BAAT Antibody (N-Term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
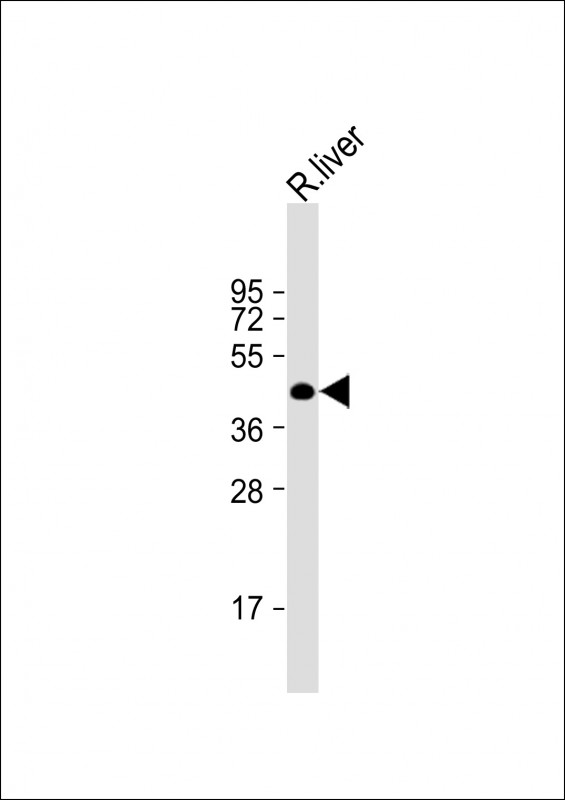
Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q14032 |
| Reactivity | Human, Rat, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 46299 Da |
| Gene ID | 570 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase, BACAT, BAT, 2.3.1.65, Glycine N-choloyltransferase, Long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA hydrolase, 3.1.2.2, BAAT |
| Target/Specificity | This BAAT antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 63-95 amino acids from human BAAT. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:2000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | BAAT Antibody (N-Term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | BAAT |
|---|---|
| Function | Catalyzes the amidation of bile acids (BAs) with the amino acids taurine and glycine (PubMed:12239217, PubMed:12810727, PubMed:2037576, PubMed:8034703). More than 95% of the BAs are N-acyl amidates with glycine and taurine (PubMed:8034703). Amidation of BAs in the liver with glycine or taurine prior to their excretion into bile is an important biochemical event in bile acid metabolism (PubMed:12810727). This conjugation (or amidation) plays several important biological roles in that it promotes the secretion of BAs and cholesterol into bile and increases the detergent properties of BAs in the intestine, which facilitates lipid and vitamin absorption (PubMed:12810727). May also act as an acyl-CoA thioesterase that regulates intracellular levels of free fatty acids (PubMed:12239217, PubMed:12810727, PubMed:8034703). In vitro, catalyzes the hydrolysis of long- and very long-chain saturated acyl-CoAs to the free fatty acid and coenzyme A (CoASH), and conjugates glycine to these acyl-CoAs (PubMed:12810727). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Peroxisome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63276} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the gallbladder mucosa and pancreas (PubMed:12810727, PubMed:2037576). Expressed in hepatocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:12810727, PubMed:2037576, PubMed:23415802) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Involved in bile acid metabolism. In liver hepatocytes catalyzes the second step in the conjugation of C24 bile acids (choloneates) to glycine and taurine before excretion into bile canaliculi. The major components of bile are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. In a first step the bile acids are converted to an acyl-CoA thioester, either in peroxisomes (primary bile acids deriving from the cholesterol pathway), or cytoplasmic at the endoplasmic reticulum (secondary bile acids). May catalyze the conjugation of primary or secondary bile acids, or both. The conjugation increases the detergent properties of bile acids in the intestine, which facilitates lipid and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. In turn, bile acids are deconjugated by bacteria in the intestine and are recycled back to the liver for reconjugation (secondary bile acids). May also act as an acyl-CoA thioesterase that regulates intracellular levels of free fatty acids. In vitro, catalyzes the hydrolysis of long- and very long-chain saturated acyl-CoAs to the free fatty acid and coenzyme A (CoASH), and conjugates glycine to these acyl-CoAs.
REFERENCES
Falany C.N.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 269:19375-19379(1994).
Ebert L.,et al.Submitted (JUN-2004) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Humphray S.J.,et al.Nature 429:369-374(2004).
Mural R.J.,et al.Submitted (JUL-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Johnson M.R.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 266:10227-10233(1991).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。