PP1C Antibody
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Mab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
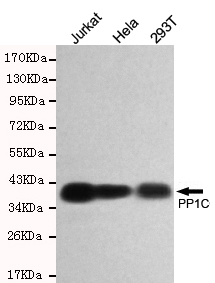
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P36873 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Calculated MW | 36984 Da |
| Gene ID | 5501 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | EC 3.1.3.16;PP 1G;PP-1G;PP1G;PP1G_HUMAN;PP1gamma;PPP 1G;PPP1CC;PPP1CC protein;PPP1G; Protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit gamma isoform;Protein phosphatase 1C catalytic subunit;Protein phosphatase 1C subunit;Protein phosphatase 2C gamma isoform; Serine/threonine phosphatase 1 gamma;Serine/threonine protein phosphatase PP1 gamma catalytic subunit;Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-gamma catalytic subunit. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500 |
| Format | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide, pH 7.3. |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Name | PPP1CC |
|---|---|
| Function | Protein phosphatase that associates with over 200 regulatory proteins to form highly specific holoenzymes which dephosphorylate hundreds of biological targets (PubMed:17936702, PubMed:25012651). Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) is essential for cell division, and participates in the regulation of glycogen metabolism, muscle contractility and protein synthesis. Dephosphorylates RPS6KB1 (PubMed:17936702). Involved in regulation of ionic conductances and long-term synaptic plasticity. May play an important role in dephosphorylating substrates such as the postsynaptic density- associated Ca(2+)/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II. Component of the PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex, which plays a role in the control of chromatin structure and cell cycle progression during the transition from mitosis into interphase (PubMed:20516061). In balance with CSNK1D and CSNK1E, determines the circadian period length, through the regulation of the speed and rhythmicity of PER1 and PER2 phosphorylation (PubMed:21712997). May dephosphorylate CSNK1D and CSNK1E (By similarity). Regulates the recruitment of the SKA complex to kinetochores (PubMed:28982702). Dephosphorylates the 'Ser-418' residue of FOXP3 in regulatory T-cells (Treg) from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, thereby inactivating FOXP3 and rendering Treg cells functionally defective (PubMed:23396208). Together with PPP1CA (PP1- alpha subunit), dephosphorylates IFIH1/MDA5 and RIG-I leading to their activation and a functional innate immune response (PubMed:23499489). Core component of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1c (SMP) holophosphatase complex that regulates the MAPK pathway activation (PubMed:35768504, PubMed:35831509). The SMP complex specifically dephosphorylates the inhibitory phosphorylation at 'Ser-259' of RAF1 kinase, 'Ser-365' of BRAF kinase and 'Ser-214' of ARAF kinase, stimulating their kinase activities (PubMed:35768504, PubMed:35831509). Dephosphorylates MKI67 at the onset of anaphase (PubMed:25012651). The SMP complex enhances the dephosphorylation activity and substrate specificity of PP1c (PubMed:35768504, PubMed:35831509). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Nucleus, nucleolus. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus speckle. Chromosome, centromere, kinetochore. Cleavage furrow. Midbody Mitochondrion. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center Note=Colocalizes with SPZ1 in the nucleus (By similarity). Colocalizes with URI1 at mitochondrion (PubMed:17936702). Rapidly exchanges between the nucleolar, nucleoplasmic and cytoplasmic compartments (PubMed:11739654). Highly mobile in cells and can be relocalized through interaction with targeting subunits (PubMed:17965019). In the presence of PPP1R8 relocalizes from the nucleolus to nuclear speckles (PubMed:11739654). Shows a dynamic targeting to specific sites throughout the cell cycle (PubMed:12529430). Highly concentrated in nucleoli of interphase cells and localizes at kinetochores early in mitosis (PubMed:12529430). Relocalization to chromosome-containing regions occurs at the transition from early to late anaphase (PubMed:12529430). Also accumulates at the cleavage furrow and midbody by telophase (PubMed:12529430). Colocalizes with DYNLT4 in the microtubule organizing center (MTOC) (PubMed:23789093) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63087, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11739654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12529430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17936702, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17965019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23789093} |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Protein phosphatase that associates with over 200 regulatory proteins to form highly specific holoenzymes which dephosphorylate hundreds of biological targets. Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) is essential for cell division, and participates in the regulation of glycogen metabolism, muscle contractility and protein synthesis. Dephosphorylates RPS6KB1. Involved in regulation of ionic conductances and long-term synaptic plasticity. May play an important role in dephosphorylating substrates such as the postsynaptic density- associated Ca(2+)/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II. Component of the PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex, which plays a role in the control of chromatin structure and cell cycle progression during the transition from mitosis into interphase. In balance with CSNK1D and CSNK1E, determines the circadian period length, through the regulation of the speed and rhythmicity of PER1 and PER2 phosphorylation. May dephosphorylate CSNK1D and CSNK1E.
REFERENCES
Barker H.M.,et al.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1178:228-233(1993).
Bienvenut W.V.,et al.Submitted (MAR-2009) to UniProtKB.
Bienvenut W.V.,et al.Submitted (JAN-2010) to UniProtKB.
Norman S.A.,et al.Mamm. Genome 5:41-45(1994).
MacKintosh R.W.,et al.FEBS Lett. 371:236-240(1995).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。