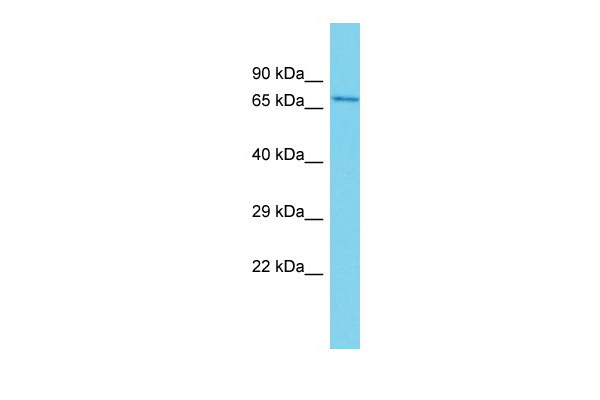
Git1 Antibody - middle region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9Z272 |
| Other Accession | NM_031814, NP_114002 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Zebrafish, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Zebrafish, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 85231 Da |
| Gene ID | 83709 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | ARF GTPase-activating protein GIT1, ARF GAP GIT1, Cool-associated and tyrosine-phosphorylated protein 1, CAT-1, CAT1, G protein-coupled receptor kinase-interactor 1, GRK-interacting protein 1, Git1 |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-Git1 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Git1 Antibody - middle region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | Git1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9826657} |
|---|---|
| Function | GTPase-activating protein for ADP ribosylation factor family members, including ARF1 (PubMed:9826657). Multidomain scaffold protein that interacts with numerous proteins and therefore participates in many cellular functions, including receptor internalization, focal adhesion remodeling, and signaling by both G protein-coupled receptors and tyrosine kinase receptors (PubMed:9826657). Through PAK1 activation, positively regulates microtubule nucleation during interphase. Plays a role in the regulation of cytokinesis; for this function, may act in a pathway also involving ENTR1 and PTPN13 (By similarity). May promote cell motility both by regulating focal complex dynamics and by the activation of RAC1 (PubMed:10938112). May act as scaffold for MAPK1/3 signal transduction, recruiting MAPK1/3 to focal adhesions after EGF stimulation via a Src-dependent pathway, hence stimulating cell migration (PubMed:15923189). Plays a role in brain development and function. Involved in the regulation of spine density and synaptic plasticity that is required for processes involved in learning (By similarity). Plays an important role in dendritic spine morphogenesis and synapse formation (PubMed:12695502, PubMed:15800193, PubMed:17310244, PubMed:24297929, PubMed:25009255). In hippocampal neurons, recruits guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), such as ARHGEF7/beta-PIX, to the synaptic membrane. These in turn locally activate RAC1, which is an essential step for spine morphogenesis and synapse formation (PubMed:12473661). May contribute to the organization of presynaptic active zones through oligomerization and formation of a Piccolo/PCLO-based protein network, which includes ARHGEF7/beta-PIX and FAK1 (PubMed:12473661). In neurons, through its interaction with liprin-alpha family members, may be required for AMPA receptor (GRIA2/3) proper targeting to the cell membrane (PubMed:12629171). In complex with GABA(A) receptors and ARHGEF7, plays a crucial role in regulating GABA(A) receptor synaptic stability, maintaining GPHN/gephyrin scaffolds and hence GABAergic inhibitory synaptic transmission, by locally coordinating RAC1 and PAK1 downstream effector activity, leading to F-actin stabilization (PubMed:25284783). May also be important for RAC1 downstream signaling pathway through PAK3 and regulation of neuronal inhibitory transmission at presynaptic input (By similarity). Required for successful bone regeneration during fracture healing. The function in intramembranous ossification may, at least partly, exerted by macrophages in which GIT1 is a key negative regulator of redox homeostasis, IL1B production, and glycolysis, acting through the ERK1/2/NRF2/NFE2L2 axis (By similarity). May also play a role in angiogenesis during fracture healing (By similarity). In this process, may regulate activation of the canonical NF-kappa-B signal in bone mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing the interaction between NEMO and 'Lys-63'-ubiquitinated RIPK1/RIP1, eventually leading to enhanced production of VEGFA and others angiogenic factors (By similarity). Essential for VEGF signaling through the activation of phospholipase C- gamma and ERK1/2, hence may control endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y2X7}. Synapse. Presynapse. Postsynapse. Postsynaptic density. Cell junction, focal adhesion. Cell projection, lamellipodium {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y2X7}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y2X7} Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y2X7} Note=Cycles between at least 3 distinct intracellular compartments, including focal adhesions, cytosolic complexes, containing at least PXN/paxillin, ARHGEF7 and PAK1, and membrane protrusions. During cell migration, moves from the disassembling adhesions into the cytosol and towards the leading edge. In adherent cells, localizes to adhesions Recruitment to adhesions may be mediated by RAC1 and active tyrosine- phosphorylated PXN (By similarity). May be present in both excitatory, as well as inhibitory synapses (PubMed:12695502, PubMed:25284783). In hippocampal neurons, recruitment of GIT1 to synapses is regulated by ephrinB activation and ephrinB downstream effector GRB4/NCK2 (PubMed:17310244). In hippocampal neurons, partially colocalizes with PCLO (PubMed:12473661). Interaction with GRIN3A limits GIT1 synaptic localization (PubMed:24297929). Localization to the centrosome does not depend upon the presence of gamma-tubulin (By similarity) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y2X7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12695502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17310244, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24297929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25284783} |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed (PubMed:9826657). Expressed at high levels in testis (at protein level) (PubMed:10938112). Expressed in the brain, including in CA1 hippocampal neurons, in the amygdala, and thalamic nuclei (at protein level) (PubMed:10938112, PubMed:12473661, PubMed:12629171, PubMed:12695502, PubMed:15800193, PubMed:17310244, PubMed:24297929, PubMed:25284783) |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
REFERENCES
Premont R.T.,et al.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95:14082-14087(1998).
Zhao Z.-S.,et al.Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:6354-6363(2000).
Nishiya N.,et al.J. Biochem. 132:279-289(2002).
Ko J.,et al.J. Neurosci. 23:1667-1677(2003).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。