eIF4A3 Rabbit pAb
eIF4A3 Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
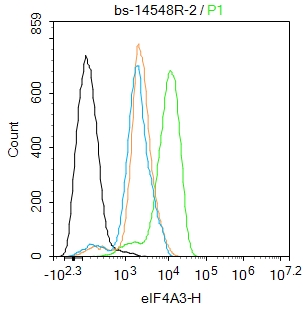
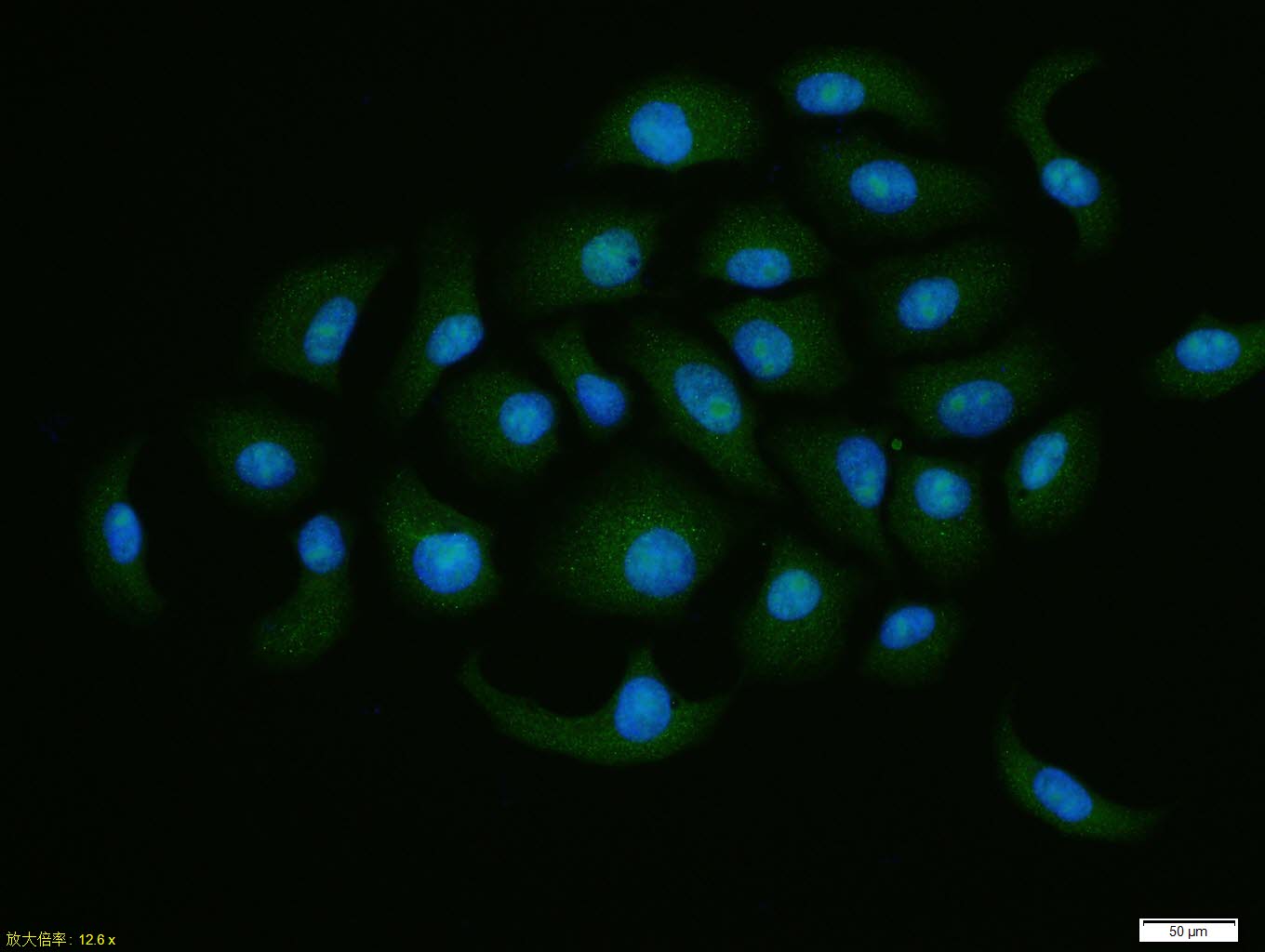
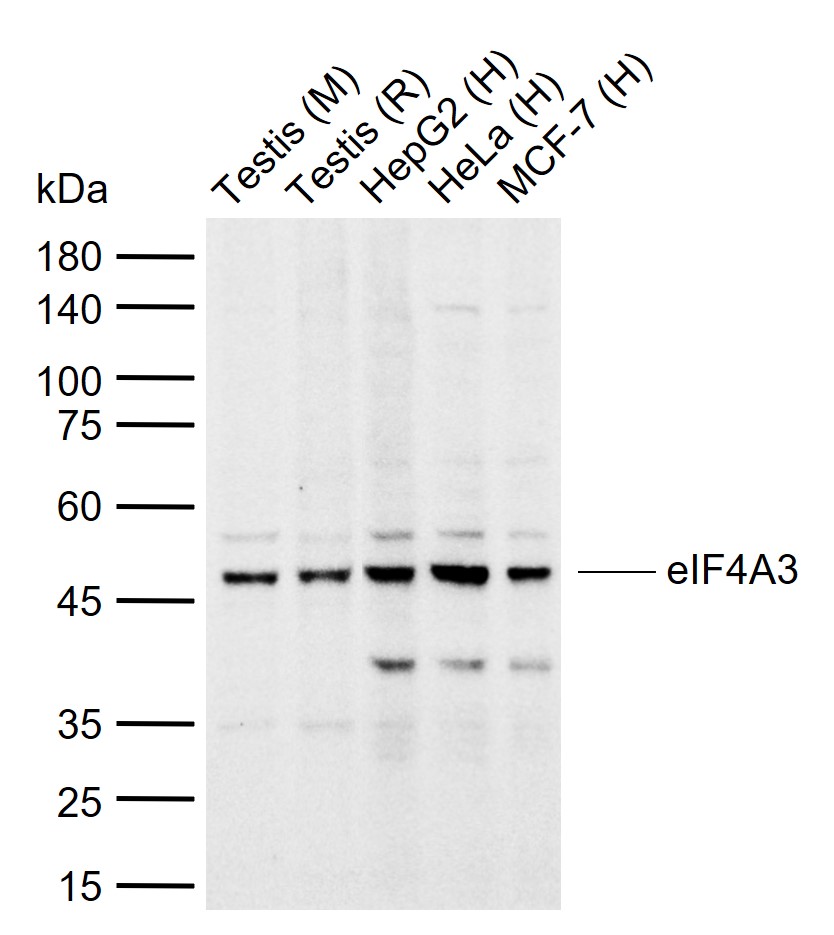
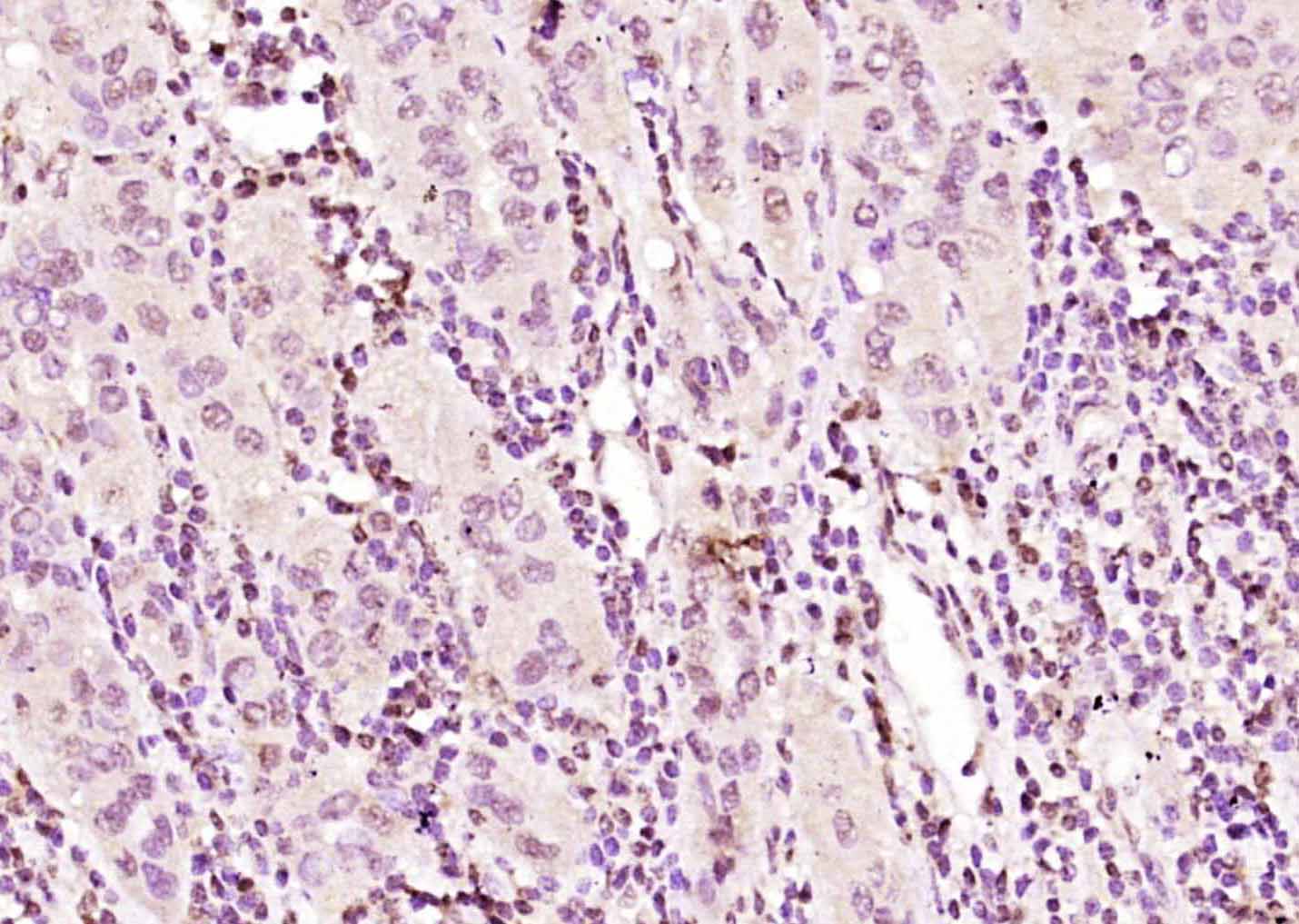
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P38919 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Predicted | Chicken, Dog, Horse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 46871 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human eIF4A3 |
| Epitope Specificity | 351-411/411 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Nucleus. Nucleus speckle. Cytoplasm. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein. Travels to the cytoplasm as part of the exon junction complex (EJC) bound to mRNA. Detected in dendritic layer as well as the nuclear and cytoplasmic (somatic) compartments of neurons. Colocalizes with STAU1 and FMR1 in dendrites. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the DEAD box helicase family. eIF4A subfamily. Contains 1 helicase ATP-binding domain. Contains 1 helicase C-terminal domain. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene encodes a member of the DEAD box protein family. DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure, such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear matrix protein. Its amino acid sequence is highly similar to the amino acid sequences of the translation initiation factors eIF4AI and eIF4AII, two other members of the DEAD box protein family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Gene ID | 9775 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III, eIF-4A-III, eIF4A-III, 3.6.4.13, ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX48, ATP-dependent RNA helicase eIF4A-3, DEAD box protein 48, Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-like NUK-34, Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A isoform 3, Nuclear matrix protein 265, NMP 265, hNMP 265, Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III, N-terminally processed, EIF4A3, DDX48, KIAA0111 |
| Target/Specificity | Ubiquitously expressed. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC/IF=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,Flow-Cyt=2ug/Test |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | EIF4A3 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DDX48, KIAA0111 |
| Function | ATP-dependent RNA helicase (PubMed:16170325). Involved in pre-mRNA splicing as component of the spliceosome (PubMed:11991638, PubMed:22961380, PubMed:28076346, PubMed:28502770, PubMed:29301961). Core component of the splicing-dependent multiprotein exon junction complex (EJC) deposited at splice junctions on mRNAs (PubMed:16170325, PubMed:16209946, PubMed:16314458, PubMed:16923391, PubMed:16931718, PubMed:19033377, PubMed:20479275). The EJC is a dynamic structure consisting of core proteins and several peripheral nuclear and cytoplasmic associated factors that join the complex only transiently either during EJC assembly or during subsequent mRNA metabolism. The EJC marks the position of the exon-exon junction in the mature mRNA for the gene expression machinery and the core components remain bound to spliced mRNAs throughout all stages of mRNA metabolism thereby influencing downstream processes including nuclear mRNA export, subcellular mRNA localization, translation efficiency and nonsense- mediated mRNA decay (NMD). Its RNA-dependent ATPase and RNA-helicase activities are induced by CASC3, but abolished in presence of the MAGOH-RBM8A heterodimer, thereby trapping the ATP-bound EJC core onto spliced mRNA in a stable conformation. The inhibition of ATPase activity by the MAGOH-RBM8A heterodimer increases the RNA-binding affinity of the EJC. Involved in translational enhancement of spliced mRNAs after formation of the 80S ribosome complex. Binds spliced mRNA in sequence-independent manner, 20-24 nucleotides upstream of mRNA exon-exon junctions. Shows higher affinity for single-stranded RNA in an ATP-bound core EJC complex than after the ATP is hydrolyzed. Involved in the splicing modulation of BCL2L1/Bcl-X (and probably other apoptotic genes); specifically inhibits formation of proapoptotic isoforms such as Bcl-X(S); the function is different from the established EJC assembly (PubMed:22203037). Involved in craniofacial development (PubMed:24360810). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Nucleus speckle. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3B8Q2}. Note=Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein. Travels to the cytoplasm as part of the exon junction complex (EJC) bound to mRNA. Detected in dendritic layer as well as the nuclear and cytoplasmic (somatic) compartments of neurons. Colocalizes with STAU1 and FMR1 in dendrites (By similarity) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3B8Q2} |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes a member of the DEAD box protein family. DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure, such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear matrix protein. Its amino acid sequence is highly similar to the amino acid sequences of the translation initiation factors eIF4AI and eIF4AII, two other members of the DEAD box protein family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。