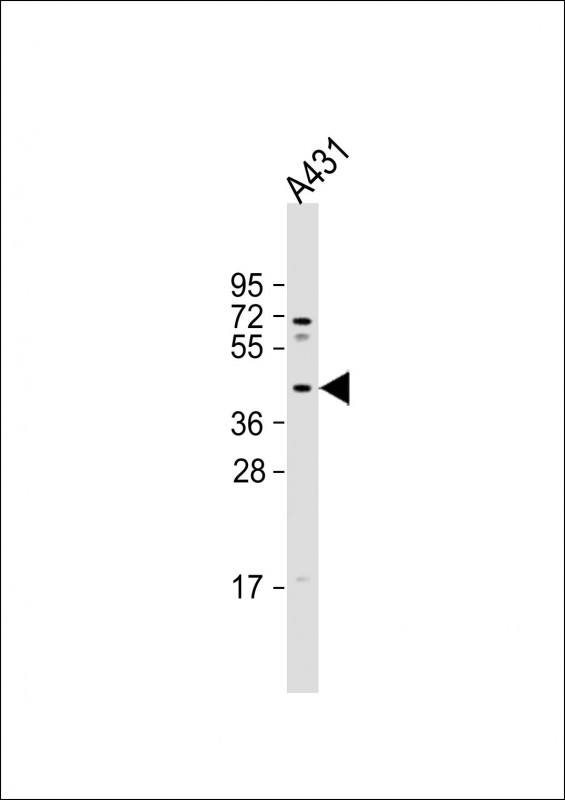
MUL1 Antibody (C-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q969V5 |
| Other Accession | Q4R7G8, NP_078820.2 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Monkey |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 39800 Da |
| Antigen Region | 272-301 aa |
| Gene ID | 79594 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase activator of NFKB 1, 632-, E3 SUMO-protein ligase MUL1, E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MUL1, Growth inhibition and death E3 ligase, Mitochondrial-anchored protein ligase, MAPL, Putative NF-kappa-B-activating protein 266, RING finger protein 218, MUL1, C1orf166, GIDE, MAPL, MULAN, RNF218 |
| Target/Specificity | This MUL1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 272-301 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MUL1. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | MUL1 Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MUL1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | C1orf166, GIDE, MAPL, MULAN, RNF218 |
| Function | Exhibits weak E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity (PubMed:18591963, PubMed:19407830, PubMed:22410793). E3 ubiquitin ligases accept ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfer the ubiquitin to targeted substrates (PubMed:18591963, PubMed:19407830, PubMed:22410793). Can ubiquitinate AKT1 preferentially at 'Lys-284' involving 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination and seems to be involved in regulation of Akt signaling by targeting phosphorylated Akt to proteasomal degradation (PubMed:22410793). Mediates polyubiquitination of cytoplasmic TP53 at 'Lys-24' which targets TP53 for proteasomal degradation, thus reducing TP53 levels in the cytoplasm and mitochondrion (PubMed:21597459). Proposed to preferentially act as a SUMO E3 ligase at physiological concentrations (PubMed:19407830). Plays a role in the control of mitochondrial morphology by promoting mitochondrial fragmentation, and influences mitochondrial localization (PubMed:18207745, PubMed:18213395, PubMed:19407830). Likely to promote mitochondrial fission through negatively regulating the mitochondrial fusion proteins MFN1 and MFN2, acting in a pathway that is parallel to the PRKN/PINK1 regulatory pathway (PubMed:24898855). May also be involved in the sumoylation of the membrane fission protein DNM1L (PubMed:18207745, PubMed:19407830). Inhibits cell growth (PubMed:18591963, PubMed:22410793). When overexpressed, activates JNK through MAP3K7/TAK1 and induces caspase-dependent apoptosis (PubMed:23399697). Involved in the modulation of innate immune defense against viruses by inhibiting RIGI-dependent antiviral response (PubMed:23399697). Can mediate RIGI sumoylation and disrupt its polyubiquitination (PubMed:23399697). |
| Cellular Location | Mitochondrion outer membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Peroxisome. Note=Transported in mitochondrion- derived vesicles from the mitochondrion to the peroxisome |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed with highest levels in the heart, skeletal muscle, placenta, kidney and liver. Barely detectable in colon and thymus. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that plays a role in the control of mitochondrial morphology. Promotes mitochondrial fragmentation and influences mitochondrial localization. Inhibits cell growth. When overexpressed, activates JNK through MAP3K7/TAK1 and induces caspase-dependent apoptosis. E3 ubiquitin ligases accept ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfer the ubiquitin to targeted substrates.
REFERENCES
Laure, L., et al. FEBS J. 277(20):4322-4337(2010)
Braschi, E., et al. EMBO Rep. 10(7):748-754(2009)
Venkatesan, K., et al. Nat. Methods 6(1):83-90(2009)
Zhang, B., et al. Cell Res. 18(9):900-910(2008)
Zhang, H., et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 366(4):898-904(2008)
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。