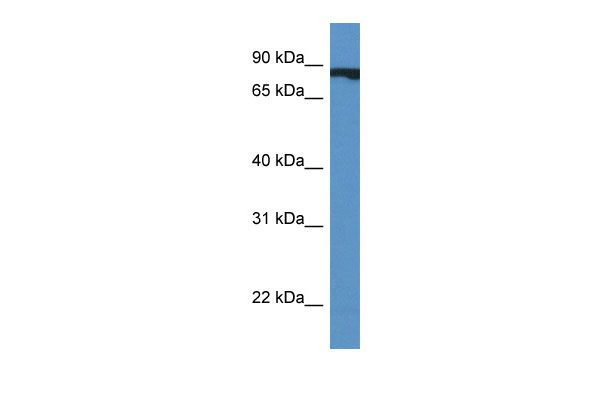
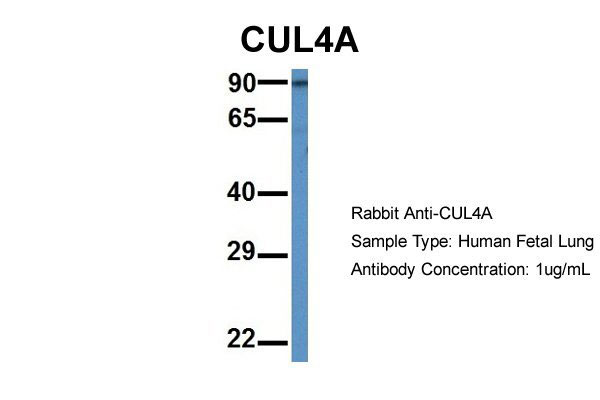
CUL4A antibody - middle region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q13619 |
| Other Accession | NM_001008895, NP_001008895 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 87680 Da |
| Gene ID | 8451 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Cullin-4A, CUL-4A, CUL4A |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-CUL4A antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | CUL4A antibody - middle region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CUL4A {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9721878, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:2554} |
|---|---|
| Function | Core component of multiple cullin-RING-based E3 ubiquitin- protein ligase complexes which mediate the ubiquitination of target proteins (PubMed:14578910, PubMed:14739464, PubMed:15448697, PubMed:15548678, PubMed:15811626, PubMed:16678110, PubMed:17041588, PubMed:24209620, PubMed:30166453, PubMed:33854232, PubMed:33854239). As a scaffold protein may contribute to catalysis through positioning of the substrate and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (PubMed:14578910, PubMed:14739464, PubMed:15448697, PubMed:15548678, PubMed:15811626, PubMed:16678110, PubMed:17041588, PubMed:24209620). The E3 ubiquitin- protein ligase activity of the complex is dependent on the neddylation of the cullin subunit and is inhibited by the association of the deneddylated cullin subunit with TIP120A/CAND1 (PubMed:14578910, PubMed:14739464, PubMed:15448697, PubMed:15548678, PubMed:15811626, PubMed:16678110, PubMed:17041588, PubMed:24209620). The functional specificity of the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex depends on the variable substrate recognition component (PubMed:14578910, PubMed:14739464, PubMed:15448697, PubMed:15548678, PubMed:15811626, PubMed:16678110, PubMed:17041588, PubMed:24209620). DCX(DET1-COP1) directs ubiquitination of JUN (PubMed:14739464). DCX(DDB2) directs ubiquitination of XPC (PubMed:15811626). DCX(DDB2) ubiquitinates histones H3-H4 and is required for efficient histone deposition during replication-coupled (H3.1) and replication-independent (H3.3) nucleosome assembly, probably by facilitating the transfer of H3 from ASF1A/ASF1B to other chaperones involved in histone deposition (PubMed:16678110, PubMed:17041588, PubMed:24209620). DCX(DTL) plays a role in PCNA-dependent polyubiquitination of CDT1 and MDM2-dependent ubiquitination of p53/TP53 in response to radiation-induced DNA damage and during DNA replication (PubMed:14578910, PubMed:15448697, PubMed:15548678). DCX(DTL) directs autoubiquitination of DTL (PubMed:23478445). In association with DDB1 and SKP2 probably is involved in ubiquitination of CDKN1B/p27kip (PubMed:16537899). Is involved in ubiquitination of HOXA9 (PubMed:14609952). The DDB1-CUL4A- DTL E3 ligase complex regulates the circadian clock function by mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of CRY1 (PubMed:26431207). The DCX(ERCC8) complex (also named CSA complex) plays a role in transcription-coupled repair (TCR) (PubMed:12732143, PubMed:32355176, PubMed:38316879). A number of DCX complexes (containing either TRPC4AP or DCAF12 as substrate-recognition component) are part of the DesCEND (destruction via C-end degrons) pathway, which recognizes a C-degron located at the extreme C terminus of target proteins, leading to their ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:29779948). The DCX(AMBRA1) complex is a master regulator of the transition from G1 to S cell phase by mediating ubiquitination of phosphorylated cyclin-D (CCND1, CCND2 and CCND3) (PubMed:33854232, PubMed:33854239). The DCX(AMBRA1) complex also acts as a regulator of Cul5-RING (CRL5) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes by mediating ubiquitination and degradation of Elongin-C (ELOC) component of CRL5 complexes (PubMed:30166453). With CUL4B, contributes to ribosome biogenesis (PubMed:26711351). |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
REFERENCES
Chen L.-C.,et al.Cancer Res. 58:3677-3683(1998).
Higa L.A.,et al.Nat. Cell Biol. 5:1008-1015(2003).
Matsuda N.,et al.DNA Repair 4:537-545(2005).
Dunham A.,et al.Nature 428:522-528(2004).
Osaka F.,et al.Genes Dev. 12:2263-2268(1998).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。