SLC22A1 Antibody
Rabbit mAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
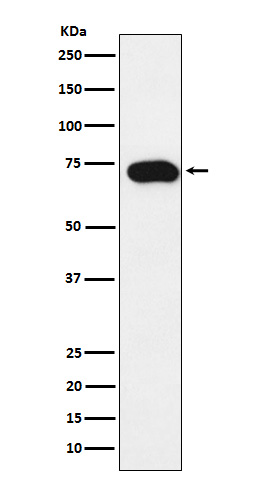
| WB, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O15245 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Other Names | hOCT1; OCT1; Slc22a1; |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Calculated MW | 61154 Da |
| Dilution | WB 1:500~1:2000 FC 1:30 |
|---|---|
| Purification | Affinity-chromatography |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human SLC22A1 |
| Description | Translocates a broad array of organic cations with various structures and molecular weights including the model compounds 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), tetraethylammonium (TEA), N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-N-methylpyridinium (ASP), the endogenous compounds choline, guanidine, histamine, epinephrine, adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine, and the drugs quinine, and metformin. |
| Storage Condition and Buffer | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. |
| Name | SLC22A1 (HGNC:10963) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | OCT1 |
| Function | Electrogenic voltage-dependent transporter that mediates the transport of a variety of organic cations such as endogenous bioactive amines, cationic drugs and xenobiotics (PubMed:11388889, PubMed:11408531, PubMed:12439218, PubMed:12719534, PubMed:15389554, PubMed:16263091, PubMed:16272756, PubMed:16581093, PubMed:19536068, PubMed:21128598, PubMed:23680637, PubMed:24961373, PubMed:34040533, PubMed:9187257, PubMed:9260930, PubMed:9655880). Functions as a pH- and Na(+)-independent, bidirectional transporter (By similarity). Cation cellular uptake or release is driven by the electrochemical potential (i.e. membrane potential and concentration gradient) and substrate selectivity (By similarity). Hydrophobicity is a major requirement for recognition in polyvalent substrates and inhibitors (By similarity). Primarily expressed at the basolateral membrane of hepatocytes and proximal tubules and involved in the uptake and disposition of cationic compounds by hepatic and renal clearance from the blood flow (By similarity). Most likely functions as an uptake carrier in enterocytes contributing to the intestinal elimination of organic cations from the systemic circulation (PubMed:16263091). Transports endogenous monoamines such as N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), guanidine, histamine, neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin and adrenaline (PubMed:12439218, PubMed:24961373, PubMed:35469921, PubMed:9260930). Also transports natural polyamines such as spermidine, agmatine and putrescine at low affinity, but relatively high turnover (PubMed:21128598). Involved in the hepatic uptake of vitamin B1/thiamine, hence regulating hepatic lipid and energy metabolism (PubMed:24961373). Mediates the bidirectional transport of acetylcholine (ACh) at the apical membrane of ciliated cell in airway epithelium, thereby playing a role in luminal release of ACh from bronchial epithelium (PubMed:15817714). Transports dopaminergic neuromodulators cyclo(his-pro) and salsolinol with lower efficency (PubMed:17460754). Also capable of transporting non-amine endogenous compounds such as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and prostaglandin F2-alpha (PGF2-alpha) (PubMed:11907186). May contribute to the transport of cationic compounds in testes across the blood- testis-barrier (Probable). Also involved in the uptake of xenobiotics tributylmethylammonium (TBuMA), quinidine, N-methyl-quinine (NMQ), N- methyl-quinidine (NMQD) N-(4,4-azo-n-pentyl)-quinuclidine (APQ), azidoprocainamide methoiodide (AMP), N-(4,4-azo-n-pentyl)-21- deoxyajmalinium (APDA) and 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-N- methylpyridinium (ASP) (PubMed:11408531, PubMed:15389554, PubMed:35469921, PubMed:9260930). |
| Cellular Location | Basolateral cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Apical cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Lateral cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Basal cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=Localized to the sinusoidal/basolateral membrane of hepatocytes (By similarity). Mainly localized to the basolateral membrane of renal proximal tubular cells (By similarity). However, also identified at the apical side of proximal tubular cells (PubMed:19536068). Mainly expressed at the lateral membrane of enterocytes (PubMed:16263091). Also observed at the apical side of enterocytes (PubMed:23680637). Localized to the luminal/apical membrane of ciliated epithelial cells in bronchi (PubMed:15817714). Localized to the basal membrane of Sertoli cells (PubMed:35307651) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15817714, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16263091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19536068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23680637, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35307651} |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed with high level in liver (PubMed:11388889, PubMed:23680637, PubMed:9187257, PubMed:9260930). In liver, expressed around the central vein (PubMed:16263091). Expressed in kidney (PubMed:9187257, PubMed:9260930). Expressed in small intestine enterocytes (PubMed:16263091, PubMed:23680637). Localized to peritubular myoid cells, Leydig cells and moderately to the basal membrane of Sertoli cells in testes (PubMed:35307651). Expressed in tracheal and bronchial ciliated epithelium in the respiratory tract (PubMed:15817714). Also expressed in skeletal muscle, stomach, spleen, heart, placentacolon, brain, granulycytes and lympohocytes (PubMed:9187257, PubMed:9260930). [Isoform 2]: Expressed in liver and in glial cell lines. [Isoform 4]: Expressed in glial cell lines. Not expressed in liver. |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.
¥ 1,500.00
Cat# AP92281























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。