CTNS Rabbit pAb
CTNS Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
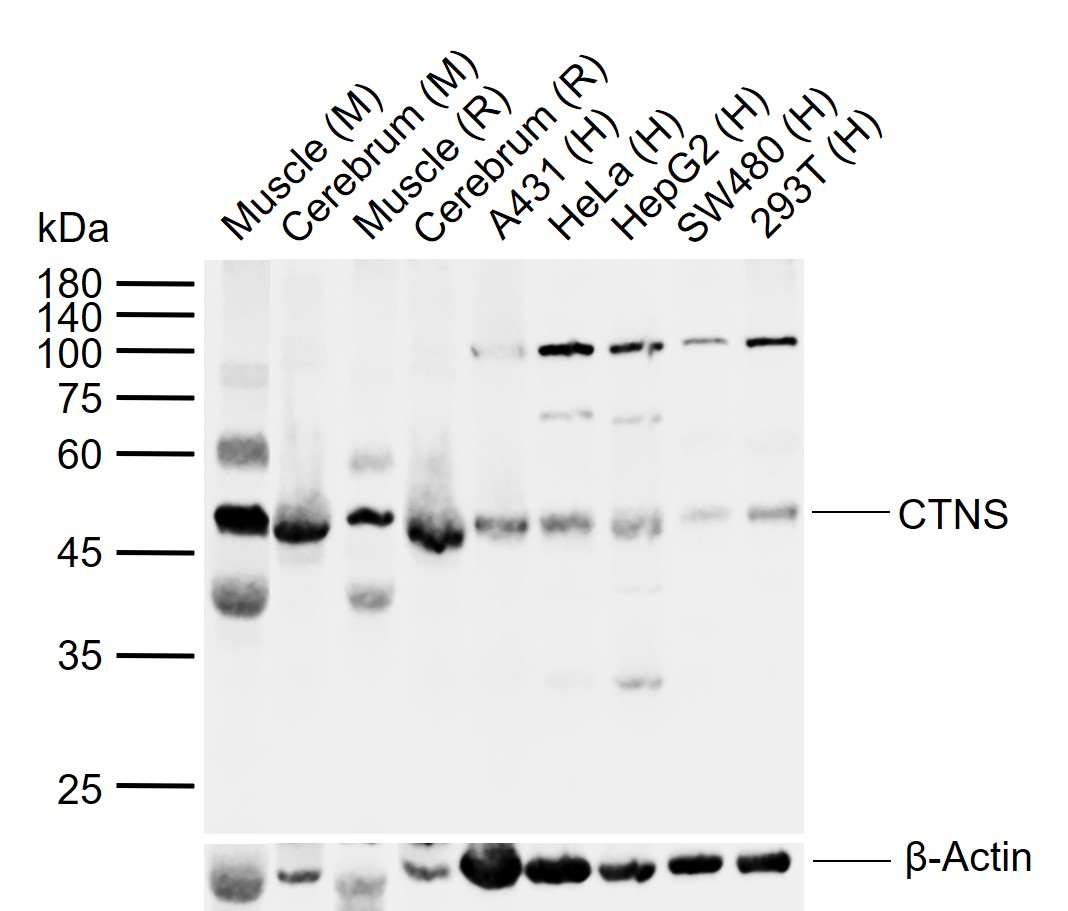
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O60931 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Predicted | Rabbit |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 41738 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human CTNS/Cystinosin |
| Epitope Specificity | 231-330/367 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Lysosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the cystinosin family. Contains 2 PQ-loop domains. |
| DISEASE | Defects in CTNS are the cause of cystinosis nephropathic type (CTNS) [MIM:219800]. It is a form of cystinosis, a lysosomal storage disease due to defective transport of cystine across the lysosomal membrane. This results in cystine accumulation and crystallization in the cells causing widespread tissue damage. The classical nephropathic form has onset in the first year of life and is characterized by a polyuro-polydipsic syndrome, marked height-weight growth delay, generalized impaired proximal tubular reabsorptive capacity, with severe fluid-electrolyte balance alterations, renal failure, ocular symptoms and other systemic complications. Defects in CTNS are the cause of cystinosis adult non-nephropathic type (CTNSANN) [MIM:219750]. It is a form of cystinosis, a lysosomal storage disease due to defective transport of cystine across the lysosomal membrane. This results in cystine accumulation and crystallization in the cells causing widespread tissue damage. Cystinosis adult non-nephropathic type is characterized by ocular features and a benigne course. Patients manifest mild photophobia due to conjunctival and corneal cystine crystals. Defects in CTNS are the cause of cystinosis late-onset juvenile or adolescent nephropathic type (CTNSJAN) [MIM:219900]. It is a form of cystinosis, a lysosomal storage disease due to defective transport of cystine across the lysosomal membrane. This results in cystine accumulation and crystallization in the cells causing widespread tissue damage. Late-onset juvenile or adolescent nephropathic cystinosis manifests itself first at age 10 to 12 years with proteinuria due to glomerular damage rather than with the manifestations of tubular damage that occur first in infantile cystinosis. There is no excess amino aciduria and stature is normal. Photophobia, late development of pigmentary retinopathy, and chronic headaches are features. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | Cystinosis is an autosomal recessive disorder resulting from defective lysosomal transport of cystine and present at birth as a failure to thrive, rickets and proximal renal tubular acidosis. The human CTNS gene on chromosome 17p13 encodes the protein Cystinosin, and mutations in CTNS are responsible for nephropathic cystinosis. The CTNS promoter contains an Sp1 binding element. Cystinosin is an integral membrane protein containing 7 transmembrane domains that functions as a H+-driven transporter responsible for cystine export from lysosomes. In humans, Cystinosin is expressed abundantly in pancreas, kidney (mature and fetal), and skeletal muscle. The mouse homolog to CTNS encodes a protein which is expressed in all tissues except skeletal muscle. In the cell, Cystinosin co-localizes with LAMP-2 to lysosomes. A C-terminal GYDQL sorting motif within Cystinosin is critical for lysosomal localization. |
| Gene ID | 1497 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Cystinosin, CTNS {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9537412, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:2518} |
| Target/Specificity | Strongly expressed in pancreas, kidney (adult and fetal) and in skeletal muscle. Expressed at lower levels in placenta and heart. Weakly expressed in lung, liver and brain (adult and fetal). |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | CTNS {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9537412, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:2518} |
|---|---|
| Function | Cystine/H(+) symporter that mediates export of cystine, the oxidized dimer of cysteine, from lysosomes (PubMed:11689434, PubMed:15128704, PubMed:18337546, PubMed:22232659, PubMed:29467429, PubMed:33208952, PubMed:36113465). Plays an important role in melanin synthesis by catalyzing cystine export from melanosomes, possibly by inhibiting pheomelanin synthesis (PubMed:22649030). In addition to cystine export, also acts as a positive regulator of mTORC1 signaling in kidney proximal tubular cells, via interactions with components of the v-ATPase and Ragulator complexes (PubMed:36113465). Also involved in small GTPase-regulated vesicle trafficking and lysosomal localization of LAMP2A, independently of cystine transporter activity (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | [Isoform 1]: Lysosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Melanosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=AP-3 complex is required for localization to the lysosome. |
| Tissue Location | Strongly expressed in pancreas, kidney (adult and fetal), skeletal muscle, melanocytes and keratinocytes (PubMed:22649030). Expressed at lower levels in placenta and heart Weakly expressed in lung, liver and brain (adult and fetal) (PubMed:22649030). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Cystinosis is an autosomal recessive disorder resulting from defective lysosomal transport of cystine and present at birth as a failure to thrive, rickets and proximal renal tubular acidosis. The human CTNS gene on chromosome 17p13 encodes the protein Cystinosin, and mutations in CTNS are responsible for nephropathic cystinosis. The CTNS promoter contains an Sp1 binding element. Cystinosin is an integral membrane protein containing 7 transmembrane domains that functions as a H+-driven transporter responsible for cystine export from lysosomes. In humans, Cystinosin is expressed abundantly in pancreas, kidney (mature and fetal), and skeletal muscle. The mouse homolog to CTNS encodes a protein which is expressed in all tissues except skeletal muscle. In the cell, Cystinosin co-localizes with LAMP-2 to lysosomes. A C-terminal GYDQL sorting motif within Cystinosin is critical for lysosomal localization.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。