SIGLEC7 (D-siglec) Antibody (N-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
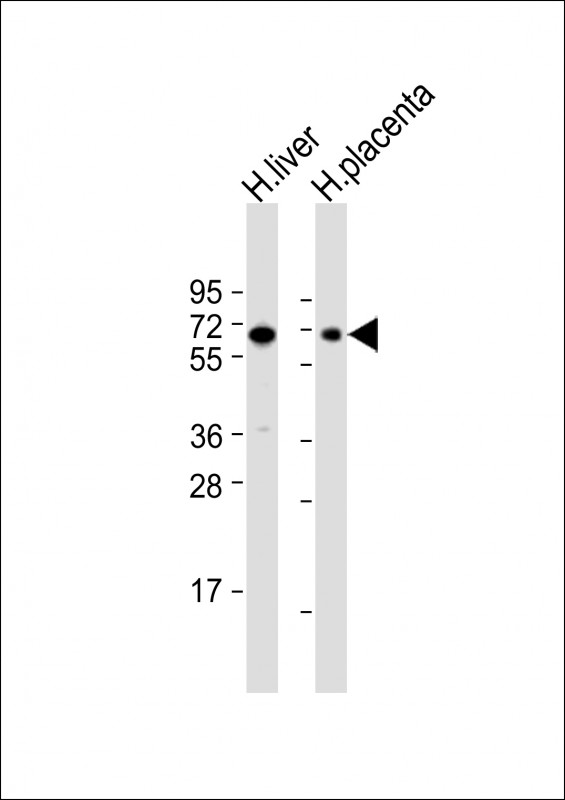
Application
| IHC-P, WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9Y286 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 51143 Da |
| Antigen Region | 1-30 aa |
| Gene ID | 27036 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 7, Siglec-7, Adhesion inhibitory receptor molecule 1, AIRM-1, CDw328, D-siglec, QA79 membrane protein, p75, CD328, SIGLEC7, AIRM1 |
| Target/Specificity | This SIGLEC7 (D-siglec) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SIGLEC7 (D-siglec). |
| Dilution | IHC-P~~1:100~500 WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | SIGLEC7 (D-siglec) Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SIGLEC7 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | AIRM1 |
| Function | Putative adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,3- and alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. Also binds disialogangliosides (disialogalactosyl globoside, disialyl lactotetraosylceramide and disialyl GalNAc lactotetraoslylceramide). The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. In the immune response, may act as an inhibitory receptor upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatase(s) via their SH2 domain(s) that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. Mediates inhibition of natural killer cells cytotoxicity. May play a role in hemopoiesis. Inhibits differentiation of CD34+ cell precursors towards myelomonocytic cell lineage and proliferation of leukemic myeloid cells (in vitro). |
| Cellular Location | Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. |
| Tissue Location | Predominantly expressed by resting and activated natural killer cells and at lower levels by granulocytes and monocytes High expression found in placenta, liver, lung, spleen, and peripheral blood leukocytes |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
SIGLECs are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily that are expressed on the cell surface. Most SIGLECs have one or more cytoplasmic immune receptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIM). SIGLECs are typically expressed on cells of the innate immune system, with the exception of the B-cell expressed SIGLEC6. Sequence analysis predicted that the 697-amino acid SIGLEC10 protein contains a signal peptide, an N-terminal V-set Ig-like domain and four C2-set Ig-like domains, five potential N-linked glycosylation sites, a transmembrane region, and a 126-residue cytoplasmic tail with 3 putative ITIMs. Northern blot analysis detected a major 3.0-kb SIGLEC10 transcript, with highest levels in spleen, lymph node, blood leukocytes, and appendix. Little or no expression was observed in pancreas, thyroid, and testis. Flow cytometric analysis demonstrated eosinophil-specific expression of SIGLEC10, but at a lower level than that of SIGLEC8. Expression was also detected on monocytes and a CD16-positive/CD56-negative natural killer-like lymphocyte population. After sialidase treatment, which is necessary for unmasking the sialic acid-binding site on SIGLECs interacting with cell surface sialic acids, cells expressing SIGLEC10 bound to red blood cells. Immunoprecipitation analysis indicated expression of a 100- to 120-kD monomeric protein, higher than the predicted molecular mass, suggesting that SIGLEC10 is glycosylated.
REFERENCES
Nicoll, G., et al., Eur. J. Immunol. 33(6):1642-1648 (2003).
Alphey, M.S., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 278(5):3372-3377 (2003).
Angata, T., et al., Glycobiology 10(4):431-438 (2000).
Falco, M., et al., J. Exp. Med. 190(6):793-802 (1999).
Nicoll, G., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 274(48):34089-34095 (1999).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。