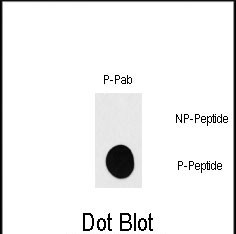
Phospho-RPS6KB1(S418) Antibody
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| DB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P23443 |
| Other Accession | P67999, P67998, Q8BSK8, Q6TJY3 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Bovine, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 59140 Da |
| Gene ID | 6198 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1, S6K-beta-1, S6K1, 70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1, P70S6K1, p70-S6K 1, Ribosomal protein S6 kinase I, Serine/threonine-protein kinase 14A, p70 ribosomal S6 kinase alpha, p70 S6 kinase alpha, p70 S6K-alpha, p70 S6KA, RPS6KB1, STK14A |
| Target/Specificity | This RPS6KB1 Antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to amino acid residues surrounding S418 of human RPS6KB1. |
| Dilution | DB~~1:500 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Phospho-RPS6KB1(S418) Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | RPS6KB1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | STK14A |
| Function | Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts downstream of mTOR signaling in response to growth factors and nutrients to promote cell proliferation, cell growth and cell cycle progression (PubMed:11500364, PubMed:12801526, PubMed:14673156, PubMed:15071500, PubMed:15341740, PubMed:16286006, PubMed:17052453, PubMed:17053147, PubMed:17936702, PubMed:18952604, PubMed:19085255, PubMed:19720745, PubMed:19935711, PubMed:19995915, PubMed:22017876, PubMed:23429703, PubMed:28178239). Regulates protein synthesis through phosphorylation of EIF4B, RPS6 and EEF2K, and contributes to cell survival by repressing the pro-apoptotic function of BAD (PubMed:11500364, PubMed:12801526, PubMed:14673156, PubMed:15071500, PubMed:15341740, PubMed:16286006, PubMed:17052453, PubMed:17053147, PubMed:17936702, PubMed:18952604, PubMed:19085255, PubMed:19720745, PubMed:19935711, PubMed:19995915, PubMed:22017876, PubMed:23429703, PubMed:28178239). Under conditions of nutrient depletion, the inactive form associates with the EIF3 translation initiation complex (PubMed:16286006). Upon mitogenic stimulation, phosphorylation by the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) leads to dissociation from the EIF3 complex and activation (PubMed:16286006). The active form then phosphorylates and activates several substrates in the pre-initiation complex, including the EIF2B complex and the cap-binding complex component EIF4B (PubMed:16286006). Also controls translation initiation by phosphorylating a negative regulator of EIF4A, PDCD4, targeting it for ubiquitination and subsequent proteolysis (PubMed:17053147). Promotes initiation of the pioneer round of protein synthesis by phosphorylating POLDIP3/SKAR (PubMed:15341740). In response to IGF1, activates translation elongation by phosphorylating EEF2 kinase (EEF2K), which leads to its inhibition and thus activation of EEF2 (PubMed:11500364). Also plays a role in feedback regulation of mTORC2 by mTORC1 by phosphorylating MAPKAP1/SIN1, MTOR and RICTOR, resulting in the inhibition of mTORC2 and AKT1 signaling (PubMed:15899889, PubMed:19720745, PubMed:19935711, PubMed:19995915). Also involved in feedback regulation of mTORC1 and mTORC2 by phosphorylating DEPTOR (PubMed:22017876). Mediates cell survival by phosphorylating the pro-apoptotic protein BAD and suppressing its pro-apoptotic function (By similarity). Phosphorylates mitochondrial URI1 leading to dissociation of a URI1-PPP1CC complex (PubMed:17936702). The free mitochondrial PPP1CC can then dephosphorylate RPS6KB1 at Thr-412, which is proposed to be a negative feedback mechanism for the RPS6KB1 anti-apoptotic function (PubMed:17936702). Mediates TNF-induced insulin resistance by phosphorylating IRS1 at multiple serine residues, resulting in accelerated degradation of IRS1 (PubMed:18952604). In cells lacking functional TSC1-2 complex, constitutively phosphorylates and inhibits GSK3B (PubMed:17052453). May be involved in cytoskeletal rearrangement through binding to neurabin (By similarity). Phosphorylates and activates the pyrimidine biosynthesis enzyme CAD, downstream of MTOR (PubMed:23429703). Following activation by mTORC1, phosphorylates EPRS and thereby plays a key role in fatty acid uptake by adipocytes and also most probably in interferon-gamma-induced translation inhibition (PubMed:28178239). |
| Cellular Location | Synapse, synaptosome. Mitochondrion outer membrane. Mitochondrion. Note=Colocalizes with URI1 at mitochondrion [Isoform Alpha II]: Cytoplasm. |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed.. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes a member of the RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase) family of serine/threonine kinases. This kinase contains 2 non-identical kinase catalytic domains and phosphorylates several residues of the S6 ribosomal protein. The kinase activity of this protein leads to an increase in protein synthesis and cell proliferation. Amplification of the region of DNA encoding this gene and overexpression of this kinase are seen in some breast cancer cell lines. Alternate translational start sites have been described and alternate transcriptional splice variants have been observed but have not been thoroughly characterized.
REFERENCES
Adem, C., et al., Genes Chromosomes Cancer 41(1):1-11 (2004).
Suzuki, Y., et al., Genome Res. 14(9):1711-1718 (2004).
Gomez-Cambronero, J., et al., Leuk. Res. 28(7):755-762 (2004).
Raught, B., et al., EMBO J. 23(8):1761-1769 (2004).
Miyakawa, M., et al., Endocr. J. 50(1):77-83 (2003).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。