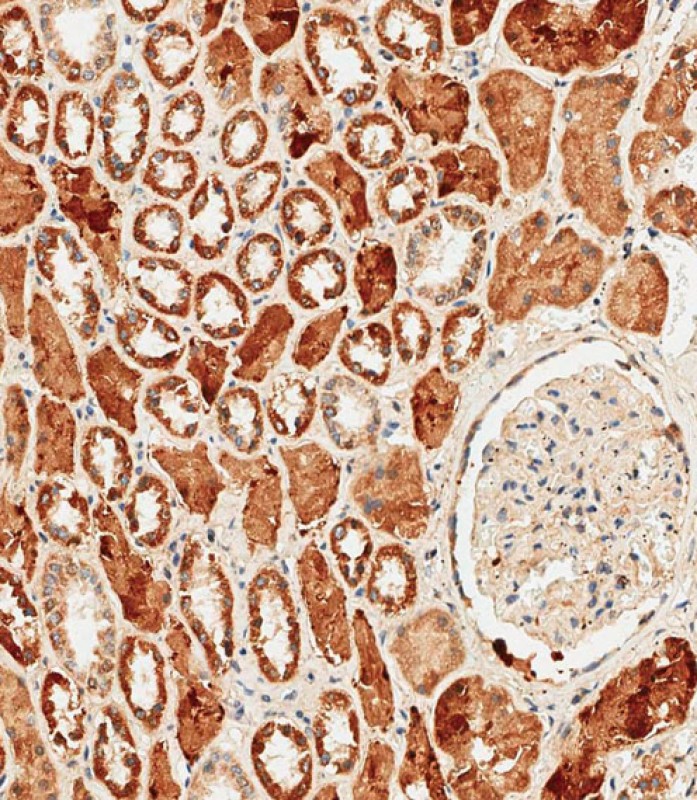
PCK1 Antibody (C-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 5
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, IHC-P-Leica, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P35558 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 69195 Da |
| Antigen Region | 592-622 aa |
| Gene ID | 5105 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, cytosolic [GTP], PEPCK-C, PCK1, PEPCK1 |
| Target/Specificity | This PCK1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 592-622 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human PCK1. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IF~~1:10~50 IHC-P-Leica~~1:250 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | PCK1 Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PCK1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:8490617, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:8724} |
|---|---|
| Function | Cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase that catalyzes the reversible decarboxylation and phosphorylation of oxaloacetate (OAA) and acts as the rate-limiting enzyme in gluconeogenesis (PubMed:24863970, PubMed:26971250, PubMed:28216384, PubMed:30193097). Regulates cataplerosis and anaplerosis, the processes that control the levels of metabolic intermediates in the citric acid cycle (PubMed:24863970, PubMed:26971250, PubMed:28216384, PubMed:30193097). At low glucose levels, it catalyzes the cataplerotic conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the rate-limiting step in the metabolic pathway that produces glucose from lactate and other precursors derived from the citric acid cycle (PubMed:30193097). At high glucose levels, it catalyzes the anaplerotic conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to oxaloacetate (PubMed:30193097). Acts as a regulator of formation and maintenance of memory CD8(+) T-cells: up- regulated in these cells, where it generates phosphoenolpyruvate, via gluconeogenesis (By similarity). The resultant phosphoenolpyruvate flows to glycogen and pentose phosphate pathway, which is essential for memory CD8(+) T-cells homeostasis (By similarity). In addition to the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity, also acts as a protein kinase when phosphorylated at Ser-90: phosphorylation at Ser-90 by AKT1 reduces the binding affinity to oxaloacetate and promotes an atypical serine protein kinase activity using GTP as donor (PubMed:32322062). The protein kinase activity regulates lipogenesis: upon phosphorylation at Ser-90, translocates to the endoplasmic reticulum and catalyzes phosphorylation of INSIG proteins (INSIG1 and INSIG2), thereby disrupting the interaction between INSIG proteins and SCAP and promoting nuclear translocation of SREBP proteins (SREBF1/SREBP1 or SREBF2/SREBP2) and subsequent transcription of downstream lipogenesis- related genes (PubMed:32322062). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Endoplasmic reticulum Note=Phosphorylation at Ser-90 promotes translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| Tissue Location | Major sites of expression are liver, kidney and adipocytes. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene is a main control point for the regulation of gluconeogenesis. The cytosolic enzyme encoded by this gene, along with GTP, catalyzes the formation of phosphoenolpyruvate from oxaloacetate, with the release of carbon dioxide and GDP. The expression of this gene can be regulated by insulin, glucocorticoids, glucagon, cAMP, and diet. A mitochondrial isozyme of the encoded protein also has been characterized.
REFERENCES
Dunten, P., et al., J. Mol. Biol. 316(2):257-264 (2002).
Strausberg, R.L., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99(26):16899-16903 (2002).
Deloukas, P., et al., Nature 414(6866):865-871 (2001).
O'Brien, R.M., et al., Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1264(3):284-288 (1995).
Ting, C.N., et al., Genomics 16(3):698-706 (1993).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。