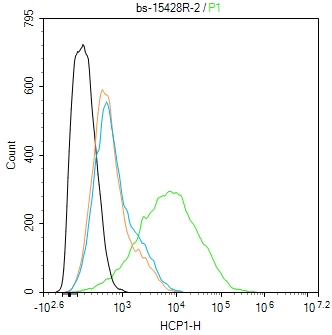
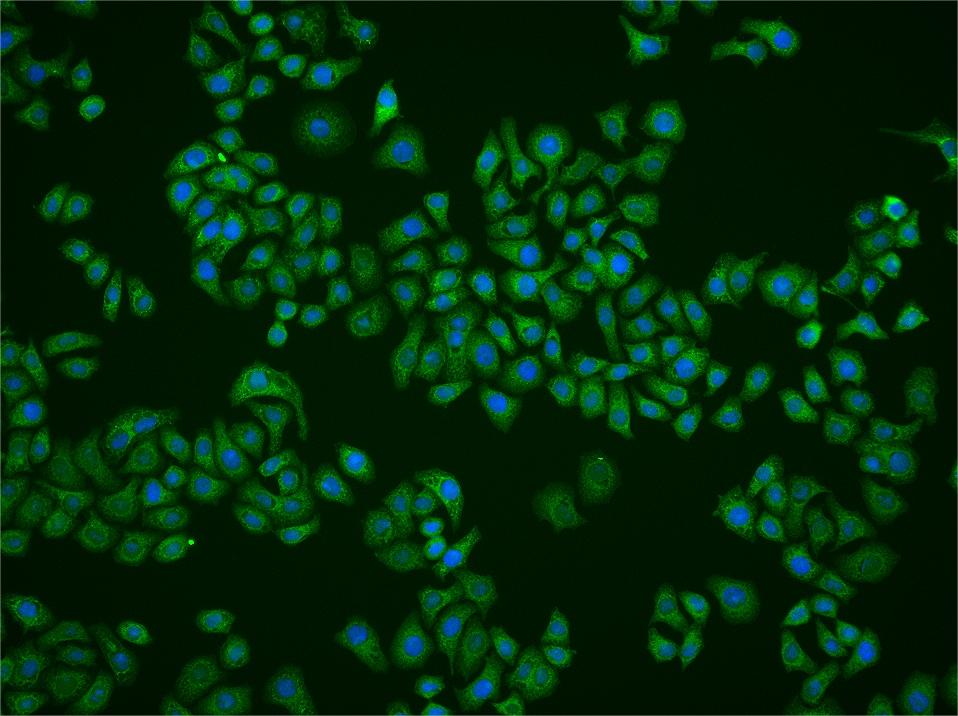
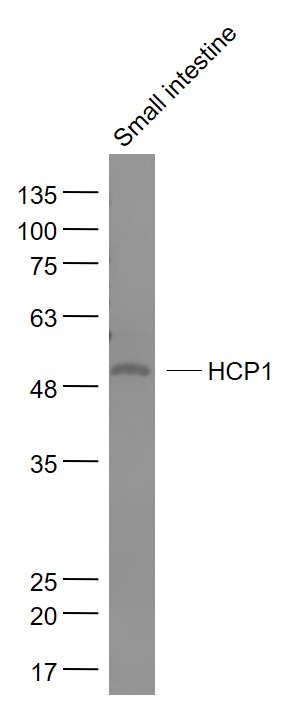
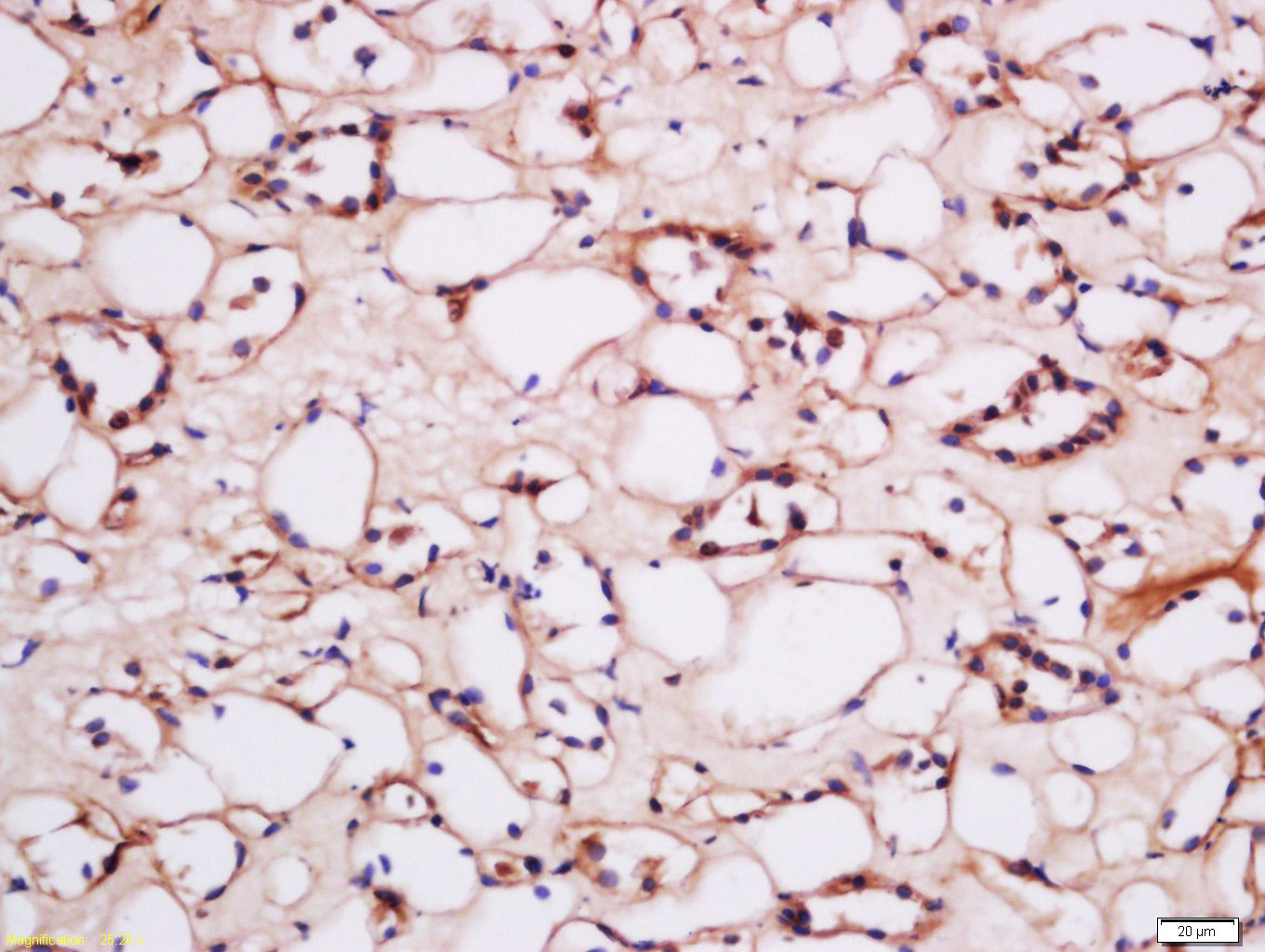
HCP1 Rabbit pAb
HCP1 Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q96NT5 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Predicted | Rat, Chicken |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 49771 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human HCP1 |
| Epitope Specificity | 341-459/459 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Apical cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm. Note=Localizes to the apical membrane of intestinal cells in iron-deficient cells, while it resides in the cytoplasm in iron-replete cells. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the major facilitator superfamily. SLC46A family. |
| DISEASE | Hereditary folate malabsorption (HFM) [MIM:229050]: Rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by impaired intestinal folate absorption with folate deficiency resulting in anemia, hypoimmunoglobulinemia with recurrent infections, and recurrent or chronic diarrhea. In many patients, neurological abnormalities such as seizures or mental retardation become apparent during early childhood, attributed to impaired transport of folates into the central nervous system. When diagnosed early, the disorder can be treated by administration of folate. If untreated, it can be fatal and, if treatment is delayed, the neurological defects can become permanent. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene encodes a transmembrane proton-coupled folate transporter protein that facilitates the movement of folate and antifolate substrates across cell membranes, optimally in acidic pH environments. This protein is also expressed in the brain and choroid plexus where it transports folates into the central nervous system. This protein further functions as a heme transporter in duodenal enterocytes, and potentially in other tissues like liver and kidney. Its localization to the apical membrane or cytoplasm of intestinal cells is modulated by dietary iron levels. Mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal recessive hereditary folate malabsorption disease. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013] |
| Gene ID | 113235 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Proton-coupled folate transporter, HsPCFT, hPCFT, Heme carrier protein 1, PCFT/HCP1, Solute carrier family 46 member 1, SLC46A1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:20686069, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:30521} |
| Target/Specificity | Expressed in kidney, liver, placenta, small intestine, spleen, retina and retinal pigment epithelium. Lower levels found in colon and testis. Very low levels in brain, lung, stomach, heart and muscle. In intestine, expressed in duodenum with lower levels in jejunum, ileum, cecum, rectum and segments of the colon. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC/IF=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,Flow-Cyt=2ug/Test |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | SLC46A1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:20686069, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:30521} |
|---|---|
| Function | Proton-coupled folate symporter that mediates folate absorption using an H(+) gradient as a driving force (PubMed:17129779, PubMed:17446347, PubMed:17475902, PubMed:19389703, PubMed:19762432, PubMed:25504888, PubMed:29344585, PubMed:30858177, PubMed:31494288, PubMed:31792273, PubMed:32893190, PubMed:34619546). Involved in the intestinal absorption of folates at the brush-border membrane of the proximal jejunum, and the transport from blood to cerebrospinal fluid across the choroid plexus (PubMed:17129779, PubMed:17446347, PubMed:17475902, PubMed:19389703, PubMed:25504888, PubMed:29344585, PubMed:30858177, PubMed:31494288, PubMed:32893190). Functions at acidic pH via alternate outward- and inward-open conformation states (PubMed:32893190, PubMed:34040256). Protonation of residues in the outward open state primes the protein for transport (PubMed:34040256). Binding of folate promotes breaking of salt bridge network and subsequent closure of the extracellular gate, leading to the inward- open state and release of protons and folate (PubMed:34040256). Also able to transport antifolate drugs, such as methotrexate and pemetrexed, which are established treatments for cancer and autoimmune diseases (PubMed:18524888, PubMed:19762432, PubMed:22345511, PubMed:25608532, PubMed:28802835, PubMed:29326243, PubMed:34040256, PubMed:34619546). Involved in FOLR1-mediated endocytosis by serving as a route of export of folates from acidified endosomes (PubMed:19074442). Also acts as a lower-affinity, pH-independent heme carrier protein and constitutes the main importer of heme in the intestine (PubMed:17156779). Imports heme in the retina and retinal pigment epithelium, in neurons of the hippocampus, in hepatocytes and in the renal epithelial cells (PubMed:32621820). Hence, participates in the trafficking of heme and increases intracellular iron content (PubMed:32621820). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Apical cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Basolateral cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6PEM8}. Note=Localizes to the apical membrane of intestinal cells in iron-deficient cells, while it resides in the cytoplasm in iron-replete cells (By similarity). Localizes to the basolateral membrane of choroid plexus (PubMed:19074442) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6PEM8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19074442} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed at highest level in the upper half of the small intestine (duodenum and jejunum), expression decreases downwardly in the subsequent quarter and is undetectable in the last quarter (the lowest ileum) (PubMed:17129779, PubMed:19762432). Also expressed in kidney, liver, placenta, spleen, retina and retinal pigment epithelium (PubMed:17129779, PubMed:17335806). Lower levels found in testis (PubMed:17129779). Very low levels in brain, lung, stomach, heart and muscle (PubMed:17129779). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes a transmembrane proton-coupled folate transporter protein that facilitates the movement of folate and antifolate substrates across cell membranes, optimally in acidic pH environments. This protein is also expressed in the brain and choroid plexus where it transports folates into the central nervous system. This protein further functions as a heme transporter in duodenal enterocytes, and potentially in other tissues like liver and kidney. Its localization to the apical membrane or cytoplasm of intestinal cells is modulated by dietary iron levels. Mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal recessive hereditary folate malabsorption disease. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。