Anti-Histone H2B (N-terminal region) Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
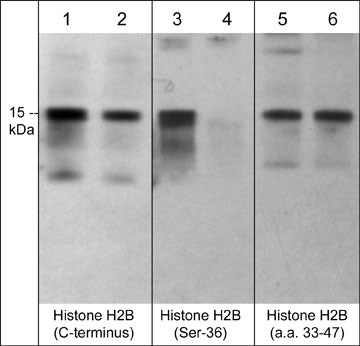
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P33778 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Rabbit Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 13950 Da |
| Gene ID | 3018 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | HIST1H2BB, H2BFF, Histone H2B type1B, H2B/f |
| Target/Specificity | The nucleosome is a protein complex consisting of four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). Two molecules of each histone forms an octamer that makes up the nucleosome. DNA wraps around repeating nucleosome units to generate chromatin structures. The structure of chromatin determines the accessiblity to transcription factors. Post-translational modification of the amino-terminal tail of histones in nucleosomes alters chromatin structure to promote or inhibit transcription. Complex alterations in acetylation, methylation, ubiquination, and/or phosphorylation determine the chromatin structural changes that occur during specific phases of the cell cycle or in response to cell stimuli. One mode of regulating histone H2B activity is through phosphorylation in the amino terminal region. Important sites of phosphorylation include Ser-14, Ser-32, and Ser-36. AMPK phosphorylates Ser-36 on histone H2B during cell stress leading to increased transcription and cell survival, while ectopic expression of an unphosphorylatable histone H2B during cell stress reduces transcription of AMPK-dependent genes and lowers cell survival. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Anti-Histone H2B (N-terminal region) Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Shipping | Blue Ice |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The nucleosome is a protein complex consisting of four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). Two molecules of each histone forms an octamer that makes up the nucleosome. DNA wraps around repeating nucleosome units to generate chromatin structures. The structure of chromatin determines the accessiblity to transcription factors. Post-translational modification of the amino-terminal tail of histones in nucleosomes alters chromatin structure to promote or inhibit transcription. Complex alterations in acetylation, methylation, ubiquination, and/or phosphorylation determine the chromatin structural changes that occur during specific phases of the cell cycle or in response to cell stimuli. One mode of regulating histone H2B activity is through phosphorylation in the amino terminal region. Important sites of phosphorylation include Ser-14, Ser-32, and Ser-36. AMPK phosphorylates Ser-36 on histone H2B during cell stress leading to increased transcription and cell survival, while ectopic expression of an unphosphorylatable histone H2B during cell stress reduces transcription of AMPK-dependent genes and lowers cell survival.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。