HSF1 Sumoylation Site Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
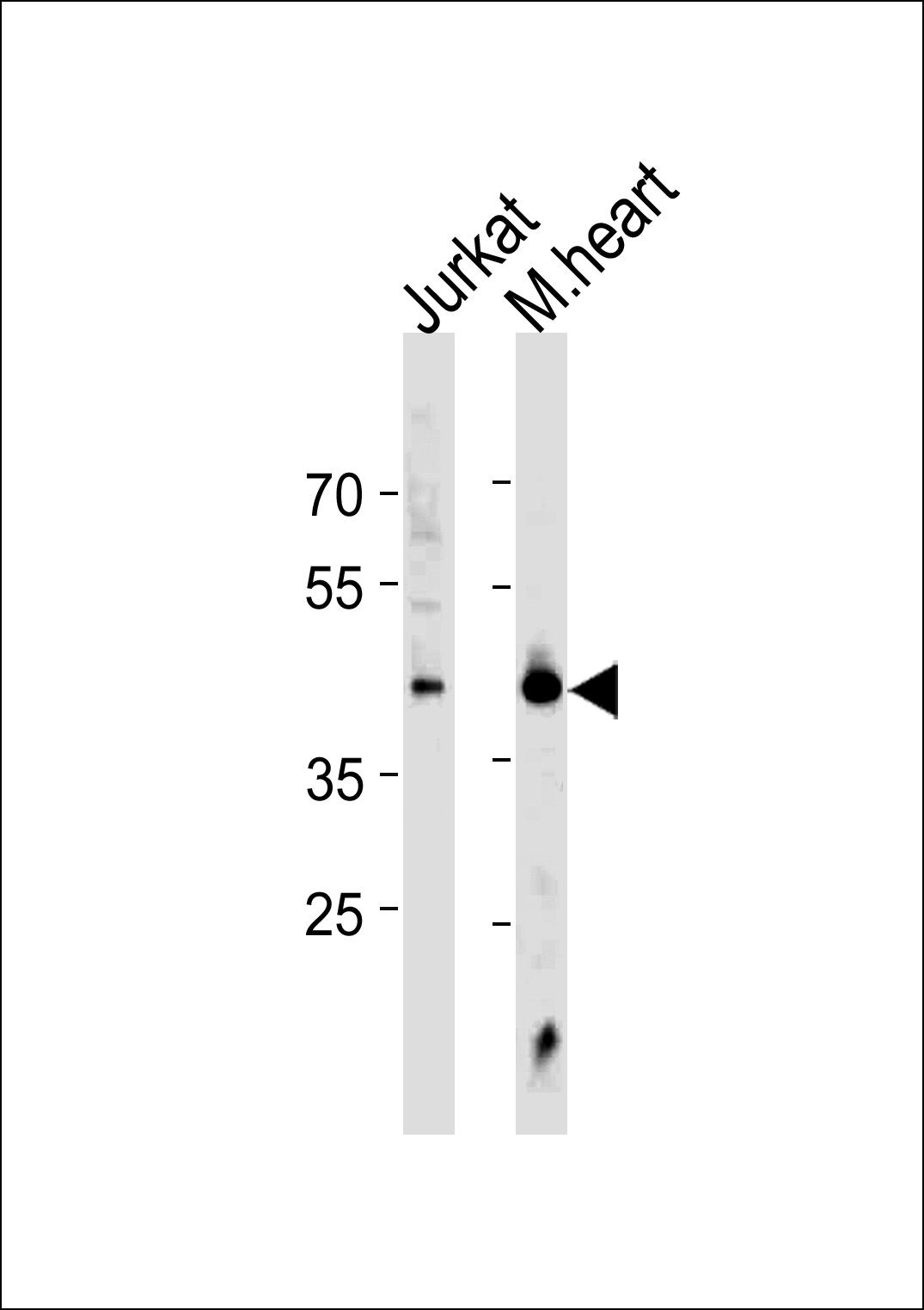
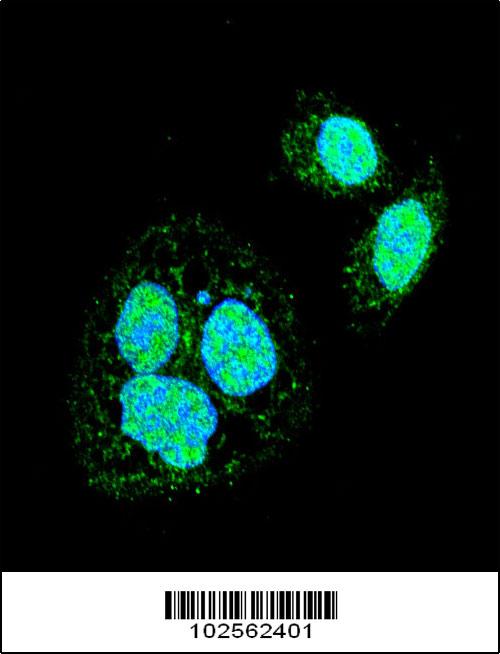
Application
| IF, WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q00613 |
| Other Accession | Q08DJ8 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Predicted | Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 57260 Da |
| Antigen Region | 278-309 aa |
| Gene ID | 3297 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Heat shock factor protein 1, HSF 1, Heat shock transcription factor 1, HSTF 1, HSF1, HSTF1 |
| Target/Specificity | This HSF1 Sumoylation Site antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 278-309 amino acids from human HSF1 Sumoylation Site. |
| Dilution | IF~~1:10~50 WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | HSF1 Sumoylation Site Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | HSF1 (HGNC:5224) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | HSTF1 |
| Function | Functions as a stress-inducible and DNA-binding transcription factor that plays a central role in the transcriptional activation of the heat shock response (HSR), leading to the expression of a large class of molecular chaperones, heat shock proteins (HSPs), that protect cells from cellular insult damage (PubMed:11447121, PubMed:12659875, PubMed:12917326, PubMed:15016915, PubMed:18451878, PubMed:1871105, PubMed:1986252, PubMed:25963659, PubMed:26754925, PubMed:7623826, PubMed:7760831, PubMed:8940068, PubMed:8946918, PubMed:9121459, PubMed:9341107, PubMed:9499401, PubMed:9535852, PubMed:9727490). In unstressed cells, is present in a HSP90-containing multichaperone complex that maintains it in a non-DNA-binding inactivated monomeric form (PubMed:11583998, PubMed:16278218, PubMed:9727490). Upon exposure to heat and other stress stimuli, undergoes homotrimerization and activates HSP gene transcription through binding to site-specific heat shock elements (HSEs) present in the promoter regions of HSP genes (PubMed:10359787, PubMed:11583998, PubMed:12659875, PubMed:16278218, PubMed:1871105, PubMed:1986252, PubMed:25963659, PubMed:26754925, PubMed:7623826, PubMed:7935471, PubMed:8455624, PubMed:8940068, PubMed:9499401, PubMed:9727490). Upon heat shock stress, forms a chromatin-associated complex with TTC5/STRAP and p300/EP300 to stimulate HSR transcription, therefore increasing cell survival (PubMed:18451878). Activation is reversible, and during the attenuation and recovery phase period of the HSR, returns to its unactivated form (PubMed:11583998, PubMed:16278218). Binds to inverted 5'-NGAAN-3' pentamer DNA sequences (PubMed:1986252, PubMed:26727489). Binds to chromatin at heat shock gene promoters (PubMed:25963659). Activates transcription of transcription factor FOXR1 which in turn activates transcription of the heat shock chaperones HSPA1A and HSPA6 and the antioxidant NADPH-dependent reductase DHRS2 (PubMed:34723967). Also serves several other functions independently of its transcriptional activity. Involved in the repression of Ras-induced transcriptional activation of the c-fos gene in heat-stressed cells (PubMed:9341107). Positively regulates pre-mRNA 3'-end processing and polyadenylation of HSP70 mRNA upon heat-stressed cells in a symplekin (SYMPK)-dependent manner (PubMed:14707147). Plays a role in nuclear export of stress- induced HSP70 mRNA (PubMed:17897941). Plays a role in the regulation of mitotic progression (PubMed:18794143). Also plays a role as a negative regulator of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair activity in a DNA damage-dependent manner (PubMed:26359349). Involved in stress-induced cancer cell proliferation in a IER5-dependent manner (PubMed:26754925). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome Chromosome, centromere, kinetochore Note=The monomeric form is cytoplasmic in unstressed cells (PubMed:26159920, PubMed:8455624). Predominantly nuclear protein in both unstressed and heat shocked cells (PubMed:10359787, PubMed:10413683). Translocates in the nucleus upon heat shock (PubMed:8455624). Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein (PubMed:26159920). Colocalizes with IER5 in the nucleus (PubMed:27354066). Colocalizes with BAG3 to the nucleus upon heat stress (PubMed:26159920, PubMed:8455624). Localizes in subnuclear granules called nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (PubMed:10359787, PubMed:10747973, PubMed:11447121, PubMed:11514557, PubMed:19229036, PubMed:24581496, PubMed:25963659). Colocalizes with SYMPK and SUMO1 in nSBs upon heat shock (PubMed:10359787, PubMed:11447121, PubMed:11514557, PubMed:12665592, PubMed:14707147) Colocalizes with PRKACA/PKA in the nucleus and nSBs upon heat shock (PubMed:21085490). Relocalizes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm during the attenuation and recovery phase period of the heat shock response (PubMed:26159920). Translocates in the cytoplasm in a YWHAE- and XPO1/CRM1-dependent manner (PubMed:12917326). Together with histone H2AX, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) (PubMed:26359349). Colocalizes with calcium- responsive transactivator SS18L1 at kinetochore region on the mitotic chromosomes (PubMed:18794143). Colocalizes with gamma tubulin at centrosome (PubMed:18794143). Localizes at spindle pole in metaphase (PubMed:18794143). Colocalizes with PLK1 at spindle poles during prometaphase (PubMed:18794143). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Heat shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1) mediates the induction of heat shock protein gene expression in cells exposed to elevated temperature and other stress conditions. In response to stress, HSF1 acquires DNA-binding ability and localizes to nuclear stress granules. SUMO modification of HSF1 converts HSF1 to the DNA-binding form. HSF1 colocalizes with SUMO-1 in nuclear stress granules, which is prevented by mutation of the HSF1 lysine targeted for sumoylation.
REFERENCES
Hilgarth, et al., Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Mar 28;303(1):196-200.
He, H., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 278(37):35465-35475 (2003).
Wang, X., et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 23(17):6013-6026 (2003).
Ignatenko, N.A., et al., Exp. Cell Res. 288(1):1-8 (2003).
Soncin, F., et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 303(2):700-706 (2003).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。