesis and endocardial development (PubMed:15226444, PubMed:17013884). Involved in the regulation of keratinocyte proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis (By similarity). Plays a role in myoblast cell differentiation (PubMed:17889962). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic granule {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q07352}. Cytoplasm, P-body {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q07352}. Note=Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in a XPO1/CRM1-dependent manner (PubMed:11796723) Component of cytoplasmic stress granules (By similarity). Localizes in processing bodies (PBs) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q07352, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11796723} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in preadipocytes and adipocytes (PubMed:22701344). Expressed in the proximal and distal tubules in the renal cortex (at protein level) (PubMed:24700863). Expressed in ovary, heart, kidney, lung, spleen and thymus (PubMed:15226444). Weakly expressed in brain, liver and testis (PubMed:15226444). Expressed in osteoblasts (PubMed:15465005). Expressed in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) (PubMed:24733888). Expressed through B lymphocyte development (PubMed:27102483). |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
REFERENCES
Varnum B.C.,et al.Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:1754-1758(1991).
Phillips R.S.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 277:11606-11613(2002).
Hodson D.J.,et al.Nat. Immunol. 11:717-724(2010).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。