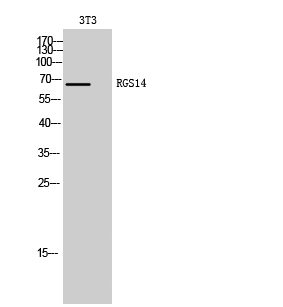
RGS14 Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O43566 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 61447 Da |
| Gene ID | 10636 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | RGS14; Regulator of G-protein signaling 14; RGS14 |
| Dilution | WB~~Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Format | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. |
| Storage Conditions | -20℃ |
| Name | RGS14 |
|---|---|
| Function | Regulates G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades. Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits, thereby driving them into their inactive GDP- bound form. Besides, modulates signal transduction via G protein alpha subunits by functioning as a GDP-dissociation inhibitor (GDI). Has GDI activity on G(i) alpha subunits GNAI1 and GNAI3, but not on GNAI2 and G(o)-alpha subunit GNAO1. Has GAP activity on GNAI0, GNAI2 and GNAI3. May act as a scaffold integrating G protein and Ras/Raf MAPkinase signaling pathways. Inhibits platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)- stimulated ERK1/ERK2 phosphorylation; a process depending on its interaction with HRAS and that is reversed by G(i) alpha subunit GNAI1. Acts as a positive modulator of microtubule polymerisation and spindle organization through a G(i)-alpha-dependent mechanism. Plays a role in cell division. Required for the nerve growth factor (NGF)-mediated neurite outgrowth. Involved in stress resistance. May be involved in visual memory processing capacity and hippocampal-based learning and memory. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Nucleus, PML body. Cytoplasm. Membrane. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Cell projection, dendrite. Cell projection, dendritic spine Postsynaptic density. Note=Associates with the perinuclear sheaths of microtubules (MTs) surrounding the pronuclei, prior to segregating to the anastral mitotic apparatus and subsequently the barrel-shaped cytoplasmic bridge between the nascent nuclei of the emerging 2-cell embryo. Localizes to a perinuclear compartment near the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC). Expressed in the nucleus during interphase and segregates to the centrosomes and astral MTs during mitosis. Relocalizes to the nucleus in PML nuclear bodies in response to heat stress. Colocalizes with RIC8A in CA2 hippocampal neurons Localizes to spindle poles during metaphase. Shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm in a CRM1-dependent manner. Recruited from the cytosol to the plasma membrane by the inactive GDP-bound forms of G(i) alpha subunits GNAI1 and GNAI3. Recruited from the cytosol to membranes by the active GTP-bound form of HRAS. Colocalizes with G(i) alpha subunit GNAI1 and RIC8A at the plasma membrane. Colocalizes with BRAF and RAF1 in both the cytoplasm and membranes (By similarity) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Regulates G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades. Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits, thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form. Besides, modulates signal transduction via G protein alpha subunits by functioning as a GDP-dissociation inhibitor (GDI). Has GDI activity on G(i) alpha subunits GNAI1 and GNAI3, but not on GNAI2 and G(o) alpha subunit GNAO1. Has GAP activity on GNAI0, GNAI2 and GNAI3. May act as a scaffold integrating G protein and Ras/Raf MAPkinase signaling pathways. Inhibits platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-stimulated ERK1/ERK2 phosphorylation; a process depending on its interaction with HRAS and that is reversed by G(i) alpha subunit GNAI1. Acts as a positive modulator of microtubule polymerisation and spindle organization through a G(i)-alpha-dependent mechanism. Plays a role in cell division. Required for the nerve growth factor (NGF)- mediated neurite outgrowth. Involved in stress resistance. May be involved in visual memory processing capacity and hippocampal- based learning and memory.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。