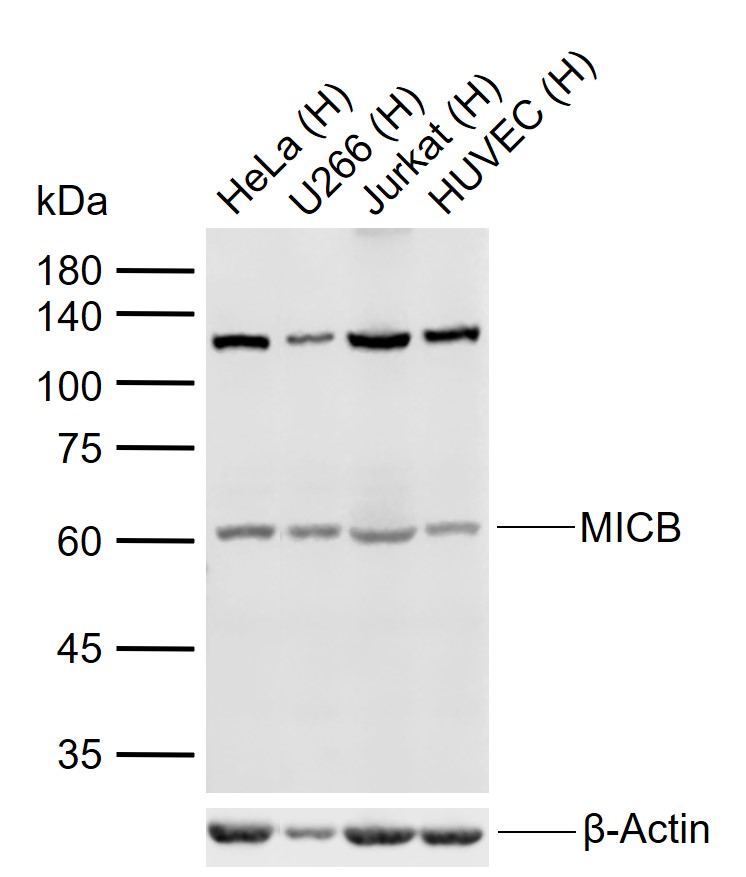
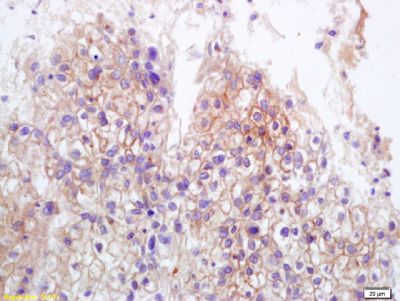
MICB Rabbit pAb
MICB Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q29980 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 42575 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human MICB |
| Epitope Specificity | 81-180/383 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Cell membrane; Single pass type I membrane protein. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the MHC class I family. MIC subfamily.Contains 1 Ig-like C1-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. |
| SUBUNIT | Unlike classical MHC class I molecules, does not form a heterodimer with beta-2-microglobulin. Binds as a monomer to a KLRK1/NKG2D homodimer. KLRK1 forms a complex with HCST/DAP10 in which KLRK1 binds MICB while HCST acts as an adapter molecule which enables signal transduction. Receptor-ligand interaction induces clustering of both proteins in ordered structures called immune synapses and also leads to their intercellular transfer. This is associated with a reduction in the cytotoxicity of KLRK1-expressing cells. Binds to human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein UL16 which causes sequestration of MICB in the endoplasmic reticulum and increases resistance to KLRK1-mediated cytotoxicity. |
| Post-translational modifications | Proteolytically cleaved and released from the cell surface of tumor cells. |
| DISEASE | Genetic variations in MICA are a cause of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [MIM:180300]. It is a systemic inflammatory disease with autoimmune features and a complex genetic component. It primarily affects the joints and is characterized by inflammatory changes in the synovial membranes and articular structures, widespread fibrinoid degeneration of the collagen fibers in mesenchymal tissues, and by atrophy and rarefaction of bony structures. Note=The MICB*004 allele is asociated with rheumatoid arthritis. Note=Genetic variation in MICB is associated with cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus I seropositivity and this may be associated with schizophrenia risk. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene encodes a heavily glycosylated protein which is a ligand for the NKG2D type II receptor. Binding of the ligand activates the cytolytic response of natural killer (NK) cells, CD8 alphabeta T cells, and gammadelta T cells which express the receptor. This protein is stress-induced and is similar to MHC class I molecules; however, it does not associate with beta-2-microglobulin or bind peptides. |
| Gene ID | 4277 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence B, MIC-B, MICB {ECO:0000312|EMBL:CAA62823.1} |
| Target/Specificity | Widely expressed with the exception of the central nervous system where it is absent. Expressed in many, but not all, epithelial tumors of lung, breast, kidney, ovary, prostate and colon. In hepatocellular carcinomas, expressed in tumor cells but not in surrounding non-cancerous tissue. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | MICB {ECO:0000312|EMBL:CAA62823.1} |
|---|---|
| Function | Widely expressed membrane-bound protein which acts as a ligand to stimulate an activating receptor KLRK1/NKG2D, expressed on the surface of essentially all human natural killer (NK), gammadelta T and CD8+ alphabeta T-cells (PubMed:11491531, PubMed:11777960). Up- regulated in stressed conditions, such as viral and bacterial infections or DNA damage response, serves as signal of cellular stress, and engagement of KLRK1/NKG2D by MICA triggers NK-cells resulting in a range of immune effector functions, such as cytotoxicity and cytokine production. |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q29983}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q29983} Note=Binding to human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein UL16 causes sequestration in the endoplasmic reticulum {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q29983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12782710} |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed with the exception of the central nervous system where it is absent. Expressed in many, but not all, epithelial tumors of lung, breast, kidney, ovary, prostate and colon In hepatocellular carcinomas, expressed in tumor cells but not in surrounding non-cancerous tissue. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes a heavily glycosylated protein which is a ligand for the NKG2D type II receptor. Binding of the ligand activates the cytolytic response of natural killer (NK) cells, CD8 alphabeta T cells, and gammadelta T cells which express the receptor. This protein is stress-induced and is similar to MHC class I molecules; however, it does not associate with beta-2-microglobulin or bind peptides.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。