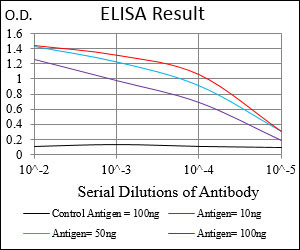
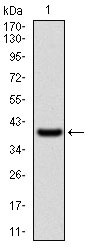
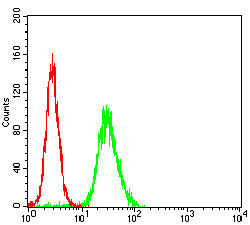
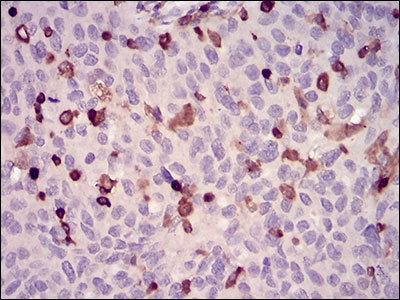
WAS Antibody
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
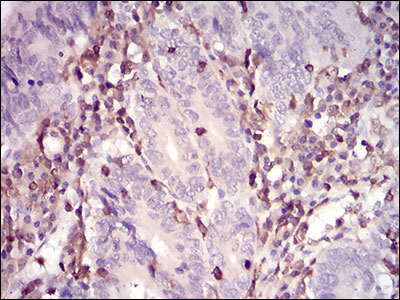
Application
| WB, IHC, FC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P42768 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 7B10E4 |
| Isotype | IgG2a |
| Calculated MW | 52913 Da |
| Description | The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) family of proteins share similar domain structure, and are involved in transduction of signals from receptors on the cell surface to the actin cytoskeleton. The presence of a number of different motifs suggests that they are regulated by a number of different stimuli, and interact with multiple proteins. Recent studies have demonstrated that these proteins, directly or indirectly, associate with the small GTPase, Cdc42, known to regulate formation of actin filaments, and the cytoskeletal organizing complex, Arp2/3. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is a rare, inherited, X-linked, recessive disease characterized by immune dysregulation and microthrombocytopenia, and is caused by mutations in the WAS gene. The WAS gene product is a cytoplasmic protein, expressed exclusively in hematopoietic cells, which show signalling and cytoskeletal abnormalities in WAS patients. A transcript variant arising as a result of alternative promoter usage, and containing a different 5' UTR sequence, has been described, however, its full-length nature is not known. |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human WAS (AA: 57-170) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Gene ID | 7454 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, WASp, WAS, IMD2 |
| Dilution | WB~~1/500 - 1/2000 IHC~~1/200 - 1/1000 FC~~1/200 - 1/400 E~~1/10000 |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | WAS Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | WAS |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | IMD2 |
| Function | Effector protein for Rho-type GTPases that regulates actin filament reorganization via its interaction with the Arp2/3 complex (PubMed:12235133, PubMed:12769847, PubMed:16275905). Important for efficient actin polymerization (PubMed:12235133, PubMed:16275905, PubMed:8625410). Possible regulator of lymphocyte and platelet function (PubMed:9405671). Mediates actin filament reorganization and the formation of actin pedestals upon infection by pathogenic bacteria (PubMed:18650809). In addition to its role in the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton, also promotes actin polymerization in the nucleus, thereby regulating gene transcription and repair of damaged DNA (PubMed:20574068). Promotes homologous recombination (HR) repair in response to DNA damage by promoting nuclear actin polymerization, leading to drive motility of double-strand breaks (DSBs) (PubMed:29925947). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Nucleus |
| Tissue Location | Expressed predominantly in the thymus. Also found, to a much lesser extent, in the spleen. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Mammalian mitochondrial ribosomal proteins are encoded by nuclear genes and help in protein synthesis within the mitochondrion. Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) consist of a small 28S subunit and a large 39S subunit. They have an estimated 75% protein to rRNA composition compared to prokaryotic ribosomes, where this ratio is reversed. Another difference between mammalian mitoribosomes and prokaryotic ribosomes is that the latter contain a 5S rRNA. Among different species, the proteins comprising the mitoribosome differ greatly in sequence, and sometimes in biochemical properties, which prevents easy recognition by sequence homology. This gene encodes a protein identified as belonging to both the 28S and the 39S subunits. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes corresponding to this gene are found on chromosomes 4q, 6p, 6q, 7p, and 15q. ;
REFERENCES
1. Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;32(15):3153-63.2. Dis Markers. 2010;29(3-4):157-75.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。