TNFRSF14 Antibody (C-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
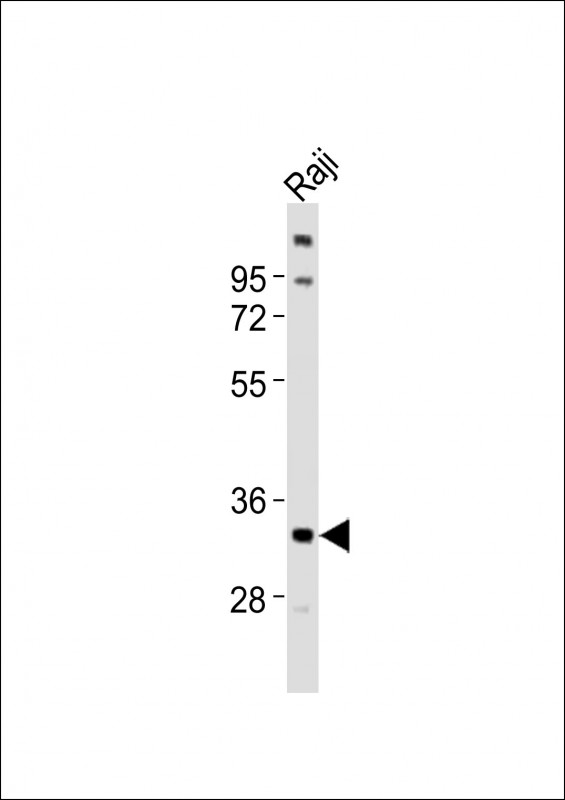
Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q92956 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 30392 Da |
| Gene ID | 8764 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14, Herpes virus entry mediator A, Herpesvirus entry mediator A, HveA, Tumor necrosis factor receptor-like 2, TR2, CD270, TNFRSF14, HVEA, HVEM |
| Target/Specificity | This TNFRSF14 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 269-302 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human TNFRSF14. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | TNFRSF14 Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | TNFRSF14 (HGNC:11912) |
|---|---|
| Function | Receptor for four distinct ligands: The TNF superfamily members TNFSF14/LIGHT and homotrimeric LTA/lymphotoxin-alpha and the immunoglobulin superfamily members BTLA and CD160, altogether defining a complex stimulatory and inhibitory signaling network (PubMed:10754304, PubMed:18193050, PubMed:23761635, PubMed:9462508). Signals via the TRAF2-TRAF3 E3 ligase pathway to promote immune cell survival and differentiation (PubMed:19915044, PubMed:9153189, PubMed:9162022). Participates in bidirectional cell-cell contact signaling between antigen presenting cells and lymphocytes. In response to ligation of TNFSF14/LIGHT, delivers costimulatory signals to T cells, promoting cell proliferation and effector functions (PubMed:10754304). Interacts with CD160 on NK cells, enhancing IFNG production and anti-tumor immune response (PubMed:23761635). In the context of bacterial infection, acts as a signaling receptor on epithelial cells for CD160 from intraepithelial lymphocytes, triggering the production of antimicrobial proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines (By similarity). Upon binding to CD160 on activated CD4+ T cells, down- regulates CD28 costimulatory signaling, restricting memory and alloantigen-specific immune response (PubMed:18193050). May interact in cis (on the same cell) or in trans (on other cells) with BTLA (By similarity) (PubMed:19915044). In cis interactions, appears to play an immune regulatory role inhibiting in trans interactions in naive T cells to maintain a resting state. In trans interactions, can predominate during adaptive immune response to provide survival signals to effector T cells (By similarity) (PubMed:19915044). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed, with the highest expression in lung, spleen and thymus. Expressed in a subpopulation of B cells and monocytes (PubMed:18193050). Expressed in naive T cells (PubMed:19915044). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Receptor for BTLA. Receptor for TNFSF14/LIGHT and homotrimeric TNFSF1/lymphotoxin-alpha. Involved in lymphocyte activation. Plays an important role in HSV pathogenesis because it enhanced the entry of several wild-type HSV strains of both serotypes into CHO cells, and mediated HSV entry into activated human T-cells.
REFERENCES
Montgomery R.I.,et al.Cell 87:427-436(1996).
Kwon B.S.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 272:14272-14276(1997).
Zhang W.,et al.Submitted (MAY-1999) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Struyf F.,et al.J. Infect. Dis. 185:36-44(2002).
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。