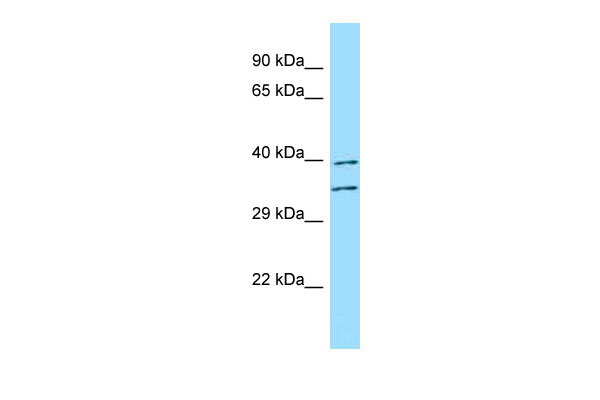
FUT3 antibody - C-terminal region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P21217 |
| Other Accession | NM_000149, NP_000140 |
| Reactivity | Human, Pig |
| Predicted | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 42117 Da |
| Gene ID | 2525 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | CD174, FT3B, FucT-III, LE, Les, MGC131739 |
| Other Names | Galactoside 3(4)-L-fucosyltransferase, 2.4.1.65, Blood group Lewis alpha-4-fucosyltransferase, Lewis FT, Fucosyltransferase 3, Fucosyltransferase III, FucT-III, FUT3, FT3B, LE |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-FUT3 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | FUT3 antibody - C-terminal region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | FUT3 (HGNC:4014) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | FT3B, LE |
| Function | Catalyzes the transfer of L-fucose, from a guanosine diphosphate-beta-L-fucose, to both the subterminal N-acetyl glucosamine (GlcNAc) of type 1 chain (beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc) glycolipids and oligosaccharides via an alpha(1,4) linkage, and the subterminal glucose (Glc) or GlcNAc of type 2 chain (beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D- GlcNAc) oligosaccharides via an alpha(1,3) linkage, independently of the presence of terminal alpha-L-fucosyl-(1,2) moieties on the terminal galactose of these acceptors (PubMed:11058871, PubMed:12668675, PubMed:1977660). Through its catalytic activity, participates in the synthesis of antigens of the Lewis blood group system, i.e. Lewis a (Le(a)), lewis b (Le(b)), Lewis x/SSEA-1 (Le(x)) and lewis y (Le(y)) antigens (PubMed:11058871, PubMed:12668675, PubMed:1977660). Also catalyzes the transfer of L-fucose to subterminal GlcNAc of sialyl- and disialyl-lactotetraosylceramide to produce sialyl Lewis a (sLe(a)) and disialyl Lewis a via an alpha(1,4) linkage and therefore may regulate cell surface sLe(a) expression and consequently regulates adhesive properties to E-selectin, cell proliferation and migration (PubMed:11058871, PubMed:12668675, PubMed:27453266). Catalyzes the transfer of an L-fucose to 3'-sialyl-N-acetyllactosamine by an alpha(1,3) linkage, which allows the formation of sialyl-Lewis x structure and therefore may regulate the sialyl-Lewis x surface antigen expression and consequently adhesive properties to E-selectin (PubMed:11058871, PubMed:29593094). Prefers type 1 chain over type 2 acceptors (PubMed:7721776). Type 1 tetrasaccharide is a better acceptor than type 1 disaccharide suggesting that a beta anomeric configuration of GlcNAc in the substrate is preferred (PubMed:7721776). Lewis- positive (Le(+)) individuals have an active enzyme while Lewis-negative (Le(-)) individuals have an inactive enzyme (PubMed:1977660). |
| Cellular Location | Golgi apparatus, Golgi stack membrane; Single- pass type II membrane protein Note=Membrane-bound form in trans cisternae of Golgi |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in stomach, colon, small intestine, lung and kidney and to a lesser extent in salivary gland, bladder, uterus and liver. |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
REFERENCES
Kukowska-Latallo J.F.,et al.Genes Dev. 4:1288-1303(1990).
Cameron H.S.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 270:20112-20122(1995).
Rahim I.,et al.Submitted (FEB-1999) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Matzhold E.M.,et al.Submitted (SEP-2008) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Grimwood J.,et al.Nature 428:529-535(2004).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。