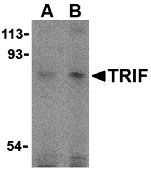
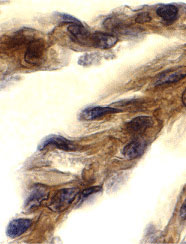
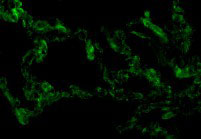
TRIF Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q8IUC6 |
| Other Accession | NP_891549, 41281981 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 76422 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | TRIF antibody can be used for detection of TRIF by Western blot at 2 to 4 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 10 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 10 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 148022 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | TRIF Antibody: TRIF, IIAE6, MyD88-3, PRVTIRB, TICAM-1, TRIF, TIR domain-containing adapter molecule 1, Proline-rich, vinculin and TIR domain-containing protein B, toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 1 |
| Target/Specificity | TICAM1; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | TRIF antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | TRIF Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | TICAM1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | PRVTIRB, TRIF |
| Function | Involved in innate immunity against invading pathogens. Adapter used by TLR3, TLR4 (through TICAM2) and TLR5 to mediate NF- kappa-B and interferon-regulatory factor (IRF) activation, and to induce apoptosis (PubMed:12471095, PubMed:12539043, PubMed:14739303, PubMed:28747347, PubMed:35215908). Ligand binding to these receptors results in TRIF recruitment through its TIR domain (PubMed:12471095, PubMed:12539043, PubMed:14739303). Distinct protein-interaction motifs allow recruitment of the effector proteins TBK1, TRAF6 and RIPK1, which in turn, lead to the activation of transcription factors IRF3 and IRF7, NF-kappa-B and FADD respectively (PubMed:12471095, PubMed:12539043, PubMed:14739303). Phosphorylation by TBK1 on the pLxIS motif leads to recruitment and subsequent activation of the transcription factor IRF3 to induce expression of type I interferon and exert a potent immunity against invading pathogens (PubMed:25636800). Component of a multi- helicase-TICAM1 complex that acts as a cytoplasmic sensor of viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and plays a role in the activation of a cascade of antiviral responses including the induction of pro- inflammatory cytokines (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome. Cytoplasm, cytosol {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80UF7}. Mitochondrion {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80UF7}. Note=Colocalizes with UBQLN1 in the autophagosome (PubMed:21695056). Colocalizes in the cytosol with DDX1, DDX21 and DHX36. Colocalizes in the mitochondria with DDX1 and poly(I:C) RNA ligand. The multi-helicase-TICAM1 complex may translocate to the mitochondria upon poly(I:C) RNA ligand stimulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80UF7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21695056} |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed but with higher levels in liver. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
TRIF Antibody: TRIF is a member of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) family, a group of proteins that include the Toll-like receptors (TLRs). TLRs are signaling molecules that recognize different pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and serve as an important link between the innate and adaptive immune responses. TRIF, along with other molecules such as TIRP, TIRAP, and MyD88, serves as an adaptor protein to several of the TLR molecules. Following activation of TLR3 and TLR4, TRIF engages the kinase TBK1 and allows its subsequent activation of the interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-3. TRIF is also involved in the activation of TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF)-6, and ultimately the activation of NF-κB.
REFERENCES
O’Neill LAJ, Fitzgerald FA, and Bowie AG. The Toll-IL-1 receptor adaptor family grows to five members. Trends in Imm. 2003; 24:286-9.
Vogel SN, Fitzgerald KA, and Fenton MJ. TLRs: differential adapter utilization by toll-like receptors mediates TLR-specific patterns of gene expression. Mol. Interv. 2003;3:466-77.
Takeda K, Kaisho T, and Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003;21:335-76.
Janeway CA Jr and Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:197-216.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。