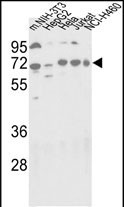
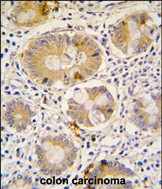
ATG16L Antibody (C-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 1
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q676U5 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 68265 Da |
| Antigen Region | 454-483 aa |
| Gene ID | 55054 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Autophagy-related protein 16-1, APG16-like 1, ATG16L1, APG16L |
| Target/Specificity | This ATG16L antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 454-483 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ATG16L. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC-P~~1:100~500 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | ATG16L Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ATG16L1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:17200669, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:21498} |
|---|---|
| Function | Plays an essential role in both canonical and non-canonical autophagy: interacts with ATG12-ATG5 to mediate the lipidation to ATG8 family proteins (MAP1LC3A, MAP1LC3B, MAP1LC3C, GABARAPL1, GABARAPL2 and GABARAP) (PubMed:23376921, PubMed:23392225, PubMed:24553140, PubMed:24954904, PubMed:27273576, PubMed:29317426, PubMed:30778222, PubMed:33909989). Acts as a molecular hub, coordinating autophagy pathways via distinct domains that support either canonical or non- canonical signaling (PubMed:29317426, PubMed:30778222). During canonical autophagy, interacts with ATG12-ATG5 to mediate the conjugation of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to ATG8 proteins, to produce a membrane-bound activated form of ATG8 (PubMed:23376921, PubMed:23392225, PubMed:24553140, PubMed:24954904, PubMed:27273576). Thereby, controls the elongation of the nascent autophagosomal membrane (PubMed:23376921, PubMed:23392225, PubMed:24553140, PubMed:24954904, PubMed:27273576). As part of the ATG8 conjugation system with ATG5 and ATG12, required for recruitment of LRRK2 to stressed lysosomes and induction of LRRK2 kinase activity in response to lysosomal stress (By similarity). Also involved in non-canonical autophagy, a parallel pathway involving conjugation of ATG8 proteins to single membranes at endolysosomal compartments, probably by catalyzing conjugation of phosphatidylserine (PS) to ATG8 (PubMed:33909989). Non-canonical autophagy plays a key role in epithelial cells to limit lethal infection by influenza A (IAV) virus (By similarity). Regulates mitochondrial antiviral signaling (MAVS)-dependent type I interferon (IFN-I) production (PubMed:22749352, PubMed:25645662). Negatively regulates NOD1- and NOD2-driven inflammatory cytokine response (PubMed:24238340). Instead, promotes an autophagy-dependent antibacterial pathway together with NOD1 or NOD2 (PubMed:20637199). Plays a role in regulating morphology and function of Paneth cell (PubMed:18849966). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Preautophagosomal structure membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Lysosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Note=Recruited to omegasomes membranes by WIPI2 (By similarity). Omegasomes are endoplasmic reticulum connected strutures at the origin of preautophagosomal structures (By similarity). Localized to preautophagosomal structure (PAS) where it is involved in the membrane targeting of ATG5 (By similarity). Also localizes to discrete punctae along the ciliary axoneme (By similarity). Upon activation of non-canonical autophagy, recruited to single-membrane endolysosomal compartments (PubMed:29317426). Under starved conditions, the ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 complex is translocated to phagophores driven by RAB33B (PubMed:32960676). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C0J2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29317426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32960676} |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Macroautophagy is the major inducible pathway for the general turnover of cytoplasmic constituents in eukaryotic cells, it is also responsible for the degradation of active cytoplasmic enzymes and organelles during nutrient starvation. Macroautophagy involves the formation of double-membrane bound autophagosomes which enclose the cytoplasmic constituent targeted for degradation in a membrane bound structure, which then fuse with the lysosome (or vacuole) releasing a single-membrane bound autophagic bodies which are then degraded within the lysosome (or vacuole). The APG12-APG5-APG16L complex is esential for the elongation of autophagic isolation membranes. This complex initially associates in uniform distribution with small vesicle membranes. During membrane elongation, the complex partitions, with a great concentration building on the outer side of the isolation membrane. Upon completion of the formation of the autophagosome, the APG12-APG5-APG16L dissociates from the membrane.
REFERENCES
Baehrecke EH. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6(6):505-10. (2005)
Lum JJ, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6(6):439-48. (2005)
Greenberg JT. Dev Cell. 8(6):799-801. (2005)
Levine B. Cell. 120(2):159-62. (2005)
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ. Science. 306(5698):990-5. (2004)
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。