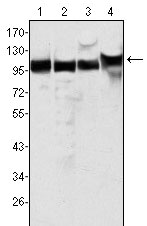
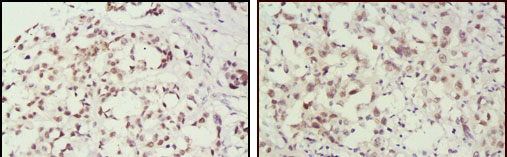
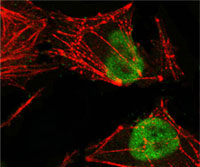
MSH2 Antibody
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB, IHC, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P43246 |
| Reactivity | Human, Monkey |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 1B3; 3A2B8C |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Calculated MW | 104743 Da |
| Description | MSH2 is a 100 kDa nuclear antigen and encodes a protein of 934 amino acids. The MSH2 gene is one of 4 known genes encoding proteins involved in the repair of mismatch nucleotides following DNA replication or repair. Mutations in the MSH2 gene contribute to the development of sporadic colorectal carcinoma. MSHS mutations are responsible for 50% of inherited non-polyposis colorectal (HNPCC). The repair of mismatch DNA is essential to maintaining the integrity of genetic information over time. An alteration of microsatellite repeats is the result of slippage owing to strand misalignment during DNA replication and is referred to as microsatellite instability (MSI). These defects in DNA repair pathways have been related to human carcinogenesis. MSH-2 is involved in the initial cognition of mismatch nucleotides during the replication mismatch repair process. |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human MSH2 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
| Gene ID | 4436 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2, hMSH2, MutS protein homolog 2, MSH2 |
| Dilution | WB~~1/500 - 1/2000 IHC~~1/200 - 1/1000 ICC~~N/A E~~N/A |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | MSH2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MSH2 |
|---|---|
| Function | Component of the post-replicative DNA mismatch repair system (MMR). Forms two different heterodimers: MutS alpha (MSH2-MSH6 heterodimer) and MutS beta (MSH2-MSH3 heterodimer) which binds to DNA mismatches thereby initiating DNA repair. When bound, heterodimers bend the DNA helix and shields approximately 20 base pairs. MutS alpha recognizes single base mismatches and dinucleotide insertion-deletion loops (IDL) in the DNA. MutS beta recognizes larger insertion-deletion loops up to 13 nucleotides long. After mismatch binding, MutS alpha or beta forms a ternary complex with the MutL alpha heterodimer, which is thought to be responsible for directing the downstream MMR events, including strand discrimination, excision, and resynthesis. Recruits DNA helicase MCM9 to chromatin which unwinds the mismatch containing DNA strand (PubMed:26300262). ATP binding and hydrolysis play a pivotal role in mismatch repair functions. The ATPase activity associated with MutS alpha regulates binding similar to a molecular switch: mismatched DNA provokes ADP-->ATP exchange, resulting in a discernible conformational transition that converts MutS alpha into a sliding clamp capable of hydrolysis-independent diffusion along the DNA backbone. This transition is crucial for mismatch repair. MutS alpha may also play a role in DNA homologous recombination repair. In melanocytes may modulate both UV-B-induced cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Chromosome |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed. |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
REFERENCES
1. Papadopoulos, N. 1994. Science 263: 1625-1629. 2. Palombo, F. 1994. Nature 367:417-418.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。