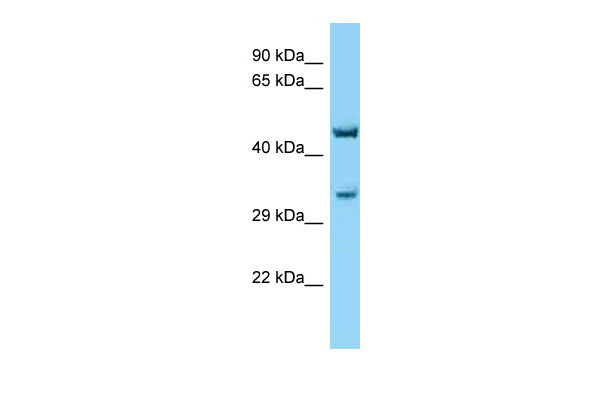
Cnr1 antibody - C-terminal region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P47746 |
| Other Accession | NM_007726, NP_031752 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Zebrafish, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish, Pig, Chicken, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 52831 Da |
| Gene ID | 12801 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | CB1, CB-R, CB1R |
| Other Names | Cannabinoid receptor 1, CB-R, CB1, Brain-type cannabinoid receptor, Cnr1 |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-Cnr1 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Cnr1 antibody - C-terminal region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | Cnr1 |
|---|---|
| Function | G-protein coupled receptor for cannabinoids, including endocannabinoids (eCBs), such as N-arachidonoylethanolamide (also called anandamide or AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) (PubMed:22388959, PubMed:9888857). Mediates many cannabinoid-induced effects, acting, among others, on food intake, memory loss, gastrointestinal motility, catalepsy, ambulatory activity, anxiety, chronic pain (PubMed:27828947, PubMed:9888857). Signaling typically involves reduction in cyclic AMP (PubMed:27828947, PubMed:8832654). In the hypothalamus, may have a dual effect on mitochondrial respiration depending upon the agonist dose and possibly upon the cell type. Increases respiration at low doses, while decreases respiration at high doses (PubMed:25707796, PubMed:27828947). At high doses, CNR1 signal transduction involves G-protein alpha-i protein activation and subsequent inhibition of mitochondrial soluble adenylate cyclase, decrease in cyclic AMP concentration, inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent phosphorylation of specific subunits of the mitochondrial electron transport system, including NDUFS2 (PubMed:27828947). In the hypothalamus, inhibits leptin-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation and mediates cannabinoid- induced increase in SREBF1 and FASN gene expression (PubMed:25869131). In response to cannabinoids, drives the release of orexigenic beta- endorphin, but not that of melanocyte-stimulating hormone alpha/alpha- MSH, from hypothalamic POMC neurons, hence promoting food intake (PubMed:25707796). In the hippocampus, regulates cellular respiration and energy production in response to cannabinoids. Involved in cannabinoid-dependent depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition (DSI), a process in which depolarization of CA1 postsynaptic pyramidal neurons mobilizes eCBs, which retrogradely activate presynaptic CB1 receptors, transiently decreasing GABAergic inhibitory neurotransmission (PubMed:22388959). Also reduces excitatory synaptic transmission (PubMed:27828947). In superior cervical ganglions and cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells, inhibits voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels in a constitutive, as well as agonist-dependent manner (By similarity). In cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells, cannabinoid- induced inhibition of voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels leads to vasodilation and decreased vascular tone (By similarity). Induces leptin production in adipocytes and reduces LRP2-mediated leptin clearance in the kidney, hence participating in hyperleptinemia (PubMed:22841573). In adipose tissue, CNR1 signaling leads to increased expression of SREBF1, ACACA and FASN genes (PubMed:15864349). In the liver, activation by endocannabinoids leads to increased de novo lipogenesis and reduced fatty acid catabolism, associated with increased expression of SREBF1/SREBP-1, GCK, ACACA, ACACB and FASN genes (PubMed:15864349, PubMed:21987372). May also affect de novo cholesterol synthesis and HDL-cholesteryl ether uptake (PubMed:21987372). Peripherally modulates energy metabolism. In high carbohydrate diet-induced obesity, may decrease the expression of mitochondrial dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase/DLD in striated muscles, as well as that of selected glucose/ pyruvate metabolic enzymes, hence affecting energy expenditure through mitochondrial metabolism (PubMed:26671069). In response to cannabinoid anandamide, elicits a pro-inflammatory response in macrophages, which involves NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL1B and IL18 secretion. In macrophages infiltrating pancreatic islets, this process may participate in the progression of type-2 diabetes and associated loss of pancreatic beta- cells (PubMed:23955712). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21554}. Mitochondrion outer membrane. Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P20272}. Presynapse {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P20272}. Note=In CA1 hippocampal neurons, 15.5% of total protein is localized in mitochondria (PubMed:22388959). Found on presynaptic axon terminals in some GABAergic neurons in the somatosensory cortex (By similarity). In striated muscles, predominantly located in mitochondria (PubMed:27826249). Unexpectedly, in the mitochondria, the C-terminus is located in the mitochondrial intermembrane space, a compartment topologically considered as extracellular. In canonical seven-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptors, the C-terminus is cytosolic (PubMed:22388959) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P20272, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22388959, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27826249} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in brain neurons (at protein level) (PubMed:22388959). Detected throughout the striatum, cortex and hippocampus, with highest levels in the lateral striatum (PubMed:10891614, PubMed:15606779, PubMed:22388959). In rostral brain regions, high expression levels in the dorsal lateral striatum, while in the caudal brain regions, high levels are observed in the ventral lateral striatum (PubMed:10891614). Expressed in neurons (PubMed:10891614). In the hypothalamus, expressed in both GABAergic and glutamatergic presynaptic terminals of POMC neurons (at protein level) (PubMed:25707796, PubMed:25869131). Expressed in striated muscles, including skeletal muscles (gastrocnemius and rectus abdominis) and myocardium (at protein level) (PubMed:26671069, PubMed:27826249) Expressed in the liver, with highest levels in Kupffer cells and lower levels in endothelial cells as well as hepatocytes, particularly in perivascular areas (at protein level) (PubMed:15864349, PubMed:21987372). The hepatic expression level is up-regulated in obese mice compared to lean animals (PubMed:21987372) |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
REFERENCES
Chakrabarti A.,et al.DNA Seq. 5:385-388(1995).
Ho B.Y.,et al.Neurosci. Lett. 212:123-126(1996).
Ledent C.,et al.Science 283:401-404(1999).
McCaw E.A.,et al.Eur. J. Biochem. 271:4909-4920(2004).
Bonner T.I.,et al.Submitted (MAR-1995) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。