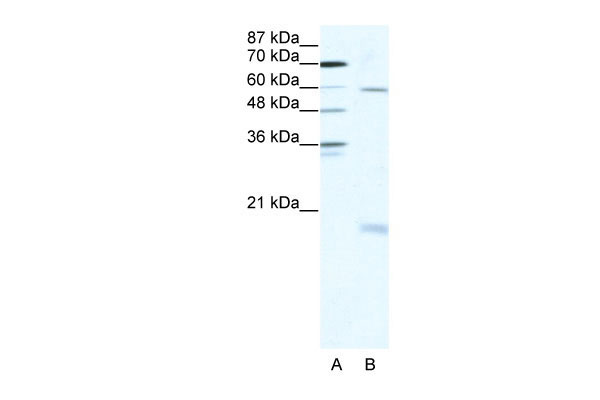
SOX9 antibody - N-terminal region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P48436 |
| Other Accession | NM_000346, NP_000337 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Bovine, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Pig, Chicken, Dog, Guinea Pig, Bovine, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 56137 Da |
| Gene ID | 6662 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | CMD1, SRA1, CMPD1 |
| Other Names | Transcription factor SOX-9, SOX9 |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 100 ul of distilled water. Final anti-SOX9 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | SOX9 antibody - N-terminal region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SOX9 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:7990924, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:11204} |
|---|---|
| Function | Transcription factor that plays a key role in chondrocytes differentiation and skeletal development (PubMed:24038782). Specifically binds the 5'-ACAAAG-3' DNA motif present in enhancers and super-enhancers and promotes expression of genes important for chondrogenesis, including cartilage matrix protein-coding genes COL2A1, COL4A2, COL9A1, COL11A2 and ACAN, SOX5 and SOX6 (PubMed:8640233). Also binds to some promoter regions (By similarity). Plays a central role in successive steps of chondrocyte differentiation (By similarity). Absolutely required for precartilaginous condensation, the first step in chondrogenesis during which skeletal progenitors differentiate into prechondrocytes (By similarity). Together with SOX5 and SOX6, required for overt chondrogenesis when condensed prechondrocytes differentiate into early stage chondrocytes, the second step in chondrogenesis (By similarity). Later, required to direct hypertrophic maturation and block osteoblast differentiation of growth plate chondrocytes: maintains chondrocyte columnar proliferation, delays prehypertrophy and then prevents osteoblastic differentiation of chondrocytes by lowering beta-catenin (CTNNB1) signaling and RUNX2 expression (By similarity). Also required for chondrocyte hypertrophy, both indirectly, by keeping the lineage fate of chondrocytes, and directly, by remaining present in upper hypertrophic cells and transactivating COL10A1 along with MEF2C (By similarity). Low lipid levels are the main nutritional determinant for chondrogenic commitment of skeletal progenitor cells: when lipids levels are low, FOXO (FOXO1 and FOXO3) transcription factors promote expression of SOX9, which induces chondrogenic commitment and suppresses fatty acid oxidation (By similarity). Mechanistically, helps, but is not required, to remove epigenetic signatures of transcriptional repression and deposit active promoter and enhancer marks at chondrocyte-specific genes (By similarity). Acts in cooperation with the Hedgehog pathway-dependent GLI (GLI1 and GLI3) transcription factors (By similarity). In addition to cartilage development, also acts as a regulator of proliferation and differentiation in epithelial stem/progenitor cells: involved in the lung epithelium during branching morphogenesis, by balancing proliferation and differentiation and regulating the extracellular matrix (By similarity). Controls epithelial branching during kidney development (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8640233} |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Plays an important role in the normal skeletal development. May regulate the expression of other genes involved in chondrogenesis by acting as a transcription factor for these genes.
REFERENCES
Foster J.W.,et al.Nature 372:525-530(1994).
Wagner T.,et al.Cell 79:1111-1120(1994).
Kalnine N.,et al.Submitted (MAY-2003) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Mural R.J.,et al.Submitted (JUL-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Cox J.J.,et al.N. Engl. J. Med. 364:91-93(2011).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。