PACSIN1 Antibody (N-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
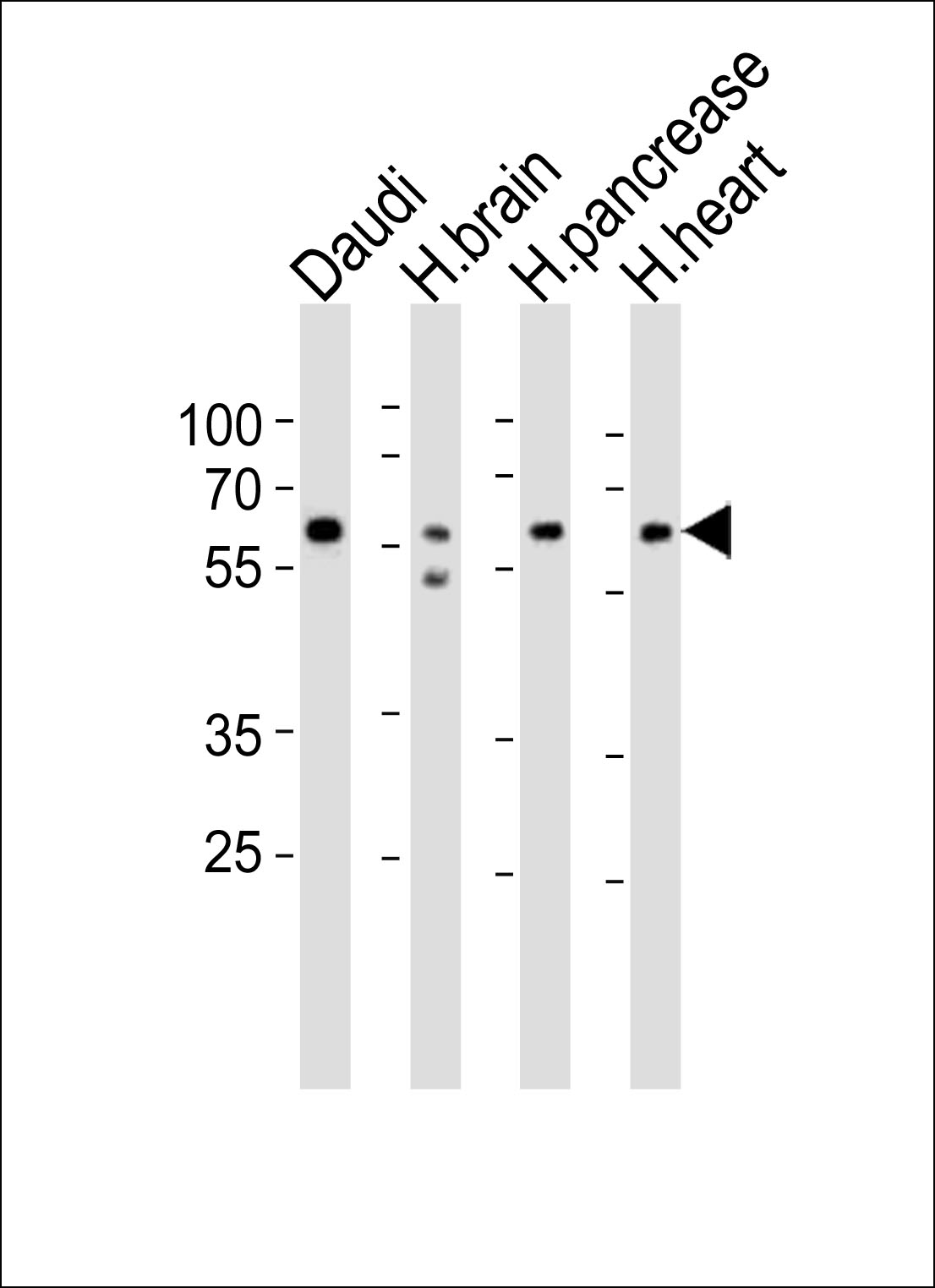
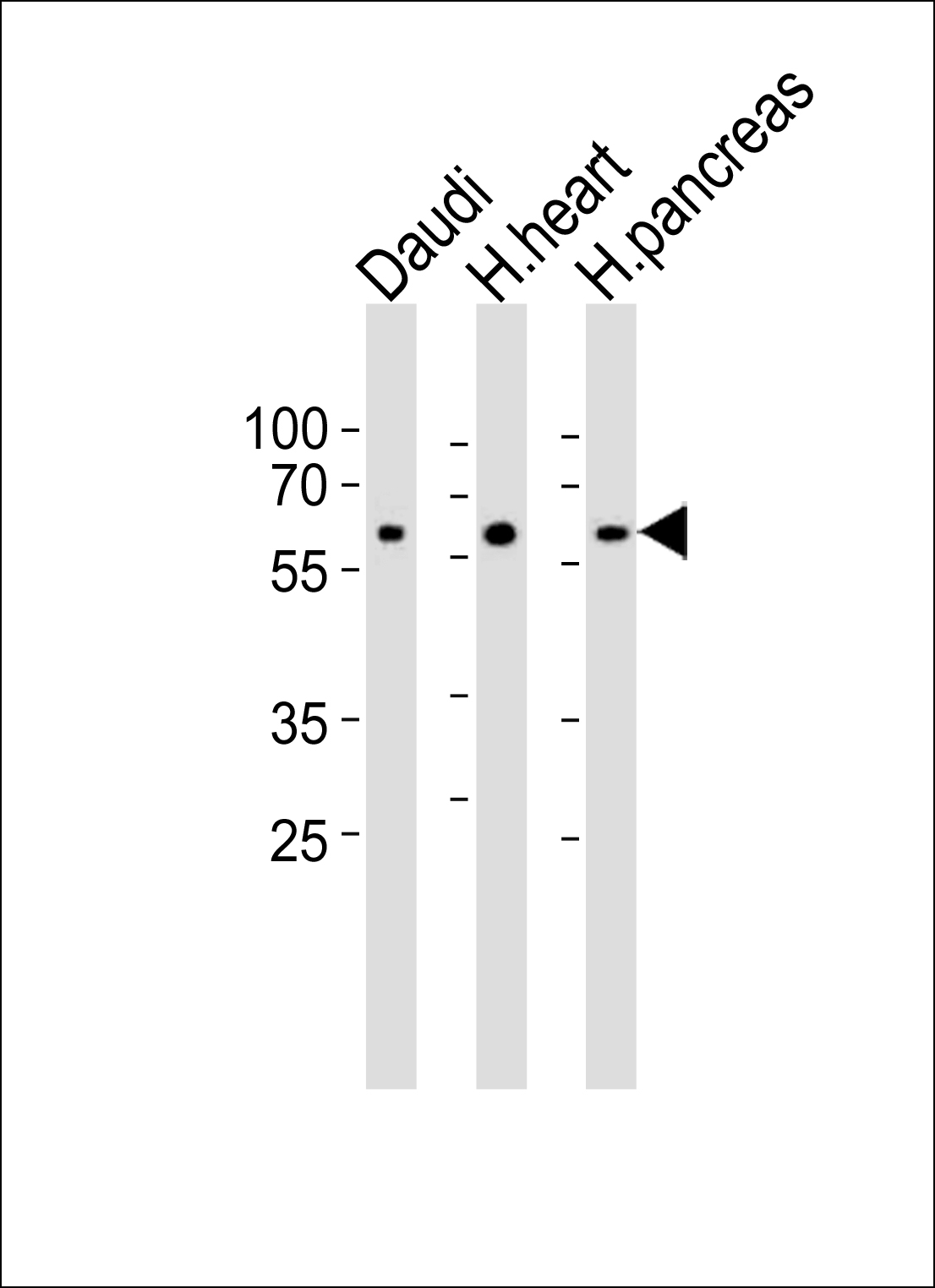
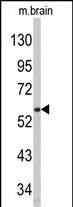
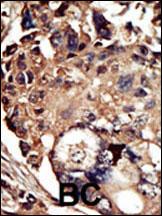
Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9BY11 |
| Other Accession | Q9DDA9, Q9QY17, Q9WVE8, Q9UNF0, O13154, Q9Z0W5, Q61644, A7MBI0 |
| Reactivity | Human, Rat, Mouse |
| Predicted | Chicken, Bovine, Xenopus |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 50966 Da |
| Antigen Region | 8-38 aa |
| Gene ID | 29993 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1, Syndapin-1, PACSIN1, KIAA1379 |
| Target/Specificity | This PACSIN1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 8-38 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human PACSIN1. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC-P~~1:100~500 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | PACSIN1 Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PACSIN1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | KIAA1379 |
| Function | Plays a role in the reorganization of the microtubule cytoskeleton via its interaction with MAPT; this decreases microtubule stability and inhibits MAPT-induced microtubule polymerization. Plays a role in cellular transport processes by recruiting DNM1, DNM2 and DNM3 to membranes. Plays a role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and in neuron morphogenesis via its interaction with COBL and WASL, and by recruiting COBL to the cell cortex. Plays a role in the regulation of neurite formation, neurite branching and the regulation of neurite length. Required for normal synaptic vesicle endocytosis; this process retrieves previously released neurotransmitters to accommodate multiple cycles of neurotransmission. Required for normal excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission (By similarity). Binds to membranes via its F-BAR domain and mediates membrane tubulation. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Cell projection. Synapse, synaptosome. Cell projection, ruffle membrane. Membrane; Peripheral membrane protein Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Synapse. Cytoplasm, cytosol Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Note=Colocalizes with MAPT in axons. In primary neuronal cultures, present at a high level in presynaptic nerve terminals and in the cell body. Colocalizes with DNM1 at vesicular structures in the cell body and neurites (By similarity). Associates with membranes via its F-BAR domain. |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in brain and, at much lower levels, in heart and pancreas. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Protein kinases are enzymes that transfer a phosphate group from a phosphate donor, generally the g phosphate of ATP, onto an acceptor amino acid in a substrate protein. By this basic mechanism, protein kinases mediate most of the signal transduction in eukaryotic cells, regulating cellular metabolism, transcription, cell cycle progression, cytoskeletal rearrangement and cell movement, apoptosis, and differentiation. With more than 500 gene products, the protein kinase family is one of the largest families of proteins in eukaryotes. The family has been classified in 8 major groups based on sequence comparison of their tyrosine (PTK) or serine/threonine (STK) kinase catalytic domains. The STE group (homologs of yeast Sterile 7, 11, 20 kinases) consists of 50 kinases related to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade families (Ste7/MAP2K, Ste11/MAP3K, and Ste20/MAP4K). MAP kinase cascades, consisting of a MAPK and one or more upstream regulatory kinases (MAPKKs) have been best characterized in the yeast pheromone response pathway. Pheromones bind to Ste cell surface receptors and activate yeast MAPK pathway.
REFERENCES
Sumoy, L., et al., Gene 262 (1-2), 199-205 (2001).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。