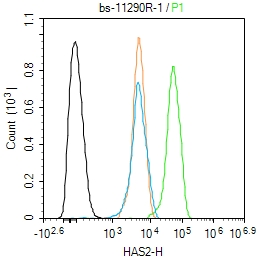
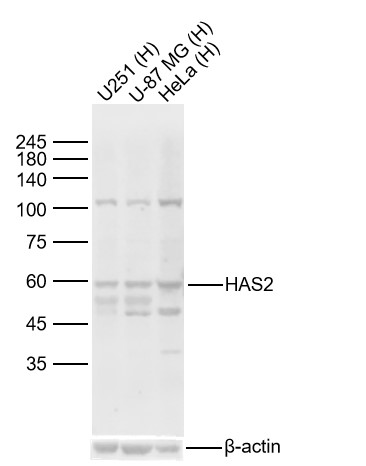
HAS2 Rabbit pAb
HAS2 Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 1
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q92819 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Pig, Horse, Rabbit, Sheep |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 63566 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human HAS2/Hyaluronan synthase 2 |
| Epitope Specificity | 401-500/552 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Membrane. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the nodC/HAS family. |
| Post-translational modifications | Autophosphorylated on several Ser and Thr residues. Autophosphorylation of Thr-451 is dependent on Thr-446 and is stimulated by dsRNA binding and dimerization. Autophosphorylation apparently leads to the activation of the kinase. |
| DISEASE | Note=A chromosomal aberration involving HAS2 may be a cause of lipoblastomas, which are benign tumors resulting from transformation of adipocytes, usually diagnosed in children. 8q12.1 to 8q24.1 intrachromosomal rearrangement with PLAG1. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | Hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA) is a high molecular weight unbranched polysaccharide synthesized by a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals, and is a constituent of the extracellular matrix. It consists of alternating glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues that are linked by beta-1-3 and beta-1-4 glycosidic bonds. HA is synthesized by membrane-bound synthase at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, and the chains are extruded through pore-like structures into the extracellular space. It serves a variety of functions, including space filling, lubrication of joints, and provision of a matrix through which cells can migrate. HA is actively produced during wound healing and tissue repair to provide a framework for ingrowth of blood vessels and fibroblasts. Changes in the serum concentration of HA are associated with inflammatory and degenerative arthropathies such as rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, the interaction of HA with the leukocyte receptor CD44 is important in tissue-specific homing by leukocytes, and overexpression of HA receptors has been correlated with tumor metastasis. HAS2 is a member of the newly identified vertebrate gene family encoding putative hyaluronan synthases, and its amino acid sequence shows significant homology to glycosaminoglycan synthetase (DG42) from Xenopus laevis, and human and murine hyaluronan synthase 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Gene ID | 3037 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Hyaluronan synthase 2, 2.4.1.212, Hyaluronate synthase 2, Hyaluronic acid synthase 2, HA synthase 2, HAS2 (HGNC:4819) |
| Target/Specificity | Expressed in fibroblasts. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,Flow-Cyt=1ug/Test |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | HAS2 (HGNC:4819) |
|---|---|
| Function | Catalyzes the addition of GlcNAc or GlcUA monosaccharides to the nascent hyaluronan polymer (Probable) (PubMed:20507985, PubMed:21228273, PubMed:23303191, PubMed:32993960). Therefore, it is essential to hyaluronan synthesis a major component of most extracellular matrices that has a structural role in tissues architectures and regulates cell adhesion, migration and differentiation (PubMed:20507985, PubMed:21228273, PubMed:8798477). This is one of three isoenzymes responsible for cellular hyaluronan synthesis and it is particularly responsible for the synthesis of high molecular mass hyaluronan (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi- pass membrane protein. Vesicle. Golgi apparatus membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Lysosome Note=Travels from endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi to plasma membrane and either back to endosomes and lysosomes, or out into extracellular vesicles (PubMed:30394292). Post-translational modifications control HAS2 trafficking (PubMed:30394292). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in fibroblasts. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA) is a high molecular weight unbranched polysaccharide synthesized by a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals, and is a constituent of the extracellular matrix. It consists of alternating glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues that are linked by beta-1-3 and beta-1-4 glycosidic bonds. HA is synthesized by membrane-bound synthase at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, and the chains are extruded through pore-like structures into the extracellular space. It serves a variety of functions, including space filling, lubrication of joints, and provision of a matrix through which cells can migrate. HA is actively produced during wound healing and tissue repair to provide a framework for ingrowth of blood vessels and fibroblasts. Changes in the serum concentration of HA are associated with inflammatory and degenerative arthropathies such as rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, the interaction of HA with the leukocyte receptor CD44 is important in tissue-specific homing by leukocytes, and overexpression of HA receptors has been correlated with tumor metastasis. HAS2 is a member of the newly identified vertebrate gene family encoding putative hyaluronan synthases, and its amino acid sequence shows significant homology to glycosaminoglycan synthetase (DG42) from Xenopus laevis, and human and murine hyaluronan synthase 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
REFERENCES
Watanabe K.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 271:22945-22948(1996).
Morerio C.,et al.Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 156:183-184(2005).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。