VMAT2 Rabbit pAb
VMAT2 Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
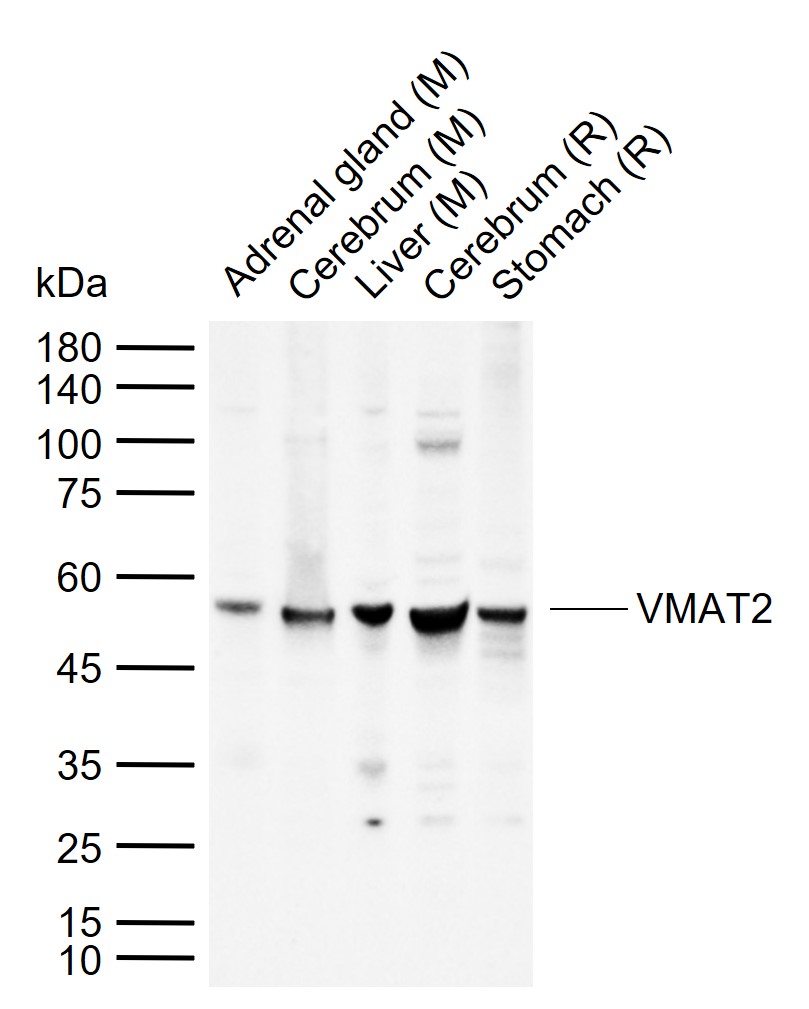
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q05940 |
| Reactivity | Mouse, Rat |
| Predicted | Human, Chicken, Dog, Pig, Horse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 55713 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human VMAT2 |
| Epitope Specificity | 421-514/514 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the major facilitator superfamily. Vesicular transporter family. |
| SUBUNIT | Interacts with SLC6A3. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | Neurotransmission depends on the regulated exocytotic release of chemical transmitter molecules. This requires the packaging of these substances into the specialized secretory vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells, a process mediated by specific vesicular transporters. The family of genes encoding the vesicular transporters of monoamines (VMAT 1 and VMAT 2) and acetylcholine (VACht) have been cloned and functionally characterized. The sequence of these integral membrane proteins predicts twelve transmembrane domains and weak homology to a class of bacterial antibiotic resistance proteins. The vesicular transport of neurotransmitter molecules has been shown to be an active ATP- and proton dependent transport mechanism. |
| Gene ID | 6571 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Synaptic vesicular amine transporter, Solute carrier family 18 member 2, Vesicular amine transporter 2, VAT2, Vesicular monoamine transporter 2, SLC18A2, SVMT, VMAT2 |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | SLC18A2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | SVMT, VMAT2 |
| Function | Electrogenic antiporter that exchanges one cationic monoamine with two intravesicular protons across the membrane of secretory and synaptic vesicles. Uses the electrochemical proton gradient established by the V-type proton-pump ATPase to accumulate high concentrations of monoamines inside the vesicles prior to their release via exocytosis. Transports a variety of catecholamines such as dopamine, adrenaline and noradrenaline, histamine, and indolamines such as serotonin (PubMed:23363473, PubMed:37914936, PubMed:38081299, PubMed:38517752, PubMed:8643547). Regulates the transvesicular monoaminergic gradient that determines the quantal size. Mediates somatodendritic dopamine release in hippocampal neurons, likely as part of a regulated secretory pathway that integrates retrograde synaptic signals (By similarity). Acts as a primary transporter for striatal dopamine loading ensuring impulse-dependent release of dopamine at the synaptic cleft (By similarity). Responsible for histamine and serotonin storage and subsequent corelease from mast cell granules (PubMed:8860238). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, synaptic vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827}; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827}; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827} Cell projection, dendrite {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827}. Note=Sorted to large dense core granules in neuroendocrine cells, presumably at the level of the trans-Golgi network. In neurons it is predominantly detected in somatodendritic tubulovesicular membranes, a distinct population of secretory vesicles that undergo calcium-dependent exocytosis in axons and dendrites upon depolarization. Localized at synaptic vesicles in axons. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01827} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in neuronal and neuroendocrine tissues. Detected in central and peripheral nervous system in particular in axonal and dendritic processes in dopaminergic cells of substantia nigra, histaminergic neuronal cell bodies of substantia nigra and tuberomammillary nucleus, in ganglion cells of sympathetic glia and in peripheral sympathetic nerve terminals in stomach and duodenum (at protein level). Highly expressed in chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla and histamine-storing enterochromaffin-like cells of oxyntic mucosa (at protein level). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Neurotransmission depends on the regulated exocytotic release of chemical transmitter molecules. This requires the packaging of these substances into the specialized secretory vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells, a process mediated by specific vesicular transporters. The family of genes encoding the vesicular transporters of monoamines (VMAT 1 and VMAT 2) and acetylcholine (VACht) have been cloned and functionally characterized. The sequence of these integral membrane proteins predicts twelve transmembrane domains and weak homology to a class of bacterial antibiotic resistance proteins. The vesicular transport of neurotransmitter molecules has been shown to be an active ATP- and proton dependent transport mechanism.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。