MST3 Antibody (C-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
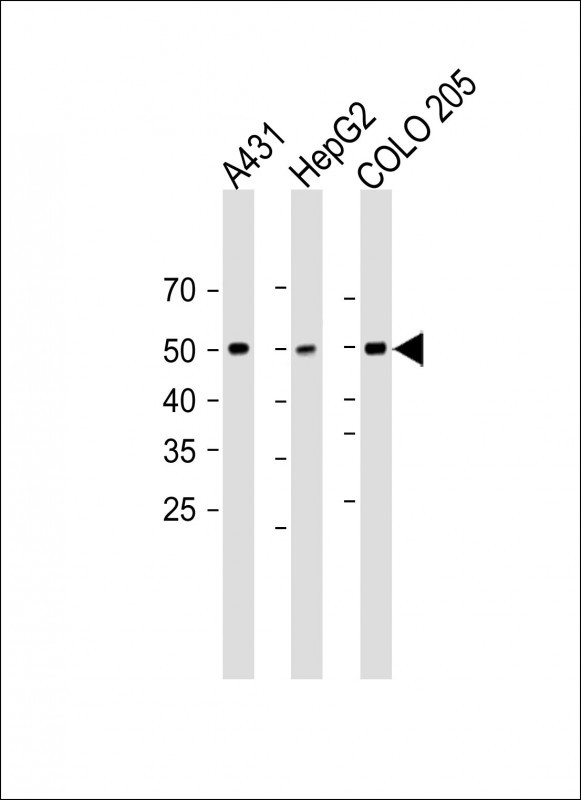
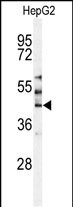
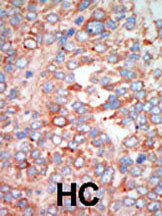
Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9Y6E0 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 49308 Da |
| Antigen Region | 345-374 aa |
| Gene ID | 8428 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 24, Mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 3, MST-3, STE20-like kinase MST3, Serine/threonine-protein kinase 24 36 kDa subunit, Mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 3 N-terminal, MST3/N, Serine/threonine-protein kinase 24 12 kDa subunit, Mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 3 C-terminal, MST3/C, STK24, MST3, STK3 |
| Target/Specificity | This MST3 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 345-374 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MST3. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC-P~~1:100~500 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.05% (V/V) Proclin 300. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | MST3 Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | STK24 (HGNC:11403) |
|---|---|
| Function | Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts on both serine and threonine residues and promotes apoptosis in response to stress stimuli and caspase activation. Mediates oxidative-stress-induced cell death by modulating phosphorylation of JNK1-JNK2 (MAPK8 and MAPK9), p38 (MAPK11, MAPK12, MAPK13 and MAPK14) during oxidative stress. Plays a role in a staurosporine-induced caspase-independent apoptotic pathway by regulating the nuclear translocation of AIFM1 and ENDOG and the DNase activity associated with ENDOG. Phosphorylates STK38L on 'Thr-442' and stimulates its kinase activity. In association with STK26 negatively regulates Golgi reorientation in polarized cell migration upon RHO activation (PubMed:27807006). Also regulates cellular migration with alteration of PTPN12 activity and PXN phosphorylation: phosphorylates PTPN12 and inhibits its activity and may regulate PXN phosphorylation through PTPN12. May act as a key regulator of axon regeneration in the optic nerve and radial nerve. Part of the striatin-interacting phosphatase and kinase (STRIPAK) complexes. STRIPAK complexes have critical roles in protein (de)phosphorylation and are regulators of multiple signaling pathways including Hippo, MAPK, nuclear receptor and cytoskeleton remodeling. Different types of STRIPAK complexes are involved in a variety of biological processes such as cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, metabolism and immune regulation (PubMed:18782753). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Membrane. Note=The truncated form (MST3/N) translocates to the nucleus. Colocalizes with STK38L in the membrane |
| Tissue Location | Isoform A is ubiquitous. Isoform B is expressed in brain with high expression in hippocampus and cerebral cortex |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The yeast 'Sterile 20' gene (STE20) functions upstream of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade. In mammals, protein kinases related to STE20 can be divided into 2 subfamilies based on their structure and regulation. Members of the PAK subfamily (see PAK3; MIM 300142) contain a C-terminal catalytic domain and an N-terminal regulatory domain that has a CDC42 (MIM 116952)-binding domain. In contrast, members of the GCK subfamily (see MAP4K2; MIM 603166), also called the Sps1 subfamily, have an N-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain without a CDC42-binding domain. STK24 belongs to the GCK subfamily of STE20-like kinases (Zhou et al., 2000 [PubMed 10644707]).[supplied by OMIM]
REFERENCES
Huang, C.Y., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 277(37):34367-34374 (2002).
Christian, S.L., et al., Genomics 79(5):635-656 (2002).
Zhou, T.H., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 275(4):2513-2519 (2000).
Schinkmann, K., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 272(45):28695-28703 (1997).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。