MADD Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q8WXG6 |
| Other Accession | AAD12154, 3289973 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 183303 Da |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
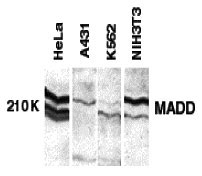
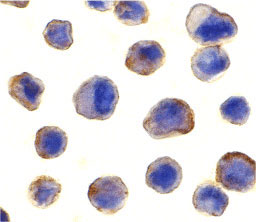
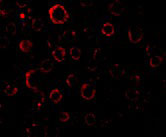
| Application Notes | MADD antibody can be used for detection of MADD by Western blot at 1 - 2 mg/mL. 200 to 220 kDa bands should be detected. Antibody can also be used for immunocytochemistry starting at 10 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 8567 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | MADD Antibody: DENN, IG20, RAB3GEP, DENN, KIAA0358, MAP kinase-activating death domain protein, Differentially expressed in normal and neoplastic cells, MAP-kinase activating death domain |
| Target/Specificity | MADD; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | MADD antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | MADD Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MADD {ECO:0000312|EMBL:AAB57735.1, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:6766} |
|---|---|
| Function | Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor that regulates small GTPases of the Rab family (PubMed:18559336, PubMed:20937701). Converts GDP-bound inactive form of RAB27A and RAB27B to the GTP-bound active forms (PubMed:18559336, PubMed:20937701). Converts GDP-bound inactive form of RAB3A, RAB3C and RAB3D to the GTP-bound active forms, GTPases involved in synaptic vesicle exocytosis and vesicle secretion (By similarity). Plays a role in synaptic vesicle formation and in vesicle trafficking at the neuromuscular junction (By similarity). Involved in up-regulating a post-docking step of synaptic exocytosis in central synapses (By similarity). Probably by binding to the motor proteins KIF1B and KIF1A, mediates motor-dependent transport of GTP-RAB3A- positive vesicles to the presynaptic nerve terminals (By similarity). Plays a role in TNFA-mediated activation of the MAPK pathway, including ERK1/2 (PubMed:32761064). May link TNFRSF1A with MAP kinase activation (PubMed:9115275). May be involved in the regulation of TNFA-induced apoptosis (PubMed:11577081, PubMed:32761064). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane. Cytoplasm. Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80U28} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in testis, ovary, brain and heart (PubMed:8988362). Expressed in spleen, thymus, prostate, testis, ovary, small instestine and colon (PubMed:9115275). Expressed in liver (PubMed:9796103). [Isoform 2]: Expressed in the brain, breast, kidney, lung, ovary, pancreas, testis, uterus, stomach and thyroid [Isoform 4]: Expressed in the brain, breast, kidney, lung, ovary, pancreas, testis, uterus, stomach and thyroid [Isoform 6]: Not detected in the brain, breast, kidney, lung, ovary, pancreas, testis, uterus, stomach and thyroid |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
MADD Antibody: MAP kinase-activating death domain protein (MADD) was initially identified as the type 1 tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR1) associated protein though their death domains. Overexpression of MADD activates MAP kinases ERK and JNK and induces the phosphorylation of cytosolic phospholipase A2. MADD shares 98% identity with DENN (for differentially expressed in neoplastic vs. normal cells), which was recently identified as a substrate for c-jun N-terminal kinase 3 (JNK3). MADD has greater than 94% overall identity to a GDP/GTP exchange protein Rab3-GEP. MADD is 87% identical to KIAA0358, a brain protein of unknown function. Identification of MADD as a component of the TNFR1 signaling complex and the similarity between MADD and Rab3-GEP provides a connection between TNFR1 activation and downstream MAP kinase activity through a guanine-nucleotide exchange protein.
REFERENCES
Schievella AR, Chen JH, Graham JR, Lin LL. MADD, a novel death domain protein that interacts with the type 1 tumor necrosis factor receptor and activates mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 1997;272:12069-12075
Chow VT, Lee SS. DENN, a novel human gene differentially expressed in normal and neoplastic cells. DNA Seq 1996;6:263-273
Zhang Y, Zhou L, Miller CA. A splicing variant of a death domain protein that is regulated by a mitogen-activated kinase is a substrate for c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the human central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95:2586-2591
Brown TL and Howe PH. MADD is highly homologous to a Rab3 guanine-nucleotide exchange protein (Rab3-GEP). Curr Biol 1998;8:R191
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。