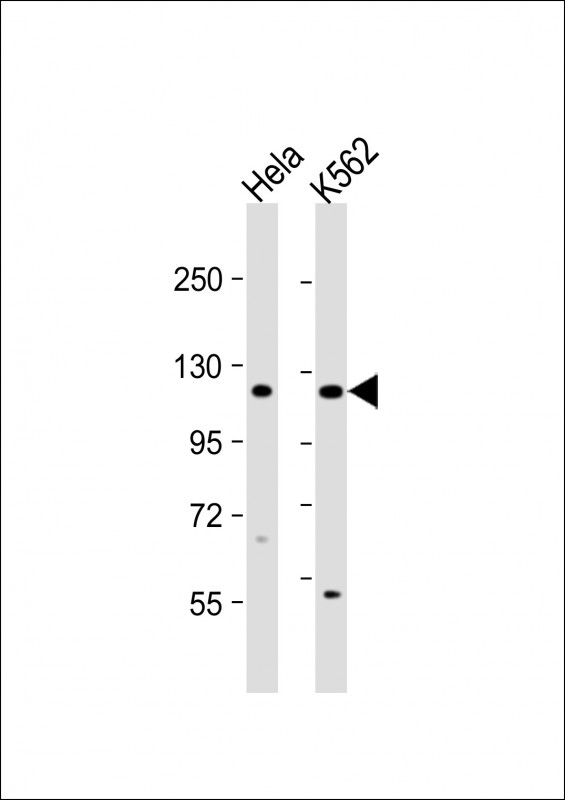
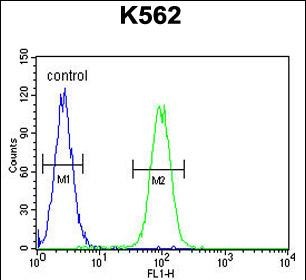
DDX11 Antibody (C-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| FC, WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q96FC9 |
| Other Accession | NP_689651.1, NP_004390.3 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 108313 Da |
| Antigen Region | 819-847 aa |
| Gene ID | 1663 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX11, CHL1-related protein 1, hCHLR1, DEAD/H box protein 11, Keratinocyte growth factor-regulated gene 2 protein, KRG-2, DDX11, CHL1, CHLR1, KRG2 |
| Target/Specificity | This DDX11 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 819-847 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human DDX11. |
| Dilution | FC~~1:10~50 WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | DDX11 Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | DDX11 (HGNC:2736) |
|---|---|
| Function | DNA-dependent ATPase and ATP-dependent DNA helicase that participates in various functions in genomic stability, including DNA replication, DNA repair and heterochromatin organization as well as in ribosomal RNA synthesis (PubMed:10648783, PubMed:21854770, PubMed:23797032, PubMed:26089203, PubMed:26503245). Its double-stranded DNA helicase activity requires either a minimal 5'-single-stranded tail length of approximately 15 nt (flap substrates) or 10 nt length single- stranded gapped DNA substrates of a partial duplex DNA structure for helicase loading and translocation along DNA in a 5' to 3' direction (PubMed:10648783, PubMed:18499658, PubMed:22102414). The helicase activity is capable of displacing duplex regions up to 100 bp, which can be extended up to 500 bp by the replication protein A (RPA) or the cohesion CTF18-replication factor C (Ctf18-RFC) complex activities (PubMed:18499658). Also shows ATPase- and helicase activities on substrates that mimic key DNA intermediates of replication, repair and homologous recombination reactions, including forked duplex, anti- parallel G-quadruplex and three-stranded D-loop DNA molecules (PubMed:22102414, PubMed:26503245). Plays a role in DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair at the DNA replication fork during DNA replication recovery from DNA damage (PubMed:23797032). Recruited with TIMELESS factor upon DNA-replication stress response at DNA replication fork to preserve replication fork progression, and hence ensure DNA replication fidelity (PubMed:26503245). Also cooperates with TIMELESS factor during DNA replication to regulate proper sister chromatid cohesion and mitotic chromosome segregation (PubMed:17105772, PubMed:18499658, PubMed:20124417, PubMed:23116066, PubMed:23797032). Stimulates 5'- single-stranded DNA flap endonuclease activity of FEN1 in an ATP- and helicase-independent manner; and hence it may contribute in Okazaki fragment processing at DNA replication fork during lagging strand DNA synthesis (PubMed:18499658). Its ability to function at DNA replication fork is modulated by its binding to long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) cohesion regulator non-coding RNA DDX11-AS1/CONCR, which is able to increase both DDX11 ATPase activity and binding to DNA replicating regions (PubMed:27477908). Also plays a role in heterochromatin organization (PubMed:21854770). Involved in rRNA transcription activation through binding to active hypomethylated rDNA gene loci by recruiting UBTF and the RNA polymerase Pol I transcriptional machinery (PubMed:26089203). Plays a role in embryonic development and prevention of aneuploidy (By similarity). Involved in melanoma cell proliferation and survival (PubMed:23116066). Associates with chromatin at DNA replication fork regions (PubMed:27477908). Binds to single- and double-stranded DNAs (PubMed:18499658, PubMed:22102414, PubMed:9013641). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Nucleus, nucleolus. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Midbody Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Note=During the early stages of mitosis, localizes to condensed chromatin and is released from the chromatin with progression to metaphase. Also localizes to the spindle poles throughout mitosis and at the midbody at later stages of mitosis (metaphase to telophase) (PubMed:17105772). In interphase, colocalizes with nucleolin in the nucleolus (PubMed:26089203) |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in melanoma cells. Not detected in epidermal melanocytes of normal skin (at protein level) (PubMed:23116066). Highly expressed in spleen, B-cells, thymus, testis, ovary, small intestine and pancreas (PubMed:9013641). Very low expression seen in brain (PubMed:9013641). Expressed in dividing cells and/or cells undergoing high levels of recombination (PubMed:9013641) No expression detected in cells signaled to terminally differentiate (PubMed:9013641). Expressed weakly in keratinocytes (PubMed:8798685) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. This gene encodes a DEAD box protein, which is an enzyme that possesses both ATPase and DNA helicase activities. This gene is a homolog of the yeast CHL1 gene, and may function to maintain chromosome transmission fidelity and genome stability. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.
REFERENCES
Leman, A.R., et al. J. Cell. Sci. 123 (PT 5), 660-670 (2010) :
Farina, A., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 283(30):20925-20936(2008)
Parish, J.L., et al. Mol. Cell 24(6):867-876(2006)
Parish, J.L., et al. J. Cell. Sci. 119 (PT 23), 4857-4865 (2006) :
Vasa-Nicotera, M., et al. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 76(1):147-151(2005)
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。