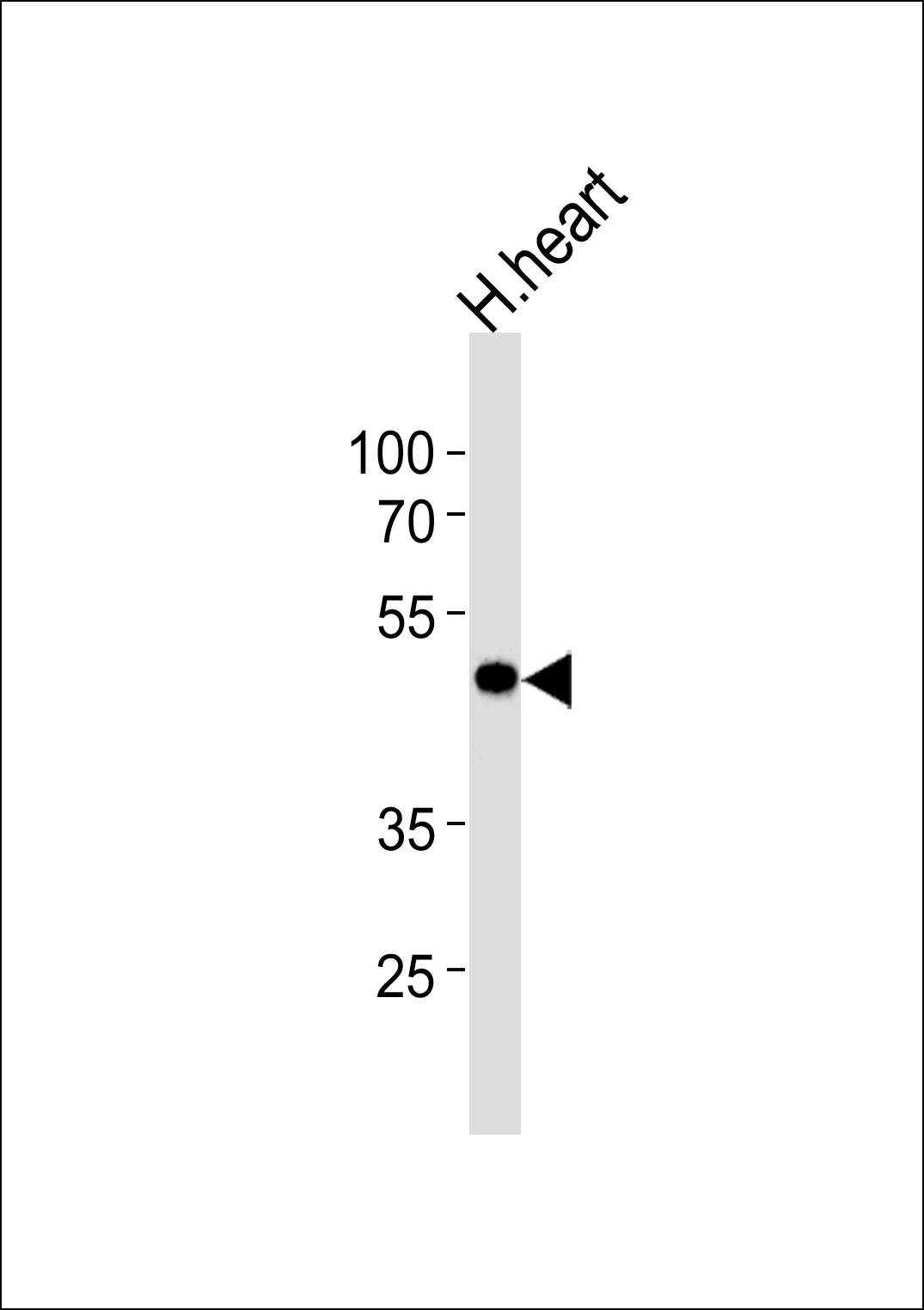
KCNAB1 Antibody(N-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q14722 |
| Other Accession | NP_003462.2 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 46563 Da |
| Antigen Region | 15-44 aa |
| Gene ID | 7881 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit beta-1, K(+) channel subunit beta-1, Kv-beta-1, KCNAB1, KCNA1B |
| Target/Specificity | This KCNAB1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 15-44 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human KCNAB1. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | KCNAB1 Antibody(N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | KCNAB1 (HGNC:6228) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | KCNA1B |
| Function | Regulatory subunit of the voltage-gated potassium (Kv) Shaker channels composed of pore-forming and potassium-conducting alpha subunits and of regulatory beta subunits (PubMed:17156368, PubMed:17540341, PubMed:19713757, PubMed:7499366, PubMed:7603988). The beta-1/KCNAB1 cytoplasmic subunit mediates closure of delayed rectifier potassium channels by physically obstructing the pore via its N- terminal domain and increases the speed of channel closure for other family members (PubMed:9763623). Promotes the inactivation of Kv1.1/KCNA1, Kv1.2/KCNA2, Kv1.4/KCNA4, Kv1.5/KCNA5 and Kv1.6/KCNA6 alpha subunit-containing channels (PubMed:12077175, PubMed:12130714, PubMed:15361858, PubMed:17156368, PubMed:17540341, PubMed:19713757, PubMed:7499366, PubMed:7603988, PubMed:7649300, PubMed:7890764, PubMed:9763623). Displays nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent aldoketoreductase activity by catalyzing the NADPH- dependent reduction of a variety of endogenous aldehydes and ketones (By similarity). The binding of NADPH is required for efficient down- regulation of potassium channel activity (PubMed:17540341). Oxidation of the bound NADPH restrains N-terminal domain from blocking the channel, thereby decreasing N-type inactivation of potassium channel activity (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63144}; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Note=Recruited to the cytoplasmic side of the cell membrane via its interaction with pore-forming potassium channel alpha subunits. |
| Tissue Location | In brain, expression is most prominent in caudate nucleus, hippocampus and thalamus. Significant expression also detected in amygdala and subthalamic nucleus. Also expressed in both healthy and cardiomyopathic heart. Up to four times more abundant in left ventricle than left atrium. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Potassium channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. Four sequence-related potassium channel genes - shaker, shaw, shab, and shal - have been identified in Drosophila, and each has been shown to have human homolog(s). This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, shaker-related subfamily. This member includes three distinct isoforms which are encoded by three alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene. These three isoforms are beta subunits, which form heteromultimeric complex with alpha subunits and modulate the activity of the pore-forming alpha subunits.
REFERENCES
Rose, J.E., et al. Mol. Med. 16 (7-8), 247-253 (2010) :
Decher, N., et al. EMBO J. 27(23):3164-3174(2008)
Cavalleri, G.L., et al. Lancet Neurol 6(11):970-980(2007)
Lamesch, P., et al. Genomics 89(3):307-315(2007)
Lunetta, K.L., et al. BMC Med. Genet. 8 SUPPL 1, S13 (2007) :
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。