MUC2 Antibody
Rabbit mAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
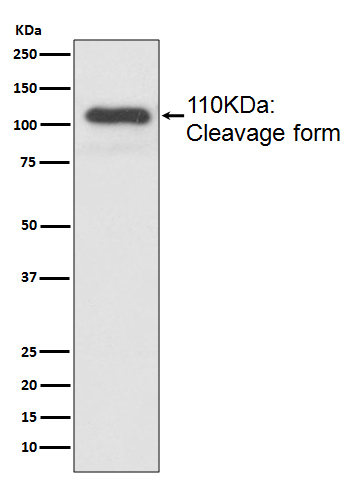
| WB, IHC, IF, FC, ICC, IP, IHF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q02817 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Other Names | Intestinal mucin 2; MLP; Muc2; Mucin 2 intestinal/tracheal; Mucin2; SMUC; |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Calculated MW | 550850 Da |
| Dilution | WB 1:500~1:2000 IHC 1:50~1:200 ICC/IF 1:50~1:200 IP 1:50 FC 1:50 |
|---|---|
| Purification | Affinity-chromatography |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human MUC2 |
| Description | Coats the epithelia of the intestines, airways, and other mucus membrane-containing organs. Thought to provide a protective, lubricating barrier against particles and infectious agents at mucosal surfaces. Major constituent of both the inner and outer mucus layers of the colon and may play a role in excluding bacteria from the inner mucus layer. |
| Storage Condition and Buffer | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. |
| Name | MUC2 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:8300571, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:7512} |
|---|---|
| Function | Coats the epithelia of the intestines and other mucus membrane-containing organs to provide a protective, lubricating barrier against particles and infectious agents at mucosal surfaces (PubMed:17058067, PubMed:19432394, PubMed:33031746). Major constituent of the colon mucus, which is mainly formed by large polymeric networks of MUC2 secreted by goblet cells that cover the exposed surfaces of intestine (PubMed:19432394, PubMed:33031746). MUC2 networks form hydrogels that guard the underlying epithelium from pathogens and other hazardous matter entering from the outside world, while permitting nutrient absorption and gas exchange (PubMed:33031746, PubMed:36206754). Acts as a divalent copper chaperone that protects intestinal cells from copper toxicity and facilitates nutritional copper unptake into cells (PubMed:36206754). Binds both Cu(2+) and its reduced form, Cu(1+), at two juxtaposed binding sites: Cu(2+), once reduced to Cu(1+) by vitamin C (ascorbate) or other dietary antioxidants, transits to the other binding site (PubMed:36206754). MUC2-bound Cu(1+) is protected from oxidation in aerobic environments, and can be released for nutritional delivery to cells (PubMed:36206754). Mucin gels store antimicrobial molecules that participate in innate immunity (PubMed:33031746). Mucin glycoproteins also house and feed the microbiome, lubricate tissue surfaces, and may facilitate the removal of contaminants and waste products from the body (PubMed:33031746). Goblet cells synthesize two forms of MUC2 mucin that differ in branched chain O-glycosylation and the site of production in the colon: a (1) 'thick' mucus that wraps the microbiota to form fecal pellets is produced in the proximal, ascending colon (By similarity). 'Thick' mucus transits along the descending colon and is lubricated by a (2) 'thin' MUC2 mucus produced in the distal colon which adheres to the 'thick' mucus (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Secreted. Note=In the intestine, secreted into the inner and outer mucus layers (By similarity). Before secretion, mucin polymers are stored in dedicated secretory vesicles (PubMed:33031746). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80Z19, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33031746} |
| Tissue Location | Colon, small intestine, colonic tumors, bronchus, cervix and gall bladder. |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.
¥ 1,500.00
Cat# AP91191























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。