HAP1 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
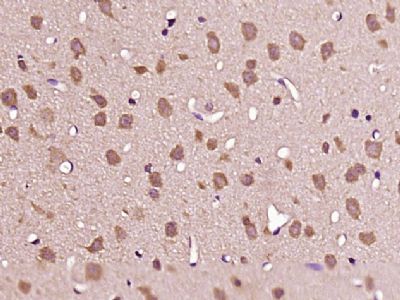
| IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P54257 |
| Reactivity | Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 75506 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human HAP1 |
| Epitope Specificity | 551-650/671 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | Preservative: 0.02% Proclin300, Constituents: 1% BSA, 0.01M PBS, pH7.4. |
| SIMILARITY | Contains 1 HAP1 N-terminal domain. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | Huntington's disease (HD), a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons, is caused by an expansion of a polyglutamine tract in the HD protein huntingtin. This gene encodes a protein that interacts with huntingtin, with two cytoskeletal proteins (dynactin and pericentriolar autoantigen protein 1), and with a hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. The interactions with cytoskeletal proteins and a kinase substrate suggest a role for this protein in vesicular trafficking or organelle transport. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Gene ID | 9001 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Huntingtin-associated protein 1, HAP-1, Neuroan 1, HAP1, HAP2, HLP1 |
| Target/Specificity | Predominantly expressed in brain. Selectively expressed in neurons. |
| Dilution | IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | HAP1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | HAP2, HLP1 |
| Function | Originally identified as neuronal protein that specifically associates with HTT/huntingtin and the binding is enhanced by an expanded polyglutamine repeat within HTT possibly affecting HAP1 interaction properties. Both HTT and HAP1 are involved in intracellular trafficking and HAP1 is proposed to link HTT to motor proteins and/or transport cargos. Seems to play a role in vesicular transport within neurons and axons such as from early endosomes to late endocytic compartments and to promote neurite outgrowth. The vesicular transport function via association with microtubule-dependent transporters can be attenuated by association with mutant HTT. Involved in the axonal transport of BDNF and its activity-dependent secretion; the function seems to involve HTT, DCTN1 and a complex with SORT1. Involved in APP trafficking and seems to facilitate APP anterograde transport and membrane insertion thereby possibly reducing processing into amyloid beta. Involved in delivery of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA(A)) receptors to synapses; the function is dependent on kinesin motor protein KIF5 and is disrupted by HTT with expanded polyglutamine repeat. Involved in regulation of autophagosome motility by promoting efficient retrograde axonal transport. Seems to be involved in regulation of membrane receptor recycling and degradation, and respective signal transduction, including GABA(A) receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, EGFR, IP3 receptor and androgen receptor. Among others suggested to be involved in control of feeding behavior (involving hypothalamic GABA(A) receptors), cerebellar and brainstem development (involving AHI1 and NTRK1/TrkA), postnatal neurogenesis (involving hypothalamic NTRK2/TrkB), and ITPR1/InsP3R1-mediated Ca(2+) release (involving HTT and possibly the effect of mutant HTT). Via association with DCTN1/dynactin p150-glued and HTT/huntingtin involved in cytoplasmic retention of REST in neurons. May be involved in ciliogenesis. Involved in regulation of exocytosis. Seems to be involved in formation of cytoplasmic inclusion bodies (STBs). In case of anomalous expression of TBP, can sequester a subset of TBP into STBs; sequestration is enhanced by an expanded polyglutamine repeat within TBP. HAP1-containing STBs have been proposed to play a protective role against neurodegeneration in Huntigton disease (HD) and spinocerebellar ataxia 17 (SCA17). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Cell projection, axon. Presynapse {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Cell projection, dendritic spine {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Cell projection, dendrite {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Lysosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Endoplasmic reticulum {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Mitochondrion. Nucleus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256} Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35668} Early endosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Cell projection, growth cone {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Cell projection, neuron projection {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, synaptic vesicle {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256}. Note=Localizes to large nonmembrane-bound cytoplasmic bodies found in various types of neurons, called stigmoid bodies (STBs). Localization to neuronal processes and neurite tips is decreased by YWHAZ. In the nucleus localizes to nuclear rods. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54256} |
| Tissue Location | Predominantly expressed in brain. Selectively expressed in neurons |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。