PHAP I Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
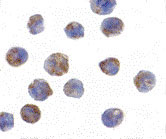
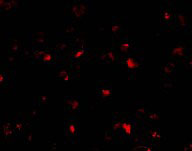
Application
| WB, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P39687 |
| Other Accession | P39687, 730318 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 28585 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
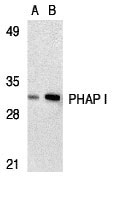
| Application Notes | PHAP I antibody can be used for detection of PHAP I by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. A band at approximately 32 kDa can be detected. Antibody can also be used for immunocytochemistry starting at 2 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 10 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 8125 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | PHAP I Antibody: LANP, MAPM, PP32, HPPCn, PHAP1, PHAPI, I1PP2A, C15orf1, LANP, Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A, Acidic nuclear phosphoprotein pp32, acidic (leucine-rich) nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family, member A |
| Target/Specificity | ANP32A; This polyclonal antibody has no cross-reaction to PHAP I2a and PHAP III. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | PHAP I antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | PHAP I Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ANP32A |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | C15orf1, LANP, MAPM, PHAP1 |
| Function | Multifunctional protein that is involved in the regulation of many processes including tumor suppression, apoptosis, cell cycle progression or transcription (PubMed:10400610, PubMed:11360199, PubMed:16341127, PubMed:18439902). Promotes apoptosis by favouring the activation of caspase-9/CASP9 and allowing apoptosome formation (PubMed:18439902). In addition, plays a role in the modulation of histone acetylation and transcription as part of the INHAT (inhibitor of histone acetyltransferases) complex. Inhibits the histone- acetyltranferase activity of EP300/CREBBP (CREB-binding protein) and EP300/CREBBP-associated factor by histone masking (PubMed:11830591). Preferentially binds to unmodified histone H3 and sterically inhibiting its acetylation and phosphorylation leading to cell growth inhibition (PubMed:16341127). Participates in other biochemical processes such as regulation of mRNA nuclear-to-cytoplasmic translocation and stability by its association with ELAVL1 (Hu-antigen R) (PubMed:18180367). Plays a role in E4F1-mediated transcriptional repression as well as inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A (PubMed:15642345, PubMed:17557114). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum. Note=Translocates to the cytoplasm during the process of neuritogenesis (By similarity). Shuttles between nucleus and cytoplasm. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18180367} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in all tissues tested. Highly expressed in kidney and skeletal muscle, moderate levels of expression in brain, placenta and pancreas, and weakly expressed in lung. Found in all regions of the brain examined (amygdala, caudate nucleus, corpus callosum, hippocampus and thalamus), with highest levels in amygdala |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
PHAP I Antibody: Apoptosis is related to many diseases and development. Caspase-9 plays a central role in cell death induced by a variety of apoptosis activators. Cytochrome c, after released from mitochondria, binds to Apaf-1, which forms an apoptosome that in turn binds to and activate procaspase-9. Activated caspase-9 cleaves and activates the effector caspases (caspase-3, -6 and -7), which are responsible for the proteolytic cleavage of many key proteins in apoptosis. The tumor suppressor putative HLA-DR-associated proteins (PHAPs) were recently identified as important regulators of mitochondrion apoptosis. PHAP appears to facilitate apoptosome-medicated caspase-9 activation and to stimulate the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. PHAP was also shown to oppose both Ras- and Myc-medicated cell transformation.
REFERENCES
Jiang X, Kim HE, Shu H, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Kofron J, Donnelly J, Burns D, Ng SC , Rosenberg S, Wang X. Distinctive roles of PHAP proteins and prothymosin-α in a death regulatory pathway. Science. 2003;299(5604):223-6.
Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA. Apoptosis. Life and death decisions. Science. 2003 10;299(5604):214-5.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。