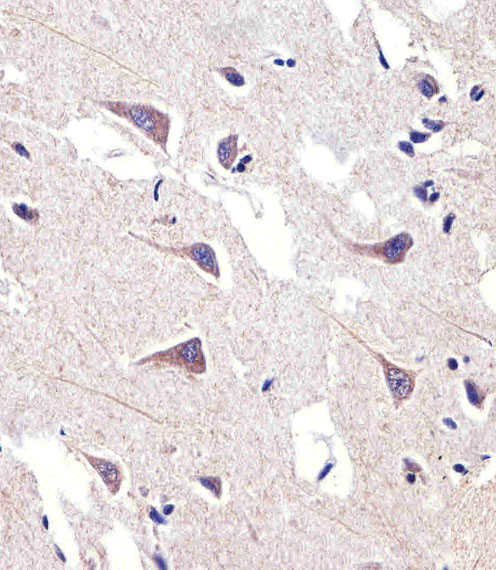
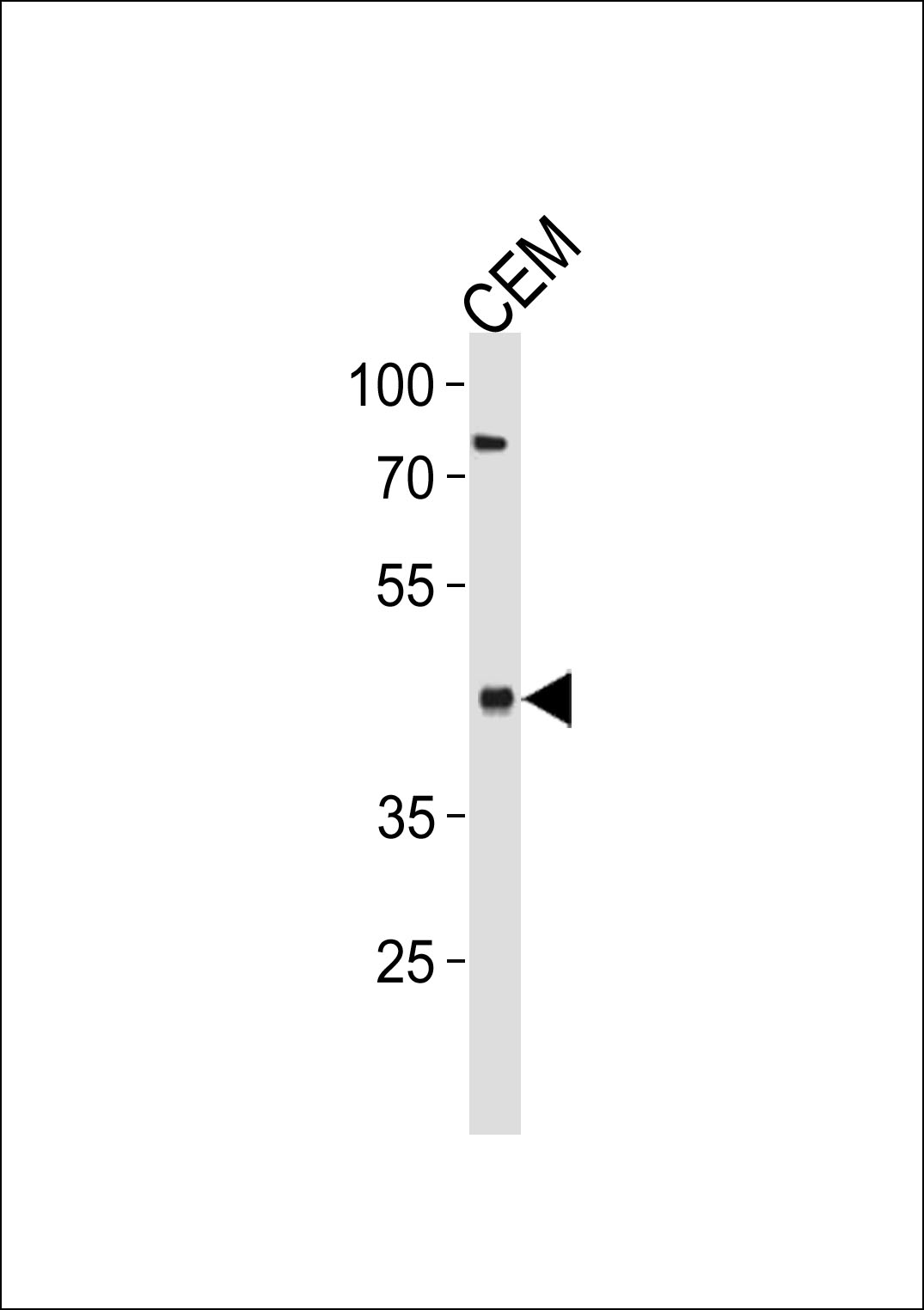
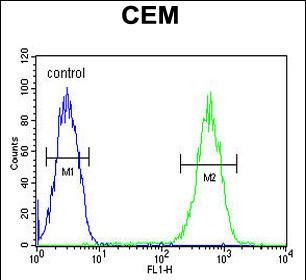
FADS2 Antibody (Center)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| FC, WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O95864 |
| Other Accession | Q6DDK2, A4FV48, NP_004256.1 |
| Reactivity | Human, Rat, Mouse |
| Predicted | Bovine, Xenopus |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 52259 Da |
| Antigen Region | 96-122 aa |
| Gene ID | 9415 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Fatty acid desaturase 2, 11419-, Delta(6) fatty acid desaturase, D6D, Delta(6) desaturase, Delta-6 desaturase, FADS2 |
| Target/Specificity | This FADS2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 96-122 amino acids of human FADS2. |
| Dilution | FC~~1:10~50 WB~~1:1000 IHC-P~~1:100~500 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | FADS2 Antibody (Center) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | FADS2 (HGNC:3575) |
|---|---|
| Function | Involved in the biosynthesis of highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA) from the essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) linoleic acid (LA) (18:2n-6) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (18:3n-3) precursors, acting as a fatty acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) desaturase that introduces a cis double bond at carbon 6 of the fatty acyl chain. Catalyzes the first and rate limiting step in this pathway which is the desaturation of LA (18:2n-6) and ALA (18:3n-3) into gamma-linoleate (GLA) (18:3n-6) and stearidonate (18:4n-3), respectively (PubMed:12713571). Subsequently, in the biosynthetic pathway of HUFA n- 3 series, it desaturates tetracosapentaenoate (24:5n-3) to tetracosahexaenoate (24:6n-3), which is then converted to docosahexaenoate (DHA)(22:6n-3), an important lipid for nervous system function (By similarity). Desaturates hexadecanate (palmitate) to produce 6Z-hexadecenoate (sapienate), a fatty acid unique to humans and major component of human sebum, that has been implicated in the development of acne and may have potent antibacterial activity (PubMed:12713571). It can also desaturate (11E)-octadecenoate (trans- vaccenoate, the predominant trans fatty acid in human milk) at carbon 6 generating (6Z,11E)-octadecadienoate (By similarity). In addition to Delta-6 activity, this enzyme exhibits Delta-8 activity with slight biases toward n-3 fatty acyl-CoA substrates (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in a wide array of tissues, highest expression is found in liver followed by brain, lung, heart, and retina. A lower level is found in breast tumor when compared with normal tissues; lowest levels were found in patients with poor prognostic index. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fatty acid desaturase (FADS) gene family. Desaturase enzymes regulate unsaturation of fatty acids through the introduction of double bonds between defined carbons of the fatty acyl chain. FADS family members are considered fusion products composed of an N-terminal cytochrome b5-like domain and a C-terminal multiple membrane-spanning desaturase portion, both of which are characterized by conserved histidine motifs. This gene is clustered with family members FADS1 and FADS2 at 11q12-q13.1; this cluster is thought to have arisen evolutionarily from gene duplication based on its similar exon/intron organization.
REFERENCES
Molto-Puigmarti, C., et al. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. (2010) In press :
Lattka, E., et al. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 21(1):64-69(2010)
Lattka, E., et al. J. Lipid Res. 51(1):182-191(2010)
Glaser, C., et al. Metab. Clin. Exp. (2009) In press :
Lattka, E., et al. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics 2(3):119-128(2009)
Tang, C., et al. J. Lipid Res. 44(4):686-695(2003)
Nara, T.Y., et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 296(1):111-117(2002)
Marquardt, A., et al. Genomics 66(2):175-183(2000)
Cho, H.P., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 274(1):471-477(1999)
Stohr, H., et al. Genome Res. 8(1):48-56(1998)
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。