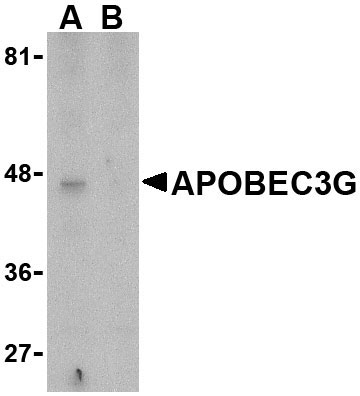
APOBEC3G Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9HC16 |
| Other Accession | NP_068594, 13399304 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 46408 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | APOBEC3G antibody can be used for detection of APOBEC3G by Western blot at 5 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 1 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 60489 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | APOBEC3G Antibody: A3G, ARCD, ARP9, ARP-9, CEM15, CEM-15, MDS019, bK150C2.7, dJ494G10.1APOBEC-related cytidine deaminase, APOBEC-related protein, apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3G |
| Target/Specificity | APOBEC3G; APOBEC3G antibody will also detect the APOBEC3F isoform. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | APOBEC3G antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | APOBEC3G Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | APOBEC3G {ECO:0000303|PubMed:14557625, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:17357} |
|---|---|
| Function | DNA deaminase (cytidine deaminase) which acts as an inhibitor of retrovirus replication and retrotransposon mobility via deaminase- dependent and -independent mechanisms (PubMed:12808465, PubMed:16527742, PubMed:17121840, PubMed:18288108, PubMed:18849968, PubMed:19153609, PubMed:21123384, PubMed:22791714, PubMed:25542899). Exhibits potent antiviral activity against Vif-deficient HIV-1 (PubMed:12167863, PubMed:12859895, PubMed:14557625, PubMed:20219927, PubMed:21835787, PubMed:22807680, PubMed:22915799, PubMed:23097438, PubMed:23152537, PubMed:31397674). After the penetration of retroviral nucleocapsids into target cells of infection and the initiation of reverse transcription, it can induce the conversion of cytosine to uracil in the minus-sense single-strand viral DNA, leading to G-to-A hypermutations in the subsequent plus-strand viral DNA (PubMed:12808465, PubMed:12808466, PubMed:12809610, PubMed:12970355, PubMed:14528300, PubMed:22807680). The resultant detrimental levels of mutations in the proviral genome, along with a deamination-independent mechanism that works prior to the proviral integration, together exert efficient antiretroviral effects in infected target cells (PubMed:12808465, PubMed:12808466, PubMed:12809610, PubMed:12970355, PubMed:14528300). Selectively targets single-stranded DNA and does not deaminate double-stranded DNA or single- or double-stranded RNA (PubMed:12808465, PubMed:12809610, PubMed:12970355, PubMed:14528300). Exhibits antiviral activity also against simian immunodeficiency viruses (SIVs), hepatitis B virus (HBV), equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV), xenotropic MuLV-related virus (XMRV) and simian foamy virus (SFV) (PubMed:15031497, PubMed:16378963, PubMed:18448976, PubMed:19458006, PubMed:20335265). May inhibit the mobility of LTR and non-LTR retrotransposons (PubMed:16527742). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus Cytoplasm, P-body. Note=Mainly cytoplasmic (PubMed:16527742, PubMed:16699599, PubMed:21835787). Small amount are found in the nucleus (PubMed:18667511). During HIV-1 infection, virion-encapsidated in absence of HIV-1 Vif (PubMed:12859895) |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in spleen, testes, ovary and peripheral blood leukocytes and CD4+ lymphocytes. Also expressed in non-permissive peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and several tumor cell lines; no expression detected in permissive lymphoid and non-lymphoid cell lines Exists only in the LMM form in peripheral blood-derived resting CD4 T- cells and monocytes, both of which are refractory to HIV-1 infection LMM is converted to a HMM complex when resting CD4 T-cells are activated or when monocytes are induced to differentiate into macrophages. This change correlates with increased susceptibility of these cells to HIV-1 infection. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
APOBEC3G Antibody: The Apoliprotein B mRNA-editing, enzyme-catalytic, polypeptide-like (APOBEC) 3 is a multi-isoform member of the cytidine deaminase family of enzymes that act on monomeric nucleoside and nucleotide substrates. Similar to TRIM5α which targets incoming retroviral capsids, APOBEC3 plays a major role in cellular defense against retroviral infection as at least two isoforms, APOBEC3G and to a lesser extent APOBEC3F, can be incorporated HIV-1 virions and induce hypermutation in the newly synthesized viral DNA and thus destabilize the viral genome. This innate mechanism of retroviral resistance is counteracted by the HIV-1 Vif protein by inducing the ubiquitization and degradation of APOBEC3G; a single amino acid substitution (D128K) blocks APOBEC3G depletion without affecting its inhibitory activity.
REFERENCES
Jarmuz A, Chester A, Bayliss J, et al. An anthropoid-specific locus of Orphan C to U RNA-editing enzymes on chromosome 22. Genomics 2002; 79:285-96.
Stremlau M, Owens CM, Perron MJ, et al. The cytoplasmic body component TRIM5a restricts HIV-1 infection in Old World monkeys. Nature 2004; 427:848-53.
Bieniasz PD. Intrinsic immunity: a front-line defense against viral attack. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5:1109-15.
Sheehy AM, Gaddis NC, Choi JD, et al. Isolation of a human gene that inhibits HIV-1 infection and is suppressed by the viral Vif protein. Nature 2002; 418:646-50.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。