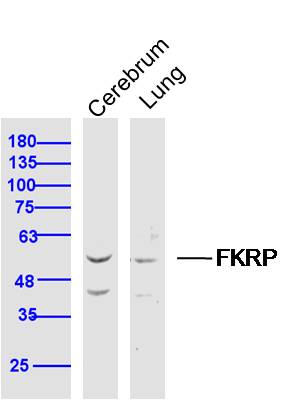
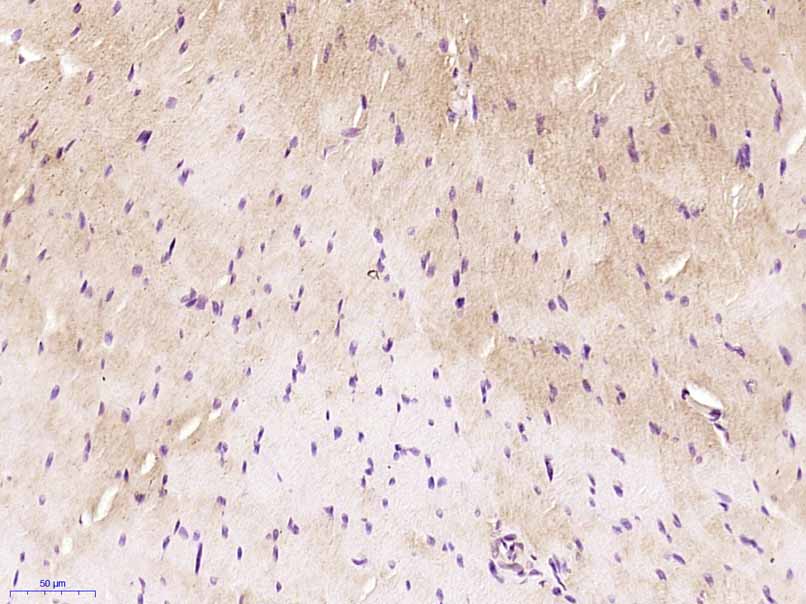
FKRP Rabbit pAb
FKRP Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9H9S5 |
| Reactivity | Mouse, Rat |
| Predicted | Human, Dog, Pig, Rabbit |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 54568 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human FKRP |
| Epitope Specificity | 1-100/495 |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Golgi apparatus. Secreted. Cell membrane > sarcolemma. Rough endoplasmic reticulum. According to some studies the N-terminal hydrophobic domain is cleaved after translocation to the Golgi apparatus and the protein is secreted. According to others the N-terminal hydrophobic domain is a transmembrane domain and the protein is a type II transmembrane type targeted to the Golgi apparatus by a non-cleavable signal anchor sequence. Localization at the cell membrane may require the presence of dystroglycan. At the Golgi apparatus localizes most likely at the cis-compartment. Detected in rough endoplasmic reticulum in myocytes. In general, mutants associated with severe clinical phenotypes are retained within the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the licD transferase family. |
| Post-translational modifications | N-glycosylated. |
| DISEASE | Defects in FKRP are the cause of muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy congenital with brain and eye anomalies type A5 (MDDGA5) [MIM:613153]. MDDGA5 is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by congenital muscular dystrophy associated with cobblestone lissencephaly and other brain anomalies, eye malformations, profound mental retardation, and death usually in the first years of life. Included diseases are the more severe Walker-Warburg syndrome and the slightly less severe muscle-eye-brain disease. Defects in FKRP are the cause of muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy congenital with or without mental retardation type B5 (MDDGB5) [MIM:606612]. MDDGB5 is a congenital muscular dystrophy characterized by a severe phenotype with inability to walk, muscle hypertrophy, marked elevation of serum creatine kinase, a secondary deficiency of laminin alpha2, and a marked reduction in alpha-dystroglycan expression. Only a subset of MDDGB5 patients have brain involvements. Defects in FKRP are the cause of muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy limb-girdle type C5 (MDDGC5) [MIM:607155]; also known as limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2I. MDDGC5 is an autosomal recessive disorder with age of onset ranging from childhood to adult life, and variable severity. Clinical features include proximal muscle weakness, waddling gait, calf hypertrophy, cardiomyopathy and respiratory insufficiency. A reduction of alpha-dystroglycan and laminin alpha-2 expression can be observed on skeletal muscle biopsy from MDDGC5 patients. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene encodes a protein which is targeted to the medial Golgi apparatus and is necessary for posttranslational modification of dystroglycan. Mutations in this gene have been associated with congenital muscular dystrophy, mental retardation, and cerebellar cysts. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] |
| Gene ID | 79147 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Ribitol 5-phosphate transferase FKRP, 2.7.8.-, Fukutin-related protein, Ribitol-5-phosphate transferase, FKRP (HGNC:17997) |
| Target/Specificity | Expressed predominantly in skeletal muscle, placenta, and heart and relatively weakly in brain, lung, liver kidney and pancreas. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500 |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | FKRP (HGNC:17997) |
|---|---|
| Function | Catalyzes the transfer of a ribitol 5-phosphate from CDP-L- ribitol to the ribitol 5-phosphate previously attached by FKTN/fukutin to the phosphorylated O-mannosyl trisaccharide (N-acetylgalactosamine- beta-3-N-acetylglucosamine-beta-4-(phosphate-6-)mannose), a carbohydrate structure present in alpha-dystroglycan (DAG1) (PubMed:26923585, PubMed:27194101, PubMed:29477842, PubMed:31949166). This constitutes the second step in the formation of the ribose 5- phosphate tandem repeat which links the phosphorylated O-mannosyl trisaccharide to the ligand binding moiety composed of repeats of 3- xylosyl-alpha-1,3-glucuronic acid-beta-1 (PubMed:25279699, PubMed:26923585, PubMed:27194101, PubMed:29477842, PubMed:31949166). |
| Cellular Location | Golgi apparatus membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Secreted. Cell membrane, sarcolemma {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CG64}. Rough endoplasmic reticulum. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CG64}. Note=According to some studies the N- terminal hydrophobic domain is cleaved after translocation to the Golgi apparatus and the protein is secreted (PubMed:19900540). Localization at the cell membrane may require the presence of dystroglycan (By similarity). At the Golgi apparatus localizes to the middle-to-trans- cisternae, as assessed by MG160 colocalization. Detected in rough endoplasmic reticulum in myocytes (PubMed:17554798, PubMed:21886772) In general, mutants associated with severe clinical phenotypes are retained within the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:15213246) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CG64, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15213246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17554798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19900540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21886772} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the retina (at protein level) (PubMed:29416295). Expressed predominantly in skeletal muscle, placenta, and heart and relatively weakly in brain, lung, liver, kidney, and pancreas (PubMed:11592034). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes a protein which is targeted to the medial Golgi apparatus and is necessary for posttranslational modification of dystroglycan. Mutations in this gene have been associated with congenital muscular dystrophy, mental retardation, and cerebellar cysts. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。